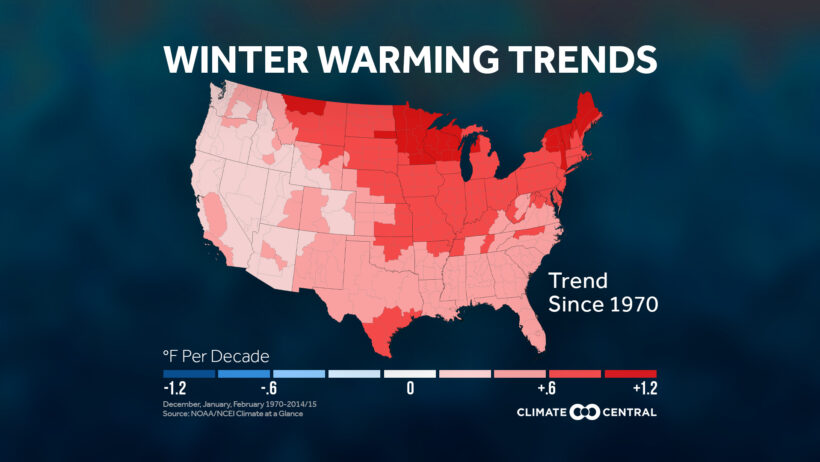
As we peer into the intricate tapestry of our planet’s climate, one predominant truth emerges: winters are becoming warmer, a phenomenon that serves as a mere glimpse of the broader and increasingly concerning climate change narrative. Understanding the multifaceted reasons behind this shift unveils a deeper understanding of our environmental predicament. In this exploration, we will dissect various interrelated elements contributing to global warming, formulating a clearer image of the issues at hand.
Climate Change: A Natural Cycle Disrupted
Throughout Earth’s history, climate has undergone natural fluctuations, oscillating between glacial and interglacial periods over millennia. However, the climate we are experiencing today diverges sharply from these historical patterns. The crux of the matter lies in the unprecedented rate at which human activities have disrupted these natural cycles.
The Industrial Revolution heralded the onset of a new era—characterized by rampant fossil fuel consumption, deforestation, and industrial emissions. This transformation has significantly elevated carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, triggering the greenhouse effect: sunlight penetrates the atmosphere, warming the Earth, while the heat struggles to escape due to an abundance of greenhouse gases, such as CO2 and methane.
Consequently, what was once a manageable equilibrium is now a perilous imbalance. The resultant warming is palpable, as evidenced by rising global temperatures, retreating ice sheets, and increasingly erratic weather patterns. The correlation between human activity and climate change has never been clearer; our present reality is a juxtaposition of technological advancement and environmental degradation.
Anthropogenic Influences: The Driving Force Behind Global Warming
Delving deeper into the anthropogenic components yields a plethora of significant factors that shape our current climate trajectory. The most salient among these factors is the fossil fuel industry, which fuels not only our automobiles and homes but also our economies.
Burning fossil fuels releases vast quantities of carbon dioxide, the primary driver of climate change. In fact, energy production contributes to approximately 70% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, the advent of unconventional oil extraction methods such as fracking has exacerbated emissions, coupled with the release of methane—a gas considerably more potent than CO2 in terms of its heat-trapping capacity.
Agriculture, on the other hand, is another formidable contributor to climate change. Livestock production emits substantial amounts of methane, primarily through enteric fermentation in ruminants. Additionally, land-use changes associated with agricultural expansion result in deforestation, the detrimental loss of vital carbon sinks. The dual impact of methane and loss of forests engenders a vicious cycle, compounding the challenges we face.
Urbanization: The Rise of Heat Islands
The phenomenon of urbanization embodies a double-edged sword in our climate narrative. On one hand, cities are socio-economic powerhouses; on the other, they represent heat islands—areas where temperatures significantly transcend surrounding rural locales. This aberration arises from the extensive use of concrete, steel, and other surfaces that absorb and retain heat, compounded by a lack of vegetation that can mitigate temperatures through evapotranspiration.
The urgency we face is further accentuated by the projections indicating that, by 2050, nearly 70% of the global population will reside in urban areas. This impending urban swell underscores the need for rigorous planning and sustainable practices that contribute to the resilience of cities against climate change.
Promoting “green” infrastructure concepts—like urban forests, green roofs, and the integration of renewable energy sources—can assuage some of the pressures exerted by urbanization. By reimagining our cities, we can combat the effects of climate change while enhancing the quality of life for their inhabitants.
Natural Feedback Loops: The Perilous Tipping Points
As we navigate the climate discourse, we cannot disregard the precarious nature of natural feedback loops that exacerbate warming. The melting of polar ice caps is not merely an aesthetic concern—it releases stored greenhouse gases and diminishes Earth’s albedo, the ability to reflect sunlight. Consequently, as ice recedes, more sunlight is absorbed by darker ocean waters, instigating further warming.
Similarly, the thawing of permafrost in the Arctic presents an impending hazard. As it melts, previously trapped methane is released into the atmosphere, further amplifying greenhouse gas concentrations. These feedback loops illustrate a disconcerting reality—while we grapple with our immediate anthropogenic impacts, nature is unveiling its own retaliatory mechanisms, which could have irreversible consequences.
Shifting Perspectives: Collective Action and Responsibility
To navigate this complex labyrinth of causation, it is imperative to foster a shift in collective perspective. Embracing a climate-conscious mindset extends beyond merely acknowledging individual responsibility; it encompasses systemic transformation. Governments, corporations, and communities must engage in concerted efforts to mitigate their environmental footprints.
The developments in renewable energy technology, responsible consumption practices, and sustainable development finance highlight pathways toward a more sustainable future. By investing in innovative solutions, such as wind and solar energy, we can gradually extricate ourselves from fossil fuel dependence. It is only through holistic engagement and united action that we may hope to reverse our trajectory and pave the way for a rosier environmental future.
Conclusion: The Path Forward Lies in Action
As we unravel the intricate web of influences behind escalating global temperatures, we confront not only the enormity of the challenges at hand but also a glimmer of hope. Awareness, education, and proactive measures are paramount in combating the repercussions of climate change. By unlocking the reasons behind our planet’s warming, we come to understand our role within this ecological framework. The confrontation of climate change is upon us; only through resolute action can we aspire to safeguard the future of our planet.