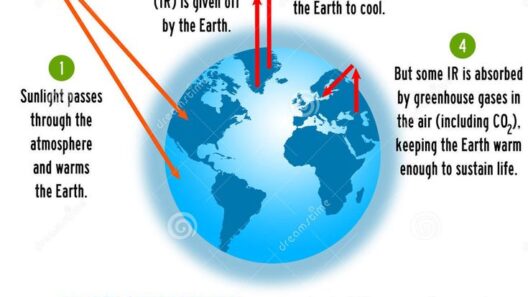
Introduction to Earth’s Temperature Regulation
The Earth, a unique and vibrant ecosystem, maintains a delicate balance of temperature critical for nurturing life as we know it. Our planet’s temperature is not merely a matter of meteorological phenomena; it is a complex interplay of various elements orchestrating a symphony that supports biodiversity and sustains ecological processes. Understanding the factors that govern this temperature regulation is not only fascinating but essential for addressing contemporary environmental challenges.
The Sun: A Celestial Architect
At the center of Earth’s thermal equilibrium lies the Sun, the primary energy source. Solar radiation, encompassing various wavelengths, permeates the atmosphere, driving weather systems and temperature fluctuations. However, the manner in which this energy interacts with Earth’s surface and atmosphere is profoundly intricate.
When sunlight strikes the Earth, it is absorbed, reflected, or transmitted depending on the surface composition. Darker surfaces, such as oceans and forests, absorb more heat, while lighter surfaces, such as ice caps and deserts, reflect a significant portion of solar energy. This differential heating creates temperature gradients that are vital for the circulation of air and ocean currents, fundamentally influencing global climate patterns.
Yet, it is not just the quantity of solar energy that matters; its quality plays a crucial role. For instance, the angle at which sunlight reaches Earth can significantly affect temperature distributions. During summer months, the Sun’s rays strike more directly, contributing to increased temperatures. Such phenomena illuminate the intricate relationship between solar dynamics and terrestrial temperature, calling attention to the nuance behind what may seem like a straightforward observation.
The Greenhouse Effect: A Double-Edged Sword
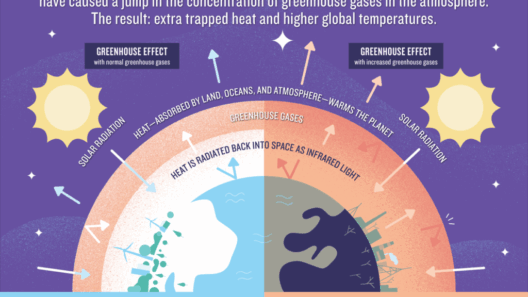
While solar energy is essential for maintaining warmth, Earth’s atmosphere, primarily populated by gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor, plays a pivotal role in retaining this warmth—a phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect. These greenhouse gases trap heat, preventing it from escaping back into space, thus maintaining average global temperatures conducive to life.
However, the escalating concentration of greenhouse gases due to human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, has exacerbated this effect, leading to global warming. This scenario highlights a critical paradox: while the greenhouse effect is vital for sustaining life, its intensification can jeopardize ecological and climatic stability.
The delicate balance inherent in the greenhouse effect also extends to its implications for weather patterns, sea levels, and the frequency of extreme weather events. An understanding of these dynamics not only encapsulates the essence of Earth’s temperature regulation but emphasizes the urgent need for mitigating anthropogenic impacts to restore equilibrium.
Oceans: The Great Temperature Buffer
The role of oceans in temperature regulation cannot be overstated. Covering over 70% of Earth’s surface, oceans act as a vast heat reservoir, absorbing and redistributing thermal energy across the globe. This remarkable capacity to moderate temperatures shields the land from the extremes of climatic variability.
Ocean currents, generated by wind patterns and the differential heating of water, serve as rivers within the seas that transport warm water from the equator towards the poles, while cold water flows back towards the equator. These currents are critical in shaping climatic conditions, influencing weather systems, and even determining the livelihood of coastal communities.
Moreover, oceans engage in a symbiotic relationship with the atmosphere through processes like evaporation, which can further regulate temperature through latent heat exchange. As water evaporates from the ocean surface, it absorbs substantial amounts of heat, thus cooling the surrounding environment. This interaction fosters a dynamic equilibrium that is essential for sustaining life, yet it remains exceptionally vulnerable to climate change, posing dire consequences if disrupted.
Forests: Vital Carbon Silos
Forests, often referred to as the lungs of the planet, also play a pivotal role in regulating atmospheric composition and, by extension, temperature. Through the process of photosynthesis, trees absorb carbon dioxide, a significant greenhouse gas, thereby mitigating its warming effects. Moreover, forests release water vapor into the atmosphere through transpiration, influencing local and regional climates.
The intricate relationships found within forest ecosystems—between flora, fauna, and microclimates—further enrich the tapestry of climate regulation. Understanding the myriad ways forests contribute to temperature control not only evokes admiration for these ecosystems but underscores the necessity of preserving and restoring forested areas crucial for climate resilience.
Human Influence: A Call for Collective Action
The interconnectedness of the Earth’s temperature regulation mechanisms illustrates the fragility of this equilibrium. Human activities, especially since the industrial revolution, have significantly altered this balance, leading to accelerated global warming and climate instability. This reality beckons a profound moral imperative for collective action and mindful stewardship of our planet.
Addressing climate change requires a multifaceted approach—transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing carbon sequestration, and advocating for sustainable agricultural practices. Such endeavors are not mere political obligations; they represent an intrinsic responsibility toward protecting the intricate web of life that thrives on Earth.
Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Future
Understanding Earth’s temperature regulation is a journey into the heart of our planet’s ecological processes. The remarkable interplay between solar energy, atmospheric composition, ocean currents, and forest ecosystems resonates with the urgency of our times. Recognizing and articulating these interconnections is the first step in nurturing a harmonious relationship with the environment. By fostering awareness and advocating for sustainable practices, we can aspire toward a more balanced and resilient Earth for generations to come.