Energy conservation is a nuanced and critical concept in our modern world, encapsulating the essence of reducing energy consumption through various means, thereby helping to mitigate environmental degradation. With the current escalating crises regarding climate change and resource scarcity, understanding energy conservation becomes pivotal for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. As we delve into this multifaceted subject, we shall illuminate its core principles, the significance of saving energy, and practical strategies to implement energy-saving measures.
Understanding Energy Conservation
At its core, energy conservation refers to the efforts made to utilize less energy by adjusting behaviors and improving efficiencies. This is not merely about using less energy but rather being strategic about energy consumption to diminish wastage. The concept can be applied broadly, encompassing everything from individual actions—like turning off lights when leaving a room—to large-scale initiatives, such as the integration of renewable energy sources in power grids.
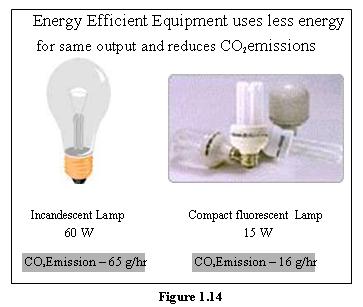
Energy conservation stands in contrast to energy efficiency, though the terms are often used interchangeably. While efficiency concerns technological improvements that achieve the same output with less energy (such as LED bulbs replacing incandescent ones), conservation emphasizes behavioral adjustments to reduce overall energy usage. By fostering a culture of consciousness regarding energy expenditures, we can collectively work towards a more sustainable future.
The Crucial Importance of Energy Conservation
Creating a sustainable society is not just a lofty ideal; it is an urgent necessity. One of the most glaring reasons for embracing energy conservation lies in its profound environmental benefits. Fossil fuels are finite resources, and our dependence on them contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. By conserving energy, we can lower the demand for these fuels, consequently reducing carbon footprints and the adverse impacts associated with climate change.
Economic advantages also underscore the necessity of energy conservation. High energy consumption leads to inflated utility bills and heightened operational costs for businesses and households alike. By implementing energy-saving measures, entities can lower their expenses and redirect those savings into other areas of growth or personal enrichment. In many instances, the transition to energy-efficient technologies—such as smart thermostats and energy-efficient appliances—initially requires investment, but the long-term savings often far outweigh those upfront costs.
Furthermore, the societal implications of energy conservation cannot be overstated. As energy resources diminish globally, the risks of energy insecurity and the possibility of energy crises escalate. By investing in energy conservation efforts, communities can cultivate resilience against fluctuating energy prices and supply shortages, thereby fostering a stable economic environment.
Transformative Strategies for Energy Conservation
In seeking to implement meaningful energy conservation strategies, both individuals and organizations can take proactive measures. The key lies in understanding and adjusting consumption patterns. Here are compelling approaches to consider:
1. Elevating Awareness and Education
Promoting awareness about energy conservation should be at the forefront of any initiative. This involves educating individuals about their energy consumption behaviors and the impacts of their choices. Community workshops, school programs, and social media campaigns can effectively disseminate valuable information and motivate behavioral change. Knowledge is empowerment; when individuals understand how their actions contribute to energy conservation, they are more likely to adopt sustainable practices.
2. Embracing Technological Advancements
Technology plays a pivotal role in the realm of energy conservation. The advent of smart home devices allows for automated energy management, enabling users to monitor and optimize their energy use seamlessly. Energy-efficient appliances not only utilize less energy but also often offer enhanced functionalities compared to their traditional counterparts. Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, can provide significant savings and decrease reliance on nonrenewable energy.
3. Advocating for Policy Changes
At a macro level, advocating for policies that promote energy conservation is essential. Governments and regulatory bodies can implement incentives for businesses and homeowners to adopt energy-efficient practices. Subsidies for renewable energy installations, tax rebates for energy-efficient upgrades, and stricter regulations on energy consumption can serve as catalysts for widespread change. When government entities prioritize energy conservation, they underscore its importance and encourage communities to follow suit.
Conclusion: A Collective Responsibility
The necessity of energy conservation transcends individual actions; it is a collective responsibility that calls for synchronized efforts across all levels of society. From altering personal habits to implementing institutional strategies, the pathway towards conserving energy is a shared journey. Understanding and embracing the significance of this concept not only contributes to a healthier planet but also engenders economic stability and social resilience. In a world where energy resources are increasingly under strain, taking proactive measures to conserve energy is not just advantageous but imperative for the sustainability of our society.