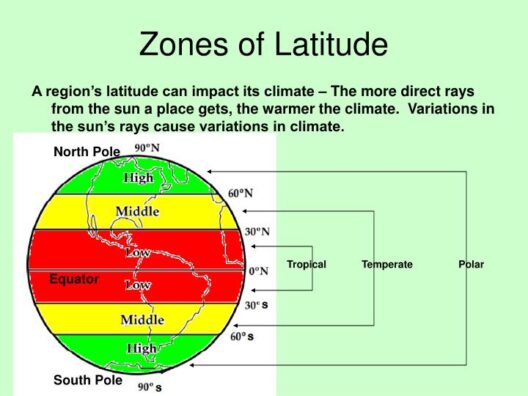
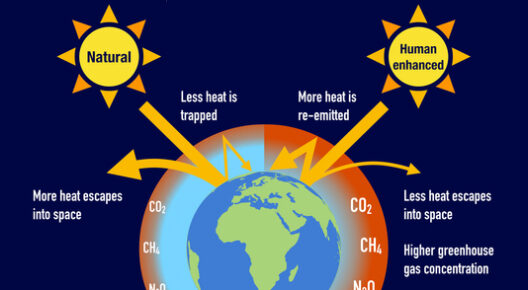
The phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect plays a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate. As an intricate interplay of natural processes, it serves as both a safeguard and a catalyst for life on our planet. Understanding this mechanism is not only fascinating but essential for grasping the impending challenges of climate change.
At its core, the greenhouse effect involves the absorption and re-emission of infrared radiation by certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases, often referred to as greenhouse gases, include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, among others. Their presence is crucial; without them, the average surface temperature of the Earth would be a frigid -18 degrees Celsius, rather than the current average of around 15 degrees Celsius that supports diverse ecosystems.
To fully appreciate the greenhouse effect, it is helpful to visualize it through an elegant diagram, showing how solar radiation interacts with the Earth’s atmosphere. This illustration emphasizes the beauty and complexity of this natural process. Now, let’s delve deeper into this captivating subject.
Understanding the Basics of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases are pivotal in the greenhouse effect. They trap heat from the sun, preventing it from escaping back into space. Carbon dioxide (CO2), often produced by human activities such as fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, is one of the most notorious greenhouse gases. However, it is by no means the only one. Methane (CH4) is another potent greenhouse gas, released primarily from agricultural practices, landfills, and natural gas extraction. Compared to CO2, methane is significantly more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere over a short time frame, making it a critical focus for climate mitigation strategies.
Nitrous oxide, though present in much smaller quantities, must also be recognized due to its powerful heat-trapping capabilities, primarily released from agricultural activities and industrial processes. Moreover, industrial gases like fluorinated gases, though used in small amounts, have a much higher global warming potential than CO2, making them worthy of examination in any discussion about greenhouse effects.
The Intricate Mechanism of the Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect operates like a double-glazed window. Incoming sunlight passes through the Earth’s atmosphere and reaches the surface, where it heats the ground and oceans. Subsequently, the Earth re-emits this energy back into the atmosphere in the form of infrared radiation.
Here, the magic—or, depending on your perspective, the menace—occurs. Greenhouse gases absorb a significant portion of this outgoing radiation, preventing it from escaping into space. Instead, they re-radiate it in all directions, including back toward the earth’s surface. This process creates a warming effect, akin to how a blanket retains warmth. Yet, this very mechanism is beginning to unravel as human activities amplify the concentration of these gases in the atmosphere, leading to an increase in global temperatures.
The Impact of Anthropogenic Activities
The last century has brought about unprecedented changes in the composition of our atmosphere due to human activities. The Industrial Revolution marked the dawn of mass production and fossil fuel consumption, transforming society but also heavily increasing the levels of greenhouse gases. As a result, global temperatures have risen markedly since the mid-19th century, igniting concerns over climate change.
Feedback loops exacerbate this situation. For example, as temperatures rise, polar ice melts, and thus, less sunlight is reflected back into space—a phenomenon known as albedo feedback. Instead, more heat is absorbed by the oceans and land. Such feedback loops can create accelerating cycles of warming, making the challenge of climate change all the more urgent.
The Aesthetic Appeal of Climate Data Visualization
Visual representations of the greenhouse effect contribute immensely to our understanding of this complex topic. Diagrams can portray intricate interactions between sunlight, the Earth’s surface, and the atmosphere in a straightforward and captivating way. The aesthetics of these illustrations are not merely for decoration; they serve an educational purpose by breaking down dense scientific concepts into accessible images, pulling in viewers and encouraging them to learn and engage.
Moreover, the juxtaposition of art and science in climate data visualization can prompt a more profound emotional response. By drawing attention to the beauty of the Earth’s systems, these visuals can cultivate a sense of urgency and responsibility in addressing climate change.
Conclusions
The greenhouse effect is a fascinating and essential component of the Earth’s climate system, illustrating the natural balance required for sustaining life. However, human influences are threatening this equilibrium. In understanding the nuances of greenhouse gases and the mechanisms involved, we can better grasp the gravity of climate change challenges. It is crucial that we not only continue to educate ourselves through engaging visual aids but also take informed action to mitigate these impacts on our planet.
In a world where the effects of climate change become more profound and visible, fostering a collective understanding of the greenhouse effect is imperative. With knowledge comes the power to effect change, ensuring that the environment we cherish continues to thrive for generations to come.