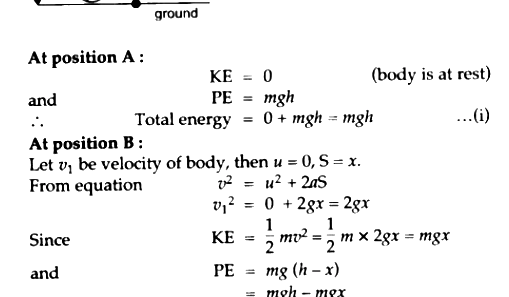
The Law of Conservation of Energy, a fundamental principle in physics, asserts that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it merely transforms from one form to another. This cardinal rule not only governs the cosmos but also deeply permeates our everyday experiences. Understanding this law can lead to significant insights into various phenomena, ranging from the mundane to the extraordinary. To elucidate this concept, we will explore practical examples that illustrate the law’s intricate workings across multiple domains.
Imagine a vibrant symphony, where each instrument plays a distinct note yet harmonizes to create a unified melody. This analogy is reminiscent of the Law of Conservation of Energy; different forms of energy converge and transform, but the total energy remains constant. Let us delve deeper into the nuanced layers of this principle.
The Mechanical Symphony: Kinetic and Potential Energy
At the heart of classical mechanics lies the dynamic interplay between kinetic and potential energy. Consider a roller coaster—a thrilling amalgamation of heights, speeds, and adrenaline. As the coaster climbs to its apex, it gains potential energy, akin to a bow drawn taut. When the roller coaster descends, that potential energy cascades into kinetic energy, propelling the ride forward at exhilarating speeds.
This transformation mirrors the ebb and flow of life; moments of stillness can lead to subsequent bursts of action. As the coaster races down the tracks, it is a vivid reminder that energy is ever-present and evolving, shaping our world in myriad ways. Every hill and dip reflects the unyielding truth of conservation, reminding spectators that energy is not lost but reshaped.
The Thermodynamic Dance: Heat Transfer and Energy Conversion
Transitioning from mechanics to thermodynamics, one encounters the subtleties of heat energy—often illustrated by the simple act of boiling water. As heat energy is applied to the water, the molecules within it begin to vibrate and move more vigorously, converting the thermal energy into kinetic energy. This fluid motion exemplifies the dynamic transformation of energy, culminating in the production of steam.
The transformation can be likened to a dance of molecules; energy flows seamlessly, from the stovetop to the water, enabling change. Moreover, this phenomenon is not limited to boiling water. It is observable in nearly every cooking process: roasting meat, baking bread, or sautéing vegetables. Each culinary endeavor embodies the principle of energy conservation, manifesting as heat energy metamorphoses into culinary delight. The act of cooking thus becomes a lesson in energy, teaching that careful management and understanding of energy forms can yield remarkable results.
The Biological Cycle: Energy in Ecosystems
Examining nature provides further compelling examples of energy conservation. The ecosystem functions as an intricate network of energy transfer, driven primarily by the sun’s radiant energy. Photosynthesis, a process that sustains life on Earth, serves as a testament to energy transformation. Plants absorb sunlight, converting it into chemical energy stored in glucose, a process that showcases the alchemical nature of energy.
Once this energy enters the food chain, it transforms again. Herbivores consume plants, converting the stored chemical energy into kinetic energy to roam vast distances. Carnivores, in turn, feast on herbivores, and the cycle of energy transfer continues. Here, the Law of Conservation of Energy presents itself in a circular fashion—each organism contributing to a collective energy economy. This chain reveals that energy is not an isolated entity but rather a shared resource, immutable in its totality while constantly reshaping its form from one life to another.
The Electrical Network: Energy in Modern Society
In the realm of technology, the principle of energy conservation manifests through electrical systems. Imagine a light bulb; when you flip the switch, electrical energy flows and illuminates the filament, transforming electrical energy into light and thermal (heat) energy. This process illustrates yet another transformation at play, revealing that while energy can shift between forms, it persists in totality.
This understanding is crucial in our quest for sustainable living. By grasping the conservation of energy, we can optimize the way we consume resources. For instance, energy-efficient appliances are designed to make the most of electrical energy, converting it into usable forms while minimizing waste. This guidance towards conservation encourages a harmonious relationship between energy consumption and environmental stewardship.
Wrapping It Up: The Unending Journey of Energy
The Law of Conservation of Energy is not merely an abstract concept; it is the very fabric of existence that connects seemingly disparate phenomena. From the exhilarating peaks and valleys of a roller coaster ride to the intricate exchanges within an ecosystem, energy remains constant, though its forms may vary dramatically. This delicate balance aspects the intelligent design of the universe—a reminder that every action, every transformation, reverberates through the corridors of time.
In our journey to understand energy, we garner the responsibility to respect and manage it judiciously. As individuals, as communities, we are tasked with honoring the intrinsic laws that govern our reality. The Law of Conservation of Energy beckons us to observe, reflect, and apply its principles towards an enlightened understanding of our world. In doing so, we embrace the essence of existence and foster a sustainable future for generations to come.