The greenhouse effect is often entangled in negative connotations, particularly due to the contemporary debates surrounding climate change and environmental degradation. However, a nuanced understanding reveals that the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon essential for life on Earth. This intricate interplay of energy exchange between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere plays a critical role in maintaining a stable climate, facilitating the delicate balance necessary for ecosystems to flourish. This article delves into the mechanisms of the greenhouse effect, highlighting its positive aspects and underscoring its significance in regulating Earth’s climate.
The Greenhouse Effect Explained
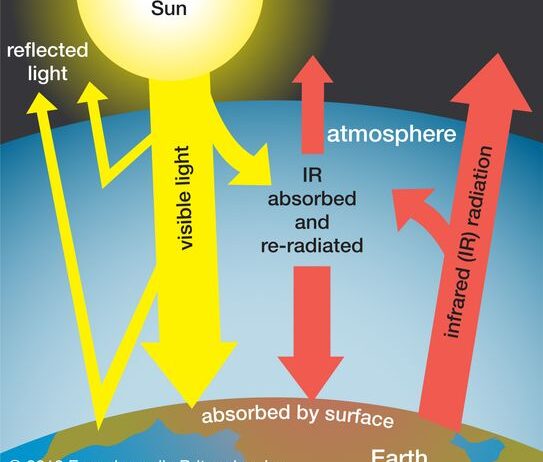
The greenhouse effect is fundamentally an atmospheric process that involves the absorption and re-emission of infrared radiation by certain gases known as greenhouse gases. These gases—such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O)—trap heat in the atmosphere, preventing it from escaping back into space. This process is indispensable for sustaining life as we know it.
Without greenhouse gases, the Earth would be inhospitable, with an average temperature drastically lower than the current climate. The Earth’s surface temperature, currently around 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius), would plummet to a frigid -2 degrees Fahrenheit (-19 degrees Celsius) in their absence. This staggering difference highlights that greenhouse gases are not merely contributors to climate woes; rather, they are life-sustaining components of our atmosphere.
The Natural Temperature Regulator
One of the paramount benefits of the greenhouse effect is its role as a natural temperature regulator. The atmosphere acts like a blanket, moderating temperature fluctuations between day and night. Under the nurturing grasp of greenhouse gases, daily temperatures are cushioned against extreme variances that would otherwise render large swathes of the planet inhospitable for many species.
This temperature moderation is critical for biodiversity. Ecosystems thrive in stable environments where organisms can adapt to existing conditions over generations. Many species are finely tuned to specific climate variables; variability can lead to ecosystem imbalances, potentially resulting in extinction for vulnerable species. A meticulous calibration of atmospheric conditions enables a rich tapestry of life across terrestrial and aquatic biomes, showcasing nature’s resilience and adaptability.
The Role in Agricultural Systems
Another noteworthy aspect of the greenhouse effect is its profound implication for agriculture and food security. Plants play a critical role in carbon absorption, utilizing CO2 for photosynthesis—a process that sustains both plant life and the fauna that rely on those plants for sustenance. Greenhouse gases promote a thriving environment for crops, ensuring that they flourish and produce the food that sustains our ever-growing population.
Furthermore, the greenhouse effect enhances the growing season in temperate regions. Warmer average temperatures can lead to longer growing seasons, thereby allowing farmers to cultivate a wider array of crops. This benefits not only local communities but also global food supply chains, enabling regions that previously endured harsher climates to produce food more efficiently. The interdependence between greenhouse gases, plant growth, and agricultural productivity exemplifies the intricacies of the Earth’s climate system.
Climate Complexity and Ecological Synergy
While the greenhouse effect harbors undeniable benefits, it is critical to recognize the complexity of Earth’s climate system and the delicate balance we must maintain. The synergy among various climate components, from oceanic patterns to land use, necessitates a keen awareness of how human activities can tip this equilibrium. The unrestrained release of greenhouse gases can exacerbate climate change, leading to adverse effects such as unpredictable weather, rising sea levels, and diminished biodiversity.
Conscious stewardship of the environment is essential to mitigate these risks and preserve the vital workings of the natural greenhouse effect. This calls for a comprehensive approach, where sustainable practices can harmonize with modern developments, allowing humanity to thrive alongside nature. Policies fostering clean energy sources, reforestation, and responsible agricultural practices can ensure an enduring delicate balance between anthropogenic activities and the well-functioning climate system.
The Path Forward: Harnessing Natural Processes
Emerging technologies and practices that embrace the greenhouse effect’s natural capabilities can guide humanity towards a sustainable balance. For instance, capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and utilizing it in innovative agricultural methods can close the loop on greenhouse gas emissions while enhancing crop yield and soil health. Furthermore, urban greening projects, incorporating trees and green spaces in cities, can improve air quality and further sequester carbon.
As global citizens, recognizing the duality of greenhouse gases is imperative. While it is crucial to mitigate intensive human emissions contributing to global warming, it is equally important to acknowledge the inherent benefits of greenhouse gases. They play indispensable roles in climate regulation, agricultural productivity, and biodiversity conservation. Our understanding of this natural phenomenon must extend beyond the urgent need for emissions reduction; it must embrace a broader perspective of synergy with the Earth’s systems.
In conclusion, the greenhouse effect is a double-edged sword, encompassing both challenges and opportunities in our fight against climate change. By adopting responsible practices and policies, humanity can work to protect the natural processes that sustain our planet while mitigating the adverse consequences of our actions. As stewards of the Earth, understanding and respecting the greenhouse effect’s positive contribution can inspire a more sustainable future for generations to come.