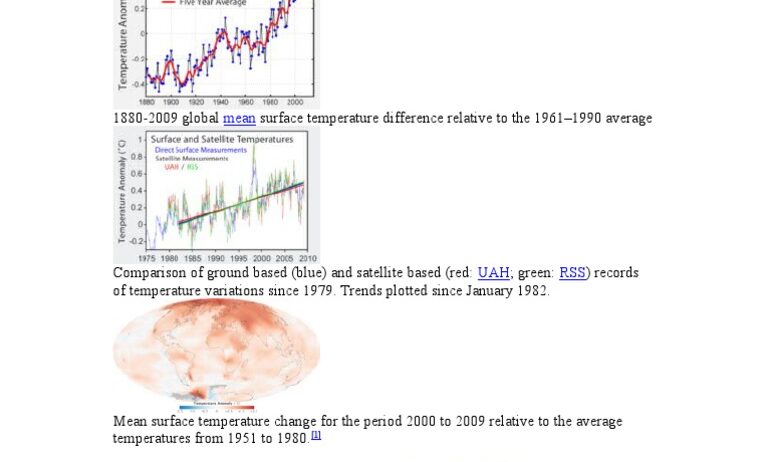
Global warming, a term that elicits a myriad of emotions, is not merely a scientific phenomenon; it is a profound alteration of the earth’s climate system, instigated primarily by human activity. The warming of our planet has repercussions that extend far beyond increasing temperatures, altering ecosystems, economies, and communities worldwide. Understanding these ramifications is imperative in our fight against climate change and in mobilizing individuals towards sustainable practices.
The most noticeable effect of global warming is the rise in average global temperatures. However, this phenomenon precipitates a cascade of additional consequences that are often overlooked.
One could argue that the fascination with global warming stems from its profound implications for biodiversity and human existence. The increase in temperatures is leading to shifting weather patterns, rising sea levels, and more frequent and severe weather events, which offer a stark glimpse into the future we may face.
As global temperatures rise, the following key areas are affected:
Ecological Disruption and Loss of Biodiversity
A warming planet directly impacts ecosystems and the myriad species that inhabit them. Habitats are being irrevocably altered, leading to mismatches between species’ needs and their environment. For instance, many plant species are unable to adapt quickly enough to the changing conditions, leading to their decline or extinction. This, in turn, affects the animals that rely on them for food and shelter. The extinction of a single species can create a domino effect, leading to the collapse of entire ecosystems.
Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are one of the most vulnerable ecosystems. Rising sea temperatures lead to coral bleaching, a process that compromises the coral’s ability to thrive. This not only threatens marine life but also the livelihoods of communities dependent on these rich ecosystems for tourism and fishing.
Agricultural Challenges and Food Security
The agricultural sector is not immune to the grip of global warming. Increased temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns have drastic implications for crop yields. Regions that were once fertile may become parched, while others might be inundated with excessive rainfall, resulting in flooding. As agricultural systems falter, food security becomes a pressing issue. It is estimated that even minor changes in temperature can reduce yields of staple crops such as wheat, rice, and maize significantly.
Consequently, food prices are expected to increase, further exacerbating inequality and hunger in vulnerable populations. The ripple effects of agricultural challenges extend beyond the farm; they influence economic stability, health, and social cohesion on a global scale.
Human Health Strain and Disease Proliferation
The implications of global warming on human health are profound. Rising temperatures contribute to more frequent heatwaves, which can lead to an uptick in heat-related illnesses and fatalities. Elderly and vulnerable populations are particularly at risk. Additionally, changing climate conditions create ideal breeding grounds for disease-carrying organisms. For example, the expansion of the habitat of mosquitoes increases the incidence of malaria, dengue, and Zika virus.
Moreover, air quality is deteriorating as a result of climate change, with increased pollutants contributing to respiratory ailments and cardiovascular diseases. The mental health implications, stemming from anxiety about climate change and its consequences, cannot be ignored either. As communities face displacement due to extreme weather events or rising sea levels, the psychological toll can be devastating.
Economic Repercussions and Infrastructure Threats
The economic ramifications of global warming are vast and multifaceted. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, wildfires, and floods, result in staggering costs for recovery and rebuilding. Infrastructure designed for stable weather conditions faces unprecedented stress and damage. Cities along coastlines, already grappling with rising sea levels, must reconsider their urban planning strategies to accommodate this new reality.
Insurance industries are gradually increasing premiums to account for heightened risks associated with climate events, which ultimately affects homeowners and businesses alike. Agricultural economies, reliant on stable growth conditions, are also subject to the fluctuations caused by climate change. Investments in renewable energy, while essential, require significant initial funding and commitment, yet these can be overshadowed by the immediate crises arising from climate impacts.
Integration of Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
Awareness of the impacts of global warming and their wide-ranging consequences is the first step towards addressing this pressing crisis. Adaptation and mitigation strategies are essential in combating these threats. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices can help lessen the burden of greenhouse emissions.
Moreover, global cooperation is needed more than ever. Climate change transcends borders, impacting all nations regardless of their contribution to the problem. International treaties, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to foster collaboration, but tangible progress requires commitment from both developed and developing countries.
The path forward involves a shared responsibility—communities, governments, and businesses must unite to tackle global warming’s looming threats. Through education, advocacy, and proactive steps, there is hope for a sustainable and resilient future.
In conclusion, the reality of global warming extends beyond mere temperature increases; it poses complex challenges that resonate throughout ecological, economic, and social landscapes. Understanding these implications is crucial in fostering a commitment to change and igniting a collective response to preserve our planet for generations to come.