Human-induced climate change has emerged as one of the most controversial yet critical issues of our time. Despite ongoing debates, a plethora of scientific evidence underscores the reality of anthropogenic, or man-made, global warming. This article aims to explore the extensive data supporting this phenomenon, debunk myths surrounding it, and delve into the future implications if this trend continues unabated.
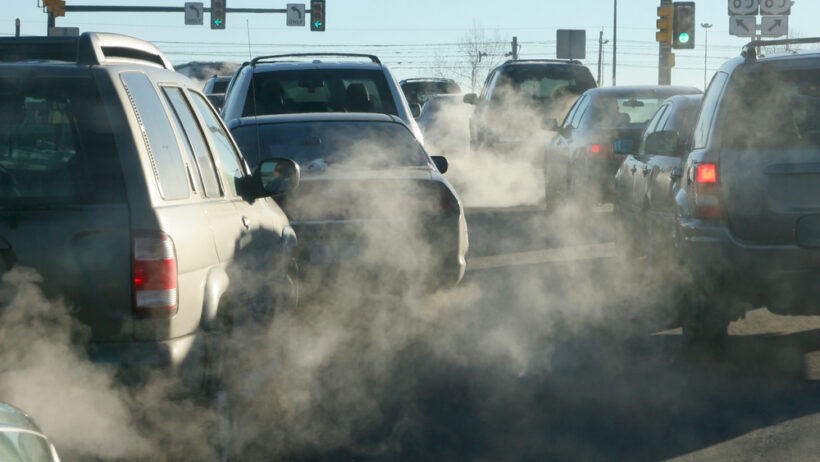
At the core of the discussion lies the greenhouse effect. Earth’s atmosphere is a delicate layer of gases that trap heat from the sun, maintaining a temperature conducive to life. However, human activities—primarily the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes—have significantly escalated the concentration of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). These emissions create a thickening blanket around the planet, which leads to an increase in average global temperatures.
Scientific consensus on climate change is robust. Over 97% of climate scientists agree that climate change is largely driven by human activities. Institutions such as NASA and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) have produced comprehensive assessments that visually demonstrate the correlation between rising CO2 levels and temperature increases. For instance, ice core samples illustrate historical CO2 concentrations and corresponding temperature fluctuations over millennia, starkly contrasting with the unprecedented surge in recent decades.
One of the most telling indicators of climate change is the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. The Arctic region has warmed at approximately twice the global average, leading to a rapid decline in sea ice extent. This phenomenon not only threatens polar ecosystems but also contributes to rising sea levels. As glaciers retreat, coastal communities face the imminent risk of submersion. Such dramatic environmental shifts serve as evidence of the profound alterations our planet is undergoing due to human actions.
The implications of climate change reverberate beyond the Arctic. Extreme weather events—such as hurricanes, heatwaves, floods, and droughts—are becoming increasingly common and intense. Scientific studies attribute these changes to the warming climate, revealing an undeniable link between human activity and the frequency of such catastrophes. For example, a warmer atmosphere can hold more moisture, leading to intense rainfall events; conversely, prolonged warm conditions exacerbate drought scenarios in many regions.
The profound impact on biodiversity also cannot be overlooked. Ecosystems are reaching tipping points, and countless species face extinction as their habitats deteriorate or are altered irreversibly. Coral reefs, often dubbed the “rainforests of the sea,” are particularly vulnerable. Ocean acidification, primarily from absorbed CO2, poses a significant threat to these ecosystems, leading to coral bleaching and massive die-offs. As species face extinction due to changing climates, the balance of ecosystems is further undermined, illustrating the interdependence of life on Earth.
Addressing the skepticism surrounding climate change requires clarity. Detractors often espouse the myth that climate has changed frequently throughout Earth’s history. However, while it is true that the planet experiences natural fluctuations, the rates and magnitude of current changes are staggering compared to historical norms. We are witnessing accelerated shifts that echo the geological timeline; however, they are occurring within an exceptionally brief period attributable singularly to human activity.
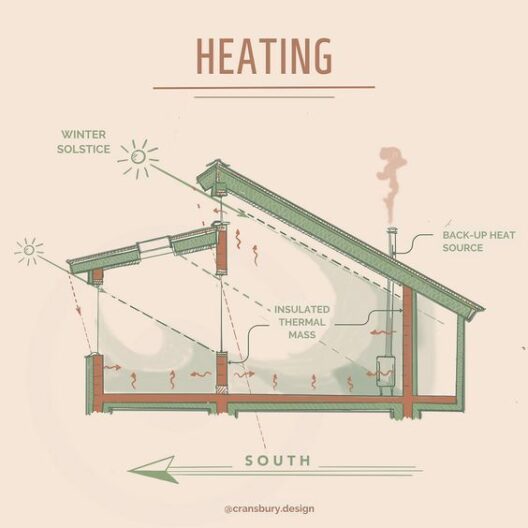
Moreover, advancements in climate modeling enable scientists to project future scenarios based on different emissions trajectories. A business-as-usual approach could result in catastrophic consequences, including uninhabitable regions, heightened food insecurity, and mass displacements of people. Alternatively, proactive measures to curtail emissions can steer the globe away from these dire outcomes. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and reforesting areas represent tangible steps that societies can undertake to combat climate change.
Such proactive measures not only mitigate the impacts of climate change but also offer economic opportunities. The advent of green technology emphasizes the potential for job creation and economic growth through sustainable practices. Investments in renewable energy can produce millions of jobs, fostering innovation while simultaneously addressing environmental concerns.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate relationships between human activity and the climate is imperative. While doubt persists in certain circles, the overwhelming evidence—with its complexity spanning evidence from atmospheric science, ecology, and meteorology—demands attention. Recognizing that the climate crisis is not a distant threat but a present reality fosters urgent action. As we stand at the precipice of significant change, the collective choices made today will indubitably forge the world of tomorrow. The narrative surrounding climate change must shift from one of uncertainty to one of action. Humanity has the capacity to alter this trajectory, but it requires concerted effort and unyielding resolve. Only then can we hope to mitigate the effects of global warming and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.