Global warming has emerged as one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time. At the heart of this phenomenon lies the concept of greenhouse gases (GHGs). Their intricate role in the Earth’s atmospheric chemistry is crucial for understanding climate change. This article will delve into the mechanics of greenhouse gases, their contributions to climate change, and the far-reaching implications they hold for both the planet and humanity.
Anatomy of Greenhouse Gases: The Vital Players
To grasp the implications of greenhouse gases on global warming, one must first understand their very nature. Greenhouse gases are atmospheric constituents that trap heat from the sun, preventing it from escaping back into space. This natural process is known as the greenhouse effect. Without it, our planet would be inhospitably cold, averaging around -18 degrees Celsius instead of the comfortable 15 degrees Celsius that sustains life as we know it.
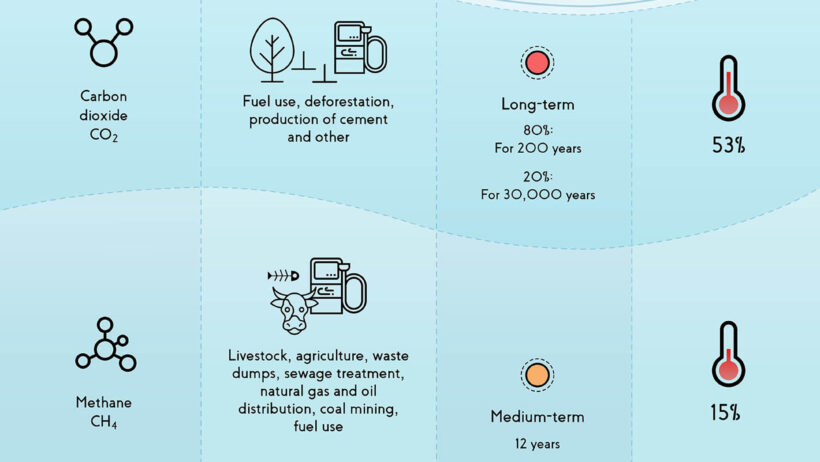
Among the primary greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor, each of which contributes differently to the greenhouse effect. Carbon dioxide is produced from the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and various industrial practices. Methane, on the other hand, is emitted during the production and transport of coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as agricultural practices, particularly from livestock. Nitrous oxide, a less abundant but potent gas, is primarily released from agricultural activities and the use of synthetic fertilizers. Understanding these gases’ sources, concentrations, and effects is essential in navigating the complexities of climate change.
The Greenhouse Effect: A Double-Edged Sword
The greenhouse effect is a natural and vital phenomenon that keeps our planet warm. However, the problem arises when human activities exacerbate the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere. The enhanced greenhouse effect, a direct result of industrialization and urbanization, has led to an alarming increase in average global temperatures. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has reported that the Earth’s surface temperature has risen by approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century, largely due to increased levels of carbon dioxide and other gases.
This rise in temperature has dire implications. It contributes to the melting of polar ice caps, resulting in rising sea levels that threaten coastal communities worldwide. Furthermore, it leads to severe weather patterns, rendering regions prone to hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires. The distribution of wildlife is also affected, as species struggle to adapt to the rapidly changing climate. The delicate balance of ecosystems is tipping dangerously toward collapse as habitats are lost and biodiversity is diminished.
Path to Mitigation: Strategies for Emission Reductions
Another strategy involves enhancing energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industries. By upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, utilizing public transport, and adopting sustainable agricultural practices, we can significantly decrease GHG emissions. Implementing carbon capture and storage technologies offers a way to remove CO2 from the atmosphere and sequester it underground. Furthermore, reforestation and afforestation initiatives play a critical role in carbon sequestration as trees absorb atmospheric CO2 through photosynthesis.
The Societal Dimensions: Climate Change and Equity
The implications of greenhouse gas emissions and climate change extend into social justice and equity. Vulnerable populations often bear the brunt of climate impacts despite contributing the least to greenhouse gas emissions. Low-income communities and developing countries frequently lack the resources and infrastructure to adapt to climate-induced changes, making them disproportionately susceptible to extreme weather events, food insecurity, and health issues. Addressing these inequities is essential in fostering a more resilient society.
Moreover, public awareness and engagement are crucial for driving action on climate change. Education about the sources and consequences of greenhouse gases can empower individuals to take actionable steps in their daily lives. An informed and motivated populace can advocate for policy changes and support initiatives geared toward sustainability.
A Call to Action: Your Role in Combatting Climate Change
Understanding the role of greenhouse gases in global warming is not just an academic exercise; it has profound implications for our collective future. Every individual can contribute, whether it’s through lifestyle changes, advocating for sustainable policies, or participating in local environmental initiatives. Tackling climate change requires a concerted effort from all sectors of society, from governments to grassroots organizations and individual citizens.
In conclusion, greenhouse gases undeniably contribute to global warming, significantly impacting our planet and all its inhabitants. The path forward requires unwavering commitment and collaboration to mitigate their effects and secure a sustainable future for generations to come. Acknowledging the intricate dance between human activity and nature’s balance is vital as we strive to safeguard our environment.