The phenomenon of rising sea levels has garnered increased attention over recent decades, as its implications threaten coastal ecosystems, human settlements, and global weather patterns. Understanding the intricacies behind this issue is imperative not only for environmentalists but for anyone concerned about the planet’s future. The multifaceted causes of rising sea levels can be categorized into two primary drivers: thermal expansion of seawater and the melting of ice masses. Let’s delve into the key factors contributing to higher ocean levels.
**Thermal Expansion: The Heat is On**
One of the fundamental causes of rising sea levels is thermal expansion, a process that occurs when seawater is heated. As the Earth’s climate warms, the ocean absorbs a significant amount of this excess heat. Water, like most substances, expands when it heats up. This thermal expansion results in increased ocean volume, contributing to elevated sea levels.
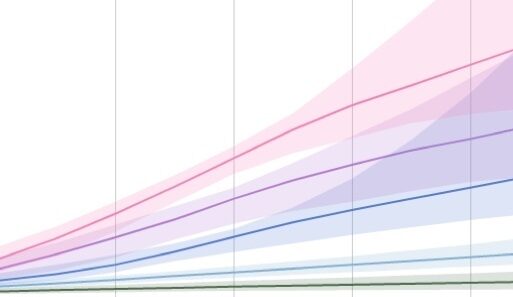
Research indicates that approximately half of the observed sea-level rise since the late 20th century can be attributed to thermal expansion. This is alarming, considering projections of ongoing global temperature increases. If current trends persist, the implications for coastal regions could be catastrophic, leading to increased flooding, loss of habitat, and heightened salinity in estuaries.
**Glacial Melt: The Ice is Melting**
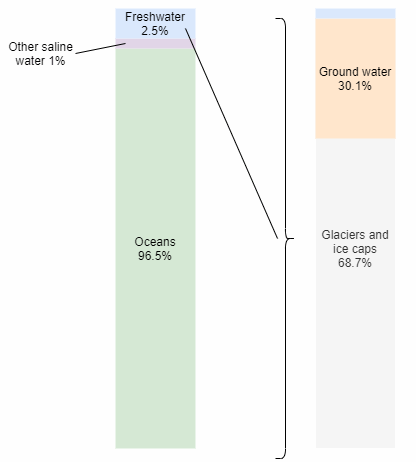
Another pivotal factor in rising sea levels is the melting of glaciers and ice sheets. The polar regions, particularly Greenland and Antarctica, house vast reservoirs of ice. As global temperatures rise, this frozen water begins to melt at unprecedented rates. This melting contributes directly to higher ocean levels, adding freshwater to the oceans.
The consequences of glacial melt extend beyond just volume increase. For instance, the melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet alone could lead to a global sea-level rise of approximately 7 meters if it were to completely melt. Simultaneously, the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, another crucial ice mass, is also facing instability due to warming ocean waters, which are eroding its ice shelves from below.
**Impact of Land Ice Loss: Not Just the Poles**
While polar ice sheets often steal the spotlight, it’s essential to consider the melting of land-based glaciers worldwide. These glaciers, found in mountain ranges like the Himalayas and the Andes, are vital sources of freshwater for millions. Their loss not only contributes to rising sea levels but also threatens water availability for populations dependent on glacial meltwater for agriculture and drinking.
As these glaciers continue to recede, their impact on sea levels becomes increasingly significant. The cumulative effect of land ice loss on rising oceans is estimated to contribute around a third of the current sea-level rise. Moreover, this phenomenon is further exacerbated by the feedback loops created by loss of reflectivity, known as albedo. The more ice melts, the less sunlight it reflects, resulting in further warming and additional melting.
**Ocean Dynamics: Circulation Changes and Water Redistribution**
Beyond thermal expansion and ice melt, ocean dynamics play an essential role in the complexities of sea-level rise. Ocean currents and cycles can redistribute water, leading to regional variations in sea levels. Factors such as wind patterns, ocean temperature gradients, and salinity differences can cause uneven distribution of ocean water. For example, El Niño events are known to influence sea levels across the Pacific Ocean, causing short-term fluctuations.
Additionally, over-extraction of groundwater and the subsequent sinking of land, known as subsidence, can lead to localized increases in sea levels. Urban areas in deltas, like New Orleans or Jakarta, are particularly susceptible to this phenomenon, where natural and anthropogenic effects exacerbate the situation.
**The Societal Implications: A Call to Action**
The ramifications of rising sea levels extend far beyond environmental concerns; they pose significant challenges to human societies. Coastal urban centers face the imminent threat of flooding, which can lead to property loss, displacement of communities, and damages to infrastructure. As sea levels rise, the frequency and intensity of storm surges also increase, further endangering coastal inhabitants.
A proactive approach towards mitigating these impacts is essential. This includes investing in sustainable coastal infrastructure, enhancing natural barriers such as wetlands, and implementing policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Public awareness and education are crucial tools in fostering community resilience against the encroaching tides.
**Conclusion: Facing the Rising Tide Together**
In conclusion, the complexity of rising sea levels stems from a confluence of various factors, with thermal expansion and ice melt at the forefront. Understanding these drivers is vital in addressing one of the most pressing challenges of our time. As a global community, acknowledging the urgency and taking decisive actions to combat climate change and its consequences is not merely an option—it is a necessity. The future of our coasts, ecosystems, and communities depends on our collective response to this critical issue.