Climate change is a complex tapestry woven from myriad threads, each contributing to the overarching narrative of our planet’s shifting dynamics. At its core, climate change results from several interlinked factors—both natural and anthropogenic. Understanding these drivers, akin to tracing the roots of an ancient tree, offers vital insights into how our actions influence the Earth’s systems.
To navigate this intricate landscape, one must first consider the primary engines of climate change. These can be categorized into two main realms: greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation, each serving as a powerful catalyst in the warming of our atmosphere.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The Invisible Blanket
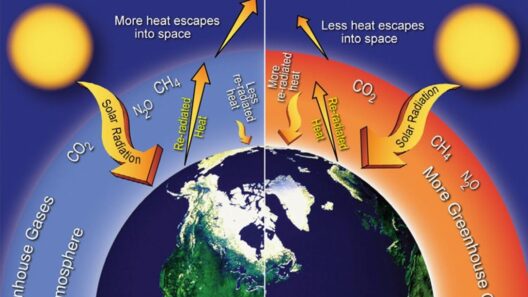
At the forefront of climate change is the phenomenon of greenhouse gas emissions. Just as a blanket retains warmth, greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), trap heat in the atmosphere. Their increasing concentration creates a chaotic dance between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere, leading to the greenhouse effect. This effect is not merely an environmental concern; it is a mechanism with far-reaching consequences on global temperatures, rainfall patterns, and weather extremes.
Carbon dioxide stands as the most significant player in this arena. It is released predominantly through the combustion of fossil fuels—coal, oil, and natural gas—used for energy production, transportation, and industrial processes. Since the dawn of the Industrial Revolution, CO2 levels in the atmosphere have skyrocketed, forming a pernicious layer that shields the Earth, ensuring temperatures continue to rise.
On the other hand, methane—a gas with a potency over 25 times greater than CO2—often emerges from agricultural practices, landfills, and the oil and gas sector. As it escapes into the atmosphere, methane contributes to a more intense greenhouse effect, accentuating the urgency of addressing its sources.
Nitrous oxide, though less prevalent, also deserves attention. Often emanating from agricultural fertilizers, its role in climate change adds another dimension, intertwining food production with environmental stability. The multifaceted impacts of these emissions illustrate the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to curtail our reliance on fossil fuels and move toward sustainable alternatives.
Deforestation: The Silent Thief of Carbon
While greenhouse gas emissions take center stage, deforestation lurks in the shadows, quietly siphoning away nature’s capacity to absorb CO2. Forests, often termed the lungs of the Earth, play an indispensable role in sequestering carbon. When trees are cut down or burned, this stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere, adding to the greenhouse gas burden and exacerbating climate change.
The drivers of deforestation range from agricultural expansion to urban development, indicating a troubling divergence between human progress and environmental preservation. In many regions, forests are cleared to make way for cattle ranching, palm oil plantations, and other agricultural pursuits. The relentless march of urbanization further compounds this issue, as cities expand at an alarming rate, often eradicating vital natural habitats in the process.
Consequently, deforestation represents not just a loss of biodiversity, but a profound alteration of the Earth’s climate system. The collective loss of trees diminishes the planet’s resilience against climate impacts, leading to more severe weather events, altered rainfall patterns, and disruptions in local ecosystems.
Industrialization and Urbanization: The Double-Edged Sword
In the quest for progress, industrialization and urbanization have birthed modern conveniences but have also intensified the drivers of climate change. The transition from agrarian societies to industrial powerhouses has led to an exponential rise in energy consumption, with an overwhelming reliance on fossil fuels to meet the surging demands of urban populations.
As cities swell with inhabitants, they become epicenters of emissions. Transportation networks, heating and cooling systems, and manufacturing industries release substantial amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. A city, in many respects, mirrors a well-oiled machine; its functionality often overshadows the ecological repercussions of its operations.
This urban conundrum segregates humanity from nature, fostering a false sense of separation. In this narrative, it is essential to reintegrate ecological principles into urban planning. Sustainable development that prioritizes green spaces, renewable energy sources, and efficient public transportation can play a pivotal role in mitigating climate change, illustrating the importance of harmonizing human advancement with environmental stewardship.
Global Interdependencies: The Ripple Effect
The drivers of climate change do not operate in isolation. They intertwine and demonstrate global interdependencies that amplify their effects. Actions taken in one part of the world can reverberate across continents, emphasizing the need for a concerted global response. Climate change knows no borders; it endeavors to challenge the very fabric of international cooperation.
Addressing climate change requires not only local solutions but also a sense of global responsibility. Nations must collaborate to share technology, resources, and knowledge. Collective action can ripple outward, creating transformations that restore balance to our cherished planet.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding the main drivers of climate change—greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, industrialization, and urbanization—provides clarity in the face of an ecological crisis. As individuals and communities grapple with these complex issues, it is crucial to recognize that our choices matter. Every action, from our energy consumption to our use of land, contributes to the tapestry of our climate. The challenge lies not just in identification, but in action. To mend the fabric of our world, we must weave together innovations, policies, and an unwavering commitment to safeguarding our shared future.