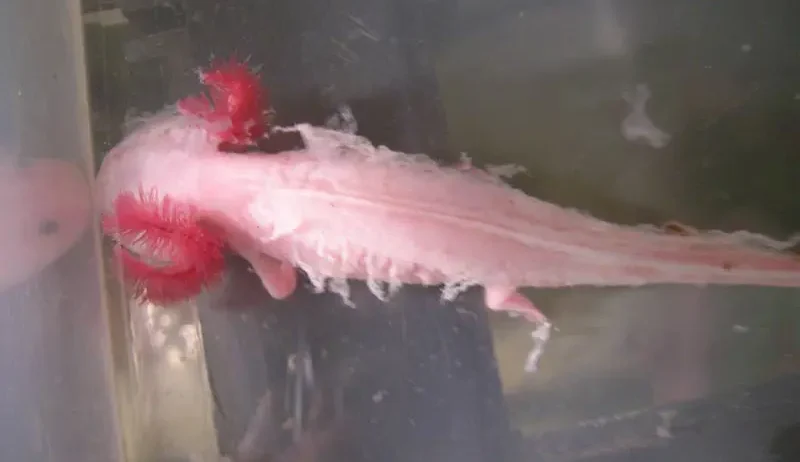
When one gazes upon the peculiar, whimsical visage of an axolotl, it is challenging to resist the urge to dive deeper into the nuances of its existence. This enchanting creature, a permanent resident of aquatic worlds, has captivated the hearts and minds of both casual observers and scientific scholars alike. With its diminutive limbs, feathery gills, and an unmistakable smile, the axolotl beckons further inquiry into its curious biology and care needs, particularly regarding its ability—or rather, inability—to thrive outside of water.
Historically, the axolotl, known scientifically as Ambystoma mexicanum, originates from the ancient lakes of Xochimilco and Chalco in Mexico. These amphibians are remarkable not only for their striking appearance but also for their extraordinary regenerative capabilities. They can regenerate lost limbs, parts of their heart, and even portions of their brain. Such astounding attributes render the axolotl a fascinating subject of study, yet it also raises a pivotal question: can axolotls live out of water?
To address this inquiry, it is imperative to understand the axolotl’s integumentary system. Unlike many terrestrial animals, axolotls possess permeable skin through which they absorb moisture and oxygen. This characteristic makes them highly susceptible to desiccation; hence, prolonged exposure to dry environments is detrimental to their survival. Their skin requires constant hydration to maintain physiological processes crucial for overall health. In a dry atmosphere, axolotls quickly lose moisture and become lethargic, paving the way for possible fatal outcomes.
As semi-aquatic creatures, axolotls exhibit neoteny—retaining juvenile characteristics throughout their entire lives. This trait permits them to maintain their gilled, aquatic form into adulthood, starkly contrasting the metamorphosis exhibited by their amphibian relatives. While some axolotls can, under specific conditions, undergo a form of metamorphosis to transition into a terrestrial form, this remains an exceptional occurrence and is influenced by environmental factors and hormonal changes. Therefore, while axolotls possess the biological hardware for terrestrial life, the typical specimen is wholly adapted to an aquatic environment.
The notion of an axolotl living for substantial periods outside of water is greatly misunderstood. A brief excursion out of water—often when exploring their environment or during tank cleaning—may be tolerable. However, prolonged exposure leads to dehydration. As a gardener might scornfully observe wilting foliage, an axolotl out of water exhibits signs of distress, which escalate rapidly without immediate intervention. These signs include a drooping posture and a reluctance to engage in typical behavior.
Understanding the care requirements of axolotls is also pivotal for enthusiasts interested in maintaining these enchanting creatures. Axelotl care encompasses several fundamental components: water quality, temperature regulation or acclimatization, and nutrition. Failure to provide suitable conditions can result in detrimental health issues. Initially, focus on water quality; axolotls thrive in clean, dechlorinated, and well-filtered tanks with temperatures ideally between 60°F and 68°F. Water that is too warm can hinder breathing and lead to stress; thus, consistent monitoring is imperative.
Every aquarist must also recognize that axolotls exhibit a carnivorous diet primarily comprising protein-rich foods. They flourish on high-quality pellets designed for carnivorous fish, live or frozen foods like bloodworms, brine shrimp, and earthworms. Providing a varied diet is advised to ensure they receive a broad spectrum of nutrients. Overfeeding should be carefully avoided, as it can lead to unhealthy growth and stress on their already delicate biology.
Moreover, the fascination with axolotls extends beyond their survival capabilities into socio-cultural aspects. In Mexican culture, axolotls are deeply embedded within folklore and tradition, often symbolizing transformation and regeneration. Efforts to conserve their natural habitat, which has been alarmingly depleted due to urbanization and pollution, resonate with broader environmental efforts aimed at safeguarding global biodiversity. The axolotl, therefore, serves as both a scientific marvel and a poignant emblem of the necessity to protect our fragile ecosystems.
Engagement in fostering awareness around the plight of axolotls contributes to larger conservation efforts. Advocacy for clean water practices and habitat preservation not only enhances the living conditions for these fascinating creatures but also serves as a clarion call for protecting numerous aquatic species threatened by human activity. Each axolotl we nurture represents a step forward in this vital mission, highlighting the intricate interplay between human intentions and ecological well-being.
In conclusion, the enchanting axolotl is a creature of remarkable characteristics, but its affinity for aquatic habitation is a non-negotiable facet of its existence. Without water, it faces severe limitations and decline. Responsible care paired with proactive ecological involvement can help ensure that this remarkable species continues to thrive—both in its native waters and in the hearts of those enthralled by its unique charm. The exploration of its world inspires not only admiration but also a collective responsibility to uphold a commitment to preserving the delicate balance of life within our ecosystems.