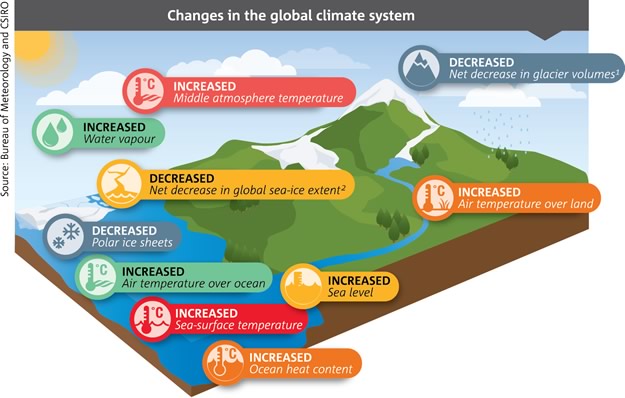
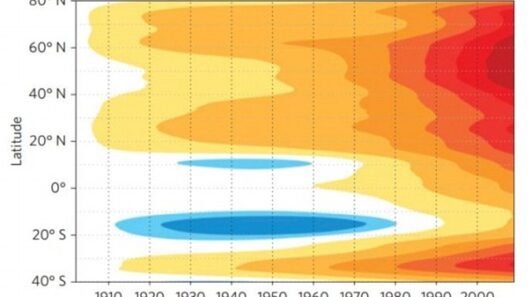
The phenomenon of “weather whiplash” is emerging as a stark manifestation of climate change, characterized by abrupt and extreme swings in weather patterns. As global warming continues to alter the atmospheric balance, these erratic conditions pose significant risks to ecological stability, human health, and economic systems. This discussion delves into the intricacies of weather whiplash, examining its causes, effects, and potential mitigation strategies.
To comprehend the essence of weather whiplash, it is essential to define the term. Weather whiplash refers to sudden shifts in weather conditions—from drought to deluge, or extreme heat to a plummet in temperatures—often occurring within a short timeframe. These transitions can severely disrupt the natural environment, agriculture, and urban infrastructure. The frequency and magnitude of these patterns have surged as a result of anthropogenic climate change, primarily driven by greenhouse gas emissions.
The underlying mechanics of weather whiplash are intricate, but they can largely be attributed to the alterations in the jet stream and other atmospheric circulations. As the Earth warms, the polar regions are experiencing a more pronounced temperature rise compared to the equatorial regions. This differential heating leads to a weakening of the jet stream, resulting in slower and more meandering atmospheric patterns. Consequently, weather systems that were once relatively stable and predictable now exhibit increased volatility.
One of the most palpable examples of weather whiplash can be observed in the realm of precipitation. Regions that traditionally experienced consistent rainfall patterns are now grappling with intense downpours followed by prolonged dry spells. This dichotomy not only exacerbates water management challenges but also straddles the line between flood and drought conditions, making it profoundly difficult for farmers to cultivate crops effectively. The agricultural sector, reliant on predictable seasonal patterns, finds itself increasingly vulnerable as these extremes disrupt planting and harvesting schedules, negatively impacting yields.
Moreover, the effects of weather whiplash extend beyond agriculture. Urban areas are particularly susceptible to these dramatic fluctuations, with intensified rainfall leading to urban flooding, overwhelmed drainage systems, and compromised infrastructure. As cities expand and impervious surfaces increase, the capacity to absorb rainfall diminishes, illustrating the critical need for adaptive urban planning strategies. Implementing green infrastructure, such as permeable pavements and green roofs, can mitigate some of these adverse effects by enhancing rainfall absorption and reducing runoff.
Beyond the physical impacts, weather whiplash has significant health implications. Abrupt changes in temperature—such as extreme heatwaves followed by sudden cold snaps—can lead to a host of health-related issues, from heat exhaustion to hypothermia. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions, are at even greater risk. Additionally, the psychological toll cannot be overlooked; the unpredictability of weather can instigate anxiety and stress within communities that rely on seasonal patterns for their livelihoods. Increased protean weather events may also lead to the resurgence of vector-borne diseases as warmer conditions expand the habitats for disease-carrying organisms.
Extreme weather events also carry hefty economic repercussions. The costs associated with responding to weather-related disasters continue to rise, stretching the capabilities of governments and relief organizations. Insurers are grappling with the growing frequency of claims attributable to weather whiplash, prompting them to reconsider underwriting practices and increase premiums. As these costs ripple through the economy, businesses face uncertain conditions, affecting profitability and consumer confidence. These economic ramifications highlight the interlinkages between environmental health and financial stability, emphasizing the imperative for sustainable development strategies.
In light of these challenges, it is crucial to engage in proactive mitigation and adaptation strategies. Climate resilience can be enhanced through a multi-faceted approach that includes policy reforms, technological innovation, and community engagement. Governments must prioritize investments in renewable energy sources to diminish greenhouse gas emissions while simultaneously adapting infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events. Integrating climate education into public discourse will empower individuals and communities to adopt sustainable practices, fostering a collective sense of responsibility towards minimizing environmental impact.
International collaboration is equally paramount in addressing weather whiplash. As climate change knows no borders, countries must invest in data-sharing initiatives and collective research efforts to better understand and predict weather patterns. By collaborating on adaptive technologies and best practices, nations can collectively enhance global resilience to the adverse impacts of climate change.
In conclusion, weather whiplash serves as a potent reminder of the tangible effects of global warming on our environment. The rapid and unpredictable shifts in weather patterns signal an urgent need for comprehensive strategies aimed at mitigation and adaptation. By fostering international cooperation, promoting sustainable practices, and enhancing climate resilience, society can better navigate the turbulent waters of an ever-changing climate. The time for action is now; the trajectory of our weather systems lies in our hands.