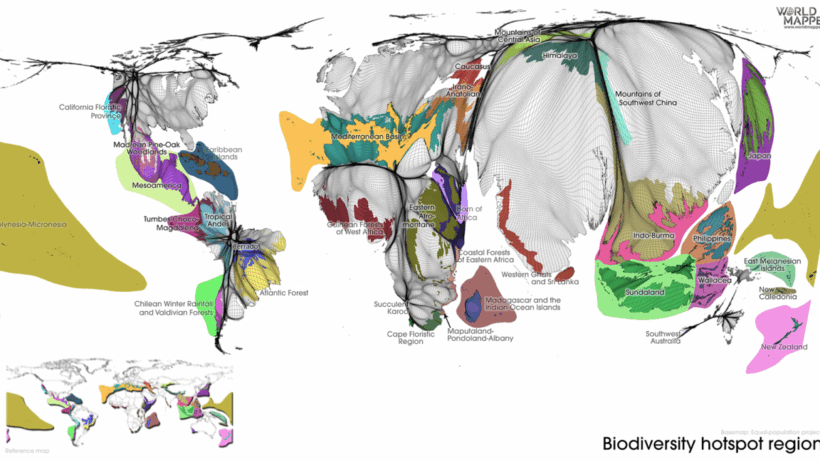
The planet is a diverse tapestry of life, yet certain regions stand out as true cradles of biodiversity. These biological hotspots, rich in endemic species and ecological richness, represent not only the pinnacle of natural beauty but also critical ecosystems in peril. The fascination with biodiversity hotspots stems from their unique ability to inspire awe while highlighting the fragility of life on Earth, making them intriguing subjects for exploration.
Before delving into specific regions, it is essential to understand what constitutes a biodiversity hotspot. Identified primarily by their high levels of endemic species—those that are found nowhere else on the planet—these areas also suffer significant habitat loss. To qualify as a hotspot, a region must have at least 1,500 species of vascular plants as endemics and it must have lost at least 70% of its original habitat. The intersection of richness and risk creates a delicate balance that is both compelling and alarming.
One of the most renowned hotspots is the Amazon Rainforest, often dubbed the “lungs of the Earth.” Covering approximately 5.5 million square kilometers across nine countries, it houses an astounding variety of flora and fauna, with millions of species yet to be identified. The dense foliage creates a microclimate, sustaining countless organisms. The Amazon River, winding through this vibrant ecosystem, is not just a waterway; it is the lifeblood for various species, from the iconic pink river dolphin to the nimble jaguar. However, rampant deforestation due to agriculture, logging, and mining threatens this ecological treasury, prompting urgent calls for conservation efforts.
Another notable hotspot is the Madagascar and the Indian Ocean Islands region. Madagascar, isolated for millions of years, boasts an extraordinary percentage of its flora and fauna that are endemic to the island. Lemurs, chameleons, and fossa are just a glimpse into its rich biodiversity, but this unique locale faces devastating challenges. The slash-and-burn practices common in agriculture and deforestation coupled with climate change are erasing habitats at alarming rates. The imminent extinction of many species looms as a shadows over this ecological gem, underscoring the importance of concerted conservation actions.
Moving to the Pacific, we uncover the Coral Triangle, the global epicenter of marine biodiversity. Encompassing six countries—Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, and Timor-Leste—this maritime hotspot features over 600 species of coral and 3,000 species of fish. The region’s reefs serve as crucial habitats for myriad marine organisms, supporting entire communities and economies. However, issues such as ocean acidification, overfishing, and pollution are threatening the delicate balance of these underwater ecosystems. Advocacy for sustainable fishing practices and marine protected areas has become imperative to preserve the astonishing life beneath the waves.
In Europe, the Mediterranean Basin is recognized as a biodiversity hotspot famed for its unique landscapes and rich plant life. Spanning across several countries, including France, Italy, and Greece, the area is a haven for numerous endemic species. Its diverse ecosystems range from coastal wetlands to mountainous terrains, each supporting a plethora of life forms. However, urbanization, unsustainable agriculture, and tourism have placed considerable stress on its natural habitats. The urgent need for sustainable development practices becomes pronounced to safeguard this intricate web of life.
The Himalayas, stretching through five countries including India and Nepal, earn their place among the top biodiversity hotspots due to their elevation-driven diversity. This majestic mountain range contributes to a variety of ecosystems, from tropical forests to alpine meadows, which in turn host a wide array of species, many of which are endemic. The region also plays a vital role in regulating climate and water resources for millions of people. Yet, the pressures of climate change, habitat degradation, and poaching threaten many species. The challenge lies in balancing conservation efforts with the needs of local communities reliant on these resources.
Lastly, one cannot overlook the Cape Floristic Region in South Africa, unique for its fynbos vegetation. This area possesses an astounding array of plant species, many of which are not found anywhere else on Earth. The fynbos serves as an essential part of the ecosystem, supporting an intricate network of pollinators and wildlife while playing a crucial role in the region’s water cycle. Unfortunately, invasive species, urban development, and agricultural encroachment are compromising this UNESCO World Heritage Site. Continuous education and community engagement are vital for promoting awareness and fostering stewardship for preserving such a rich heritage.
As we traverse through these biological hotspots, the intrinsic connection between biodiversity and human existence becomes increasingly evident. These regions are not merely repositories of beauty—they are essential for sustaining the planet’s ecosystems, balancing climate, and ultimately, supporting human life. The ongoing threats faced by these hotspots offer a poignant reminder of the fragility of life. Fostering a collective commitment to conservation and sustainable practices is not just an environmentalist’s cause; it is a global imperative.
The fascination with biodiversity hotspots lies in the intricate, symbiotic relationships that form the basis of life on Earth. Each of these regions tells a story of evolutionary wonder, ecological balance, and human interference. As stewards of the planet, it is our responsibility to protect these captivating regions, ensuring that the marvels of biodiversity continue to inspire generations to come.