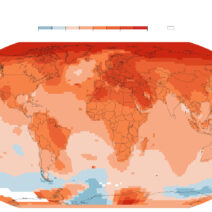
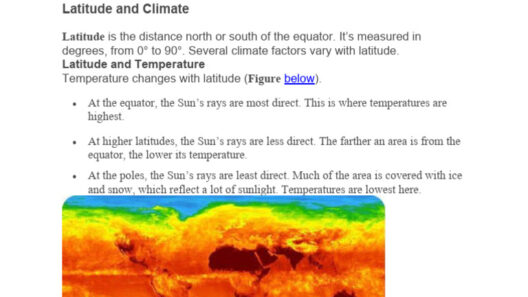
Arid climates are characterized by their distinct lack of moisture, resulting in dry, hot, and often harsh environmental conditions. This climatic region is fascinating for various reasons, particularly the resilience of life that adapts and thrives amid such unforgiving circumstances. The arid zones, encompassing deserts and semi-deserts, sport unique ecosystems and their own set of challenges. Understanding what constitutes an arid climate is essential as it unveils not just the physical aspects but also the deeper implications on biodiversity, human activity, and environmental sustainability.
Defining the Arid Climate: Nature’s Extremes
An arid climate, classified primarily by its low precipitation levels, usually receives less than 10 inches of rainfall annually. This lack of sufficient moisture creates an environment where evaporation frequently exceeds precipitation, contributing to the typically high temperatures. Aridity manifests in various geographic regions across the globe, including iconic deserts such as the Sahara in Africa, the Mojave in North America, and the Arabian Desert in the Middle East.
These climates often experience extreme daily temperature fluctuations. Daytime temperatures can soar to well over 100 degrees Fahrenheit, while at night, they can plummet to significantly cooler levels. The desiccated air holds very little humidity, adding to the stark contrast experienced during the day and night. Such conditions are not merely an observation; they hint at a complex interplay between the Earth’s atmospheric and geographical features.
The Dual Facets: Hot versus Cold Arid Climates
While arid climates are predominantly hot, it is essential to note that some cold deserts exist. Cold arid climates, found in areas like parts of Antarctica and the Gobi Desert, are marked by significantly lower temperatures, particularly during winter months. These regions display the same characteristics of low precipitation and high evaporation but can host a different array of flora and fauna as adaptions are made for surviving extreme cold alongside scarce water resources. This duality presents an intriguing dichotomy within arid climates and reveals the intricacies of ecological adaptation.
Fascinating Flora: Surprising Survivors of Desolation
Plants in arid climates have evolved remarkable survival strategies to withstand the relentless heat and scarce water. Xerophytic plants, such as cacti, succulents, and certain species of shrubs, exemplify this incredible resilience. They possess specialized structures such as thick, waxy skins and deep root systems that enable them to store and conserve water efficiently. The unique adaptations found in these plants are not merely biological wonders but also reflect the underlying themes of survival and endurance amid adversity.
Furthermore, the phenomenon of drought resistance among these species is captivating. Some plants can enter a state of dormancy during extreme drought, conserving energy and resources until conditions improve. This life strategy underscores the ingenuity of nature in coping with an inhospitable environment, prompting a reevaluation of perceptions regarding uninhabitable areas.
Animal Adaptations: Masters of Survival
Life in arid climates extends beyond plants. The animal kingdom has also birthed an array of extraordinary adaptations. Many desert-dwelling species, such as the fennec fox and the kangaroo rat, exhibit remarkable physiological and behavioral adaptations to mitigate water loss and maximize available moisture. These creatures may be nocturnal, avoiding the oppressive daytime heat, or they possess unique abilities to extract hydration from their food, thus minimizing their dependency on water sources.
The social life of these species is equally fascinating. For instance, pack behavior among certain social mammals, such as wolves or hyenas, allows for better hunting efficiency and protection from predators in harsh conditions. In arid climates, survival often necessitates cooperation and adaptation, highlighting intricate relationships that sustain both individuals and the ecosystem as a whole.
Human Endeavors: The Struggle for Survival and Development
Human impacts on arid regions have been profound, as populations gravitate towards these vast expanses for various reasons. Agriculture in arid climates relies heavily on understanding and manipulating the environment through irrigation techniques. Innovators have developed methods like drip irrigation and hydroponics, enhancing agricultural yields in these challenging terrains. These adaptations underscore mankind’s drive to conquer nature, yet they also prompt critical discussions about sustainability.
Constrained by limited water resources, communities in arid climates face unique challenges in water management. As climate change exacerbates existing conditions, the competition for water among agricultural, residential, and industrial uses intensifies. This strain on natural resources raises pertinent questions about future sustainability and the ethical implications of exploiting arid environments more and more.
Climate Change: The Unfolding Crisis
Climate change poses an imminent threat to arid climates, with projections suggesting that these areas may experience increased temperatures and altered precipitation patterns. Such changes can lead to enhanced desertification, threatening not just local ecosystems but also the livelihoods of populations dependent on these regions. The precarious balancing act between human activity and environmental health invites scrutiny regarding resource allocation and responsible management.
The allure of arid climates lies not solely in their stark beauty or unique wildlife but extends into broader discussions about adaptation, resilience, and the imperiled balance of nature. Understanding these ecosystems provides a crucial perspective on both the fragility and tenacity of life. The intricacies of arid climates exemplify how, despite the harshest conditions, life finds a way to endure. It motivates a deeper examination of our relationship with nature, one that emphasizes harmony and sustainability as humanity moves forward into an uncertain climate future.