Global warming is a term that reverberates through the corridors of climate discussions, captivating attention with the gravity of its implications. At its core, global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases. This phenomenon is not merely an environmental concern; it is a profound challenge that carries significant social, economic, and existential dimensions. To truly comprehend the implications of global warming, one must explore its mechanics, manifestations, and the urgent need for collective action.
In the intricate ballet of Earth’s climate system, energy from the sun plays a pivotal role. Typically, sunlight penetrates the atmosphere, illuminating the planet and warming its surface. Some of this energy is radiated back into space, maintaining an equilibrium. However, human activities, particularly since the dawn of the industrial age, have introduced an excess of greenhouse gases—such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide—into the atmosphere. These gases create a thickened canopy, trapping more heat and disrupting the natural balance. As a result, Earth’s temperature steadily rises, a trend that has ascended alarmingly since the late 19th century.
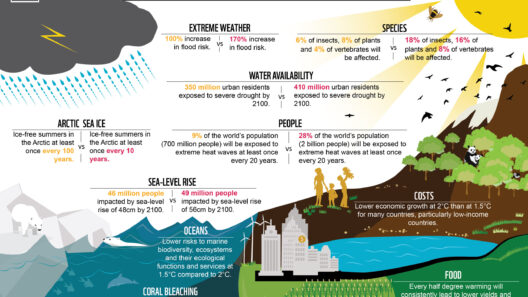
The implications of global warming extend beyond the confines of temperature change. They manifest in a myriad of ways, each echoing the fundamental shifts occurring within our atmospheric dynamics. From extreme weather patterns to disrupted ecosystems, the evidence is pervasive and multifaceted.
One of the most striking and immediate consequences of rising temperatures is the increase in extreme weather events. The intensity and frequency of hurricanes, droughts, floods, and heatwaves have surged as the climate system reacts to the excess heat. This volatile weather exacerbates vulnerabilities, particularly in regions already grappling with poverty and inadequate infrastructure. Countries around the globe find their agricultural outputs diminishing, water supplies depleting, and populations displaced, creating a tenuous situations for millions.
Furthermore, global warming fuels the accelerated melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. The Arctic and Antarctic regions, once bastions of cold, are experiencing unprecedented melting, contributing to rising sea levels that threaten coastal communities worldwide. The aesthetic beauty of glacial landscapes, sculpted over millennia, is now marred by the harsh reality of their rapid disappearance. It is a poignant reminder of nature’s fragility and the urgent need to address the underlying causes of climate change.
Coupled with these physical transformations is the impact on biodiversity. Many species struggle to adapt to the rapid pace of climate change, leading to habitat loss and potential extinction. Ecosystems that once thrived in equilibrium face disruption as organisms find themselves out of sync with their environments. The intricate web of life that sustains our planet is fraying, jeopardizing the ecological balance essential for human survival.
At the intersection of human health and global warming lies an array of additional challenges. As temperatures rise, so too does the prevalence of health-related issues. Heat-related illnesses, respiratory difficulties induced by air pollution, and the spread of vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue fever enhance the urgency around climate action. Vulnerable populations such as the elderly, children, and those with preexisting medical conditions face heightened risks, underscoring the human cost of inaction.
As we contemplate the labyrinth of consequences stemming from global warming, it becomes increasingly clear that this is not simply an environmental issue; it is a societal imperative. Solutions exist, but they require a paradigm shift in how we interact with our planet. Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power represents a key avenue toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Innovations in technology and a culture of sustainability are essential to cultivate a future where climate resilience prevails.
Moreover, individual and collective actions play a crucial role in mitigating the impacts of global warming. From reducing our carbon footprints through lifestyle changes—such as zero-waste practices, energy-efficient appliances, and sustainable transportation alternatives—to advocating for systemic policy changes, every effort counts. Engaging in community initiatives that promote environmental stewardship can create ripples of change that extend far beyond local boundaries.
The urgent nature of the climate crisis demands unprecedented collaboration across borders, industries, and communities. Global partnerships, like the Paris Agreement, exemplify the potential for unified action in the face of a common adversary. However, such agreements need to be not just aspirational, but effectively implemented, with tangible commitments driving progress.
In a world increasingly defined by the climate crisis, understanding the meaning of global warming becomes paramount. This knowledge is not just the domain of scientists; it is a collective responsibility that compels individuals and societies to act with foresight and compassion. As we stand at this critical juncture, the narratives we construct and the actions we take will determine our path forward. Only through concerted effort can we safeguard the environment for future generations, reclaiming the beauty of a balanced planet while preserving the myriad wonders of life that inhabit it.