The Law of Conservation of Energy is one of the quintessential principles in physics, serving as a cornerstone in our understanding of not just the physical world, but also our interactions with it. This law asserts that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another. Although it may sound abstract at first, this concept holds profound implications for various scientific disciplines, environmental considerations, and even our daily lives. This article ventures into the depths of this fundamental principle, elucidating its significance and far-reaching impact.
Understanding the Law of Conservation of Energy invites one to gaze through a new lens, prompting a shift in perspective that reveals the interconnectedness of all energy forms. Curiosity piqued? Let’s delve deeper.
What Exactly Is Energy? A Fundamental Inquiry
Energy manifests in myriad forms, from the kinetic energy of a rolling ball to the thermal energy radiating from a warm cup of coffee. To scratch the surface of the Law of Conservation of Energy, we must first grasp what energy is. At its core, energy is the capacity to do work. It can be classified into several types, including kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, electrical, and nuclear energy. Each form possesses unique attributes and functions, yet they adhere to the same foundational principle: energy is conserved.
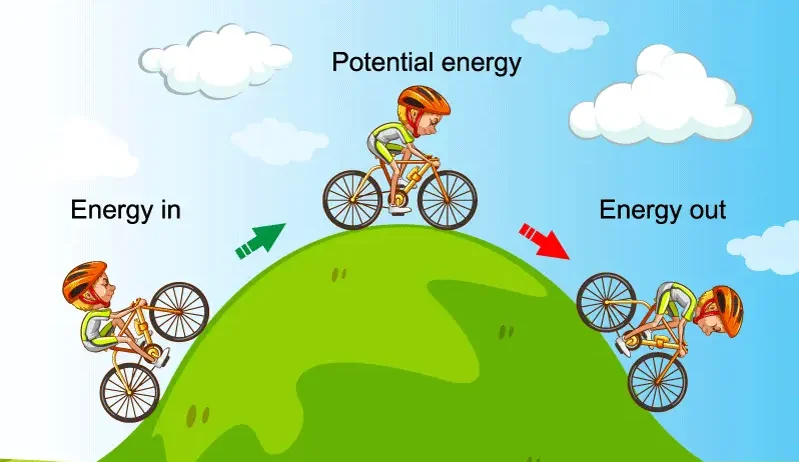
The kernel of this law reveals itself through various scientific phenomena. When a car accelerates, it converts chemical energy from gasoline into kinetic energy. Similarly, when a rollercoaster climbs to the apex of its track, it stores potential energy, which transforms back into kinetic energy as it rushes downward. In these scenarios, while the forms of energy shift, the total amount remains constant. This preservation acts as a universal constant, underlying countless processes in nature.
Examining Energy Transformations: From One Form to Another
If energy transitions seamlessly between forms, it begs the question: how fast do these transformations occur, and can they really impact our lives? Take, for example, the process of photosynthesis. In this remarkable phenomenon, plants convert solar energy into chemical energy, sequestering it in glucose molecules. In doing so, they create sustenance not only for themselves but for myriad organisms that rely on them for nourishment, thereby establishing a foundation for life on Earth.
The Law of Conservation of Energy underscores the multi-faceted interactions in ecosystems. Just as plants harness sunlight, animals convert that chemical energy into kinetic energy for movement, warmth, and growth. Even the waste produced in these processes is not energy lost; rather, it is transformed into another useful form. Understanding this intricate web of energy transformations highlights our responsibility to preserve the delicate balance within ecosystems, which is becoming increasingly threatened by human activities.
The Importance of the Law of Conservation of Energy in Science and Society
As the guardian of energy transformations, the Law of Conservation of Energy extends far beyond theoretical implications; it profoundly influences technology, environmental stewardship, and policy-making. In the realm of engineering, for instance, this law lays the groundwork for modern energy efficiency practices. Engineers harness energy transformations and strive to minimize wastage, maximizing output from limited resources. By doing so, they contribute to an innovative shift towards sustainable technologies, pivotal for addressing global challenges.
Moreover, as the climate crisis looms large, acknowledging the importance of energy conservation becomes more urgent. Policymakers and environmental activists utilize this principle to advocate for renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. By focusing on energy transformation rather than depletion, society can shift its perspective from short-term consumption to long-term sustainability. Such a transition necessitates a collective commitment to understanding and embracing this foundational law of physics.
Energy Conservation in Everyday Life: A Personal Responsibility
The implications of the Law of Conservation of Energy extend into the fabric of everyday living, shaping habits and choices. Energy conservation isn’t merely an abstract concept; it’s a personal responsibility that individuals can undertake. Simple actions, such as turning off unused appliances, utilizing energy-efficient lighting, and leveraging public transportation, reflect an understanding of this law. These small changes can aggregate into significant impacts, fostering a culture of sustainability and mindfulness.
Imagine a community where the principles of energy conservation influence not just individual behaviors but also collective actions. When people are educated about the interconnections of energy forms and the law governing them, they are empowered to make informed decisions that contribute to a healthier planet.
Conclusion: Embracing Energy Conservation as our Guiding Principle
The Law of Conservation of Energy is not just a scientific tenet; it embodies a philosophy that permeates our understanding of the universe. As we explore its intricacies—from energy transformations in nature to energy efficiency in technology—we discover the immense responsibility that accompanies our existence on this planet. As denizens of an increasingly fragile ecosystem, embracing this law invites us to rethink our relationship with energy, urging us to transform our awareness into action. In doing so, we not only honor the laws of physics but also embrace our role as custodians of Earth’s resources, making strides toward a sustainable future.