The multifaceted phenomenon of climate change has emerged as one of the most pressing issues of our time, manifesting its effects across diverse ecosystems and human systems alike. This article presents a global overview of climate change, delving into its various dimensions and impacts. The urgency of the situation compels a comprehensive understanding of the ramifications that accompany rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns.
Understanding Climate Change: A Brief Overview
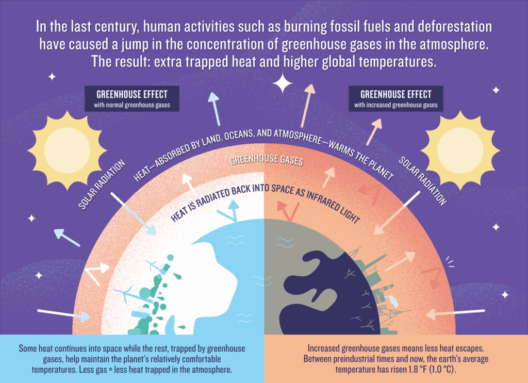
At its core, climate change refers to significant alterations in temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns over extended periods. While it is a natural occurrence over geological timescales, human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, have accelerated its pace. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) underscores that anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs) are a fundamental driver of current climate trends. The escalation in global mean temperatures leads to far-reaching consequences, altering not just the environment but also the socio-economic fabric of societies worldwide.
Temperature Extremes: The Heat is On
One of the most palpable outcomes of climate change is the increasing frequency and intensity of temperature extremes. Heatwaves, which were once rare events, are now becoming commonplace, affecting public health and the economy. Prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures can lead to heat-related illnesses, increased mortality rates, and a strained healthcare system. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and individuals with pre-existing health conditions, face disproportionate risks.
Additionally, the ramifications extend beyond immediate human health. Agricultural systems are gravely impacted, as crops suffer from heat stress, leading to reduced yields and compromised food security. The economic implications are severe, as farmers experience losses that ripple through the food supply chain, ultimately affecting consumers. In temperate regions, traditional crops may no longer thrive, prompting shifts in agricultural practices and cultivation strategies.
Rising Sea Levels: A Frightening Reality
Another profound consequence of climate change is the inexorable rise in sea levels, primarily driven by glacial melt and thermal expansion of seawater. Coastal communities are encountering escalating risks of flooding, erosion, and saltwater intrusion. Cities such as Miami, New Orleans, and Jakarta are grappling with the daunting prospect of becoming uninhabitable as sea levels continue to rise. As land becomes submerged, the displacement of populations creates significant humanitarian challenges, necessitating urgent intervention and adaptation strategies.
Yet, the consequences of rising sea levels extend far beyond local communities. There is a salient risk of geographical and socio-political instability as climate refugees flee regions rendered uninhabitable. The migration of large populations can lead to increased tensions in receiving areas, further complicating the socio-economic landscape. The international community must prepare for the complexities that arise from these movements, as traditional definitions of borders and national identity may be fundamentally challenged.
Extreme Weather Events: The New Norm
Climate change is substantially correlated with the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, including hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires. A warming atmosphere holds more moisture, leading to more intense rainfall events and subsequent flooding. Conversely, regions that experience prolonged droughts face catastrophic consequences for agriculture, water supply, and overall ecosystem health.
The impact of severe weather incidents often results in loss of life, destruction of infrastructure, and long-term economic burdens. For instance, hurricanes fueled by warmer ocean temperatures have shown an increased intensity, leading to catastrophic storm surges and widespread devastation, as evidenced by events like Hurricane Katrina and Hurricane Harvey. Communities need to bolster their resilience to withstand these intensified weather patterns, necessitating investments in infrastructure, emergency preparedness, and community education.
Ecological Disruption: Biodiversity at Stake
The ramifications of climate change penetrate deep into the natural world. Ecosystems are experiencing shifts in species distribution, timing of biological events, and overall biodiversity. Climate change alters the delicate balance of ecosystems, often leading to the extinction of vulnerable species that cannot adapt quickly enough to the changes in their habitats.
Coral reefs, which are indispensable ecosystems, face unprecedented challenges due to ocean acidification and rising temperatures. The phenomenon known as coral bleaching compromises the health of these vital marine habitats, threatening the myriad species that rely on them for survival. Additionally, terrestrial ecosystems are morphing, with some species migrating to higher altitudes or latitudes in search of suitable climates, thereby disrupting established ecological relationships.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Understanding the multifarious effects of climate change is paramount for shaping effective responses. As individuals, communities, and nations grapple with these impending realities, the importance of collective action becomes increasingly evident. Mitigation strategies such as reducing carbon emissions, fostering renewable energy sources, and advocating for sustainable land practices are critical steps in addressing this global challenge. Moreover, adaptation measures will be essential for communities on the frontlines of climate change impacts. It is incumbent upon all stakeholders—government, industry, and civil society—to unite in a resolute effort to combat climate change and safeguard the delicate balance of our planet for future generations.