Understanding Global Warming: An Overview
Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases. These emissions predominantly stem from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes. The scientific consensus acknowledges that these changes have significant implications for ecosystems, weather patterns, and human health. Understanding global warming is integral not only to environmental sustainability but also to economic stability, as its repercussions resonate across various sectors.
Defining Greenhouse Gases and Their Role
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases in the Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat. The most prevalent GHGs include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). Each of these gases has a different capacity to trap heat; for instance, methane is over 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of heat retention over a 100-year period.
Human activities contribute significantly to the concentrations of these gases. For example, burning fossil fuels for transportation and electricity generation releases vast amounts of CO2. Agriculture contributes significantly to methane emissions, primarily through livestock digestion and rice cultivation. The increase in these gases leads to an enhanced greenhouse effect, which traps more heat in the atmosphere, thereby raising global temperatures.
Scientific measurements indicate that since the pre-industrial era, the average global temperature has risen by approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius. This increase may seem minor, but even small temperature changes can trigger severe consequences, impacting weather patterns and biodiversity across the planet.
The Science Behind the Greenhouse Effect
To grasp the implications of global warming, one must first understand the greenhouse effect itself. Solar radiation from the sun reaches the Earth, where a portion is absorbed, warming the planet. The Earth then radiates this heat back toward space. However, greenhouse gases absorb some of this outgoing heat, preventing it from escaping. This process is vital for maintaining the planet’s temperature, but human-induced increases in GHG concentrations have intensified the effect, leading to climate change.
Some of the primary drivers of temperature increase due to global warming include:
- Radiative Forcing: This term refers to the difference in energy absorbed by the Earth and energy radiated back into space. An increase in GHGs enhances radiative forcing, resulting in a net increase in Earth’s energy, contributing to rising temperatures.
- Feedback Loops: Climate dynamics often involve feedback mechanisms. For instance, as polar ice melts due to rising temperatures, it exposes darker ocean or land surfaces that absorb more sunlight, leading to further warming—a cycle that can accelerate the effects of climate change.
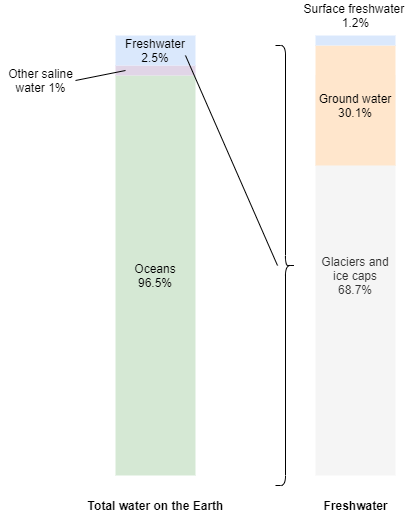
- Ocean Warming: The Earth’s oceans serve as a significant heat reservoir, absorbing approximately 93% of the excess heating produced by GHG emissions. This warming not only affects marine ecosystems but also contributes to rising sea levels through thermal expansion and melting ice sheets.
The Consequences of Global Warming
The ramifications of global warming are extensive and multifaceted, affecting various aspects of life on Earth. Understanding these consequences is crucial for grasping the urgency behind climate action.
First and foremost, global warming contributes to extreme weather events. Rising temperatures lead to increased evaporation rates, resulting in more intense storms, droughts, and heatwaves. These weather phenomena can devastate communities, disrupt agriculture, and trigger natural disasters like floods and wildfires.
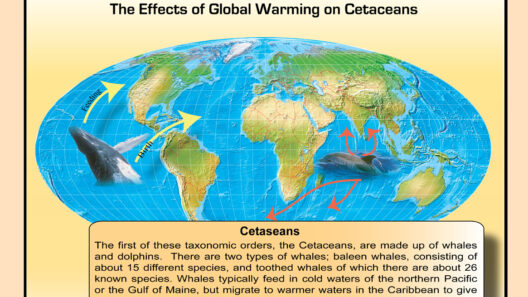
Secondly, global warming threatens biodiversity. Many species find it challenging to adapt to rapidly changing habitats, leading to shifts in ecosystems. Coral reefs, for example, are highly sensitive to temperature changes, which can result in widespread bleaching and mortality of marine life. A loss of biodiversity has cascading effects on ecosystem services, such as pollination and water purification, that humans rely upon.
Additionally, global warming poses health risks. Increased temperatures can exacerbate air quality issues, leading to respiratory problems. Further, with climate change, diseases that thrive in warmer climates may spread to new regions, posing new public health challenges.
Mitigating Global Warming: What Can Be Done?
Addressing global warming necessitates concerted global efforts. Mitigation strategies focus on reducing GHG emissions, enhancing energy efficiency, and transitioning to renewable energy sources. Some effective methods include:
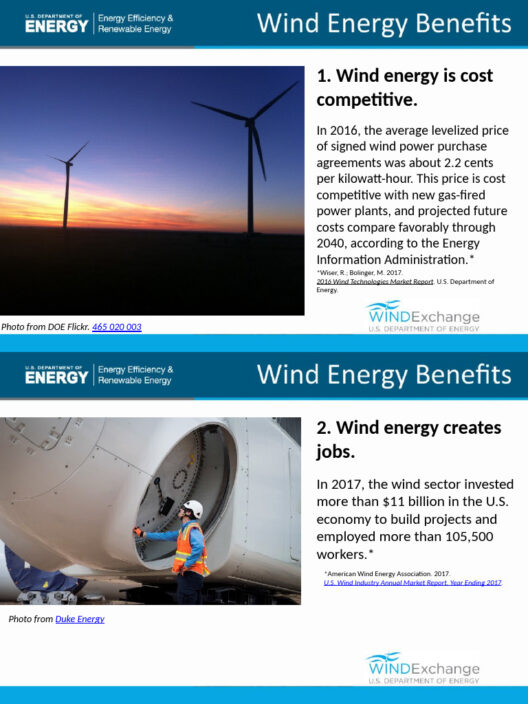
- Transitioning to Renewable Energy: Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power represent viable alternatives to fossil fuels. By investing in these clean energy sources, we can significantly curtail carbon emissions and lessen our ecological footprint.
- Enhancing Energy Efficiency: Modifying our buildings, transportation systems, and industrial processes to be more energy-efficient can drastically reduce the amount of fossil fuel needed, thus lowering GHG emissions.
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing practices such as regenerative agriculture, which enhance soil health and carbon sequestration, can mitigate methane emissions from conventional farming methods.
As global citizens, fostering a culture of sustainability and awareness around our environmental impact is paramount. Every small action contributes to the larger goal of combating climate change, thus shaping the world for future generations.
In conclusion, global warming transcends mere temperature increases; it represents a systemic challenge that intertwines with economic stability, health, and ecological integrity. Understanding the science behind it is a vital step toward advocacy, education, and action in the realm of climate justice.