The Maldives, a breathtaking archipelago in the Indian Ocean, is increasingly becoming the focal point of concern regarding rising sea levels. This nation, known for its idyllic beaches and vibrant marine life, faces a reality that could jeopardize its very existence. As global warming continues to exacerbate climate change, the Maldives is adapting and innovating in response to this pressing challenge. Let us delve into the multifaceted strategies that the Maldives is employing to combat the encroaching waters.
One might wonder why such a small collection of islands garners global attention concerning climate change. The answer lies in the stark vulnerability of the Maldives. With an average elevation of just 1.5 meters above sea level, even a modest increase in ocean levels poses a monumental threat. The plight of the Maldives serves as both a cautionary tale and a call to action, reflecting deeper issues related to ecological sustainability and global environmental responsibility.
As rising tides threaten to submerge entire stretches of land, the Maldivian government has adopted a comprehensive approach centered on both mitigation and adaptation strategies. These initiatives aim to safeguard the population, protect biodiversity, and preserve the nation’s economic vitality.
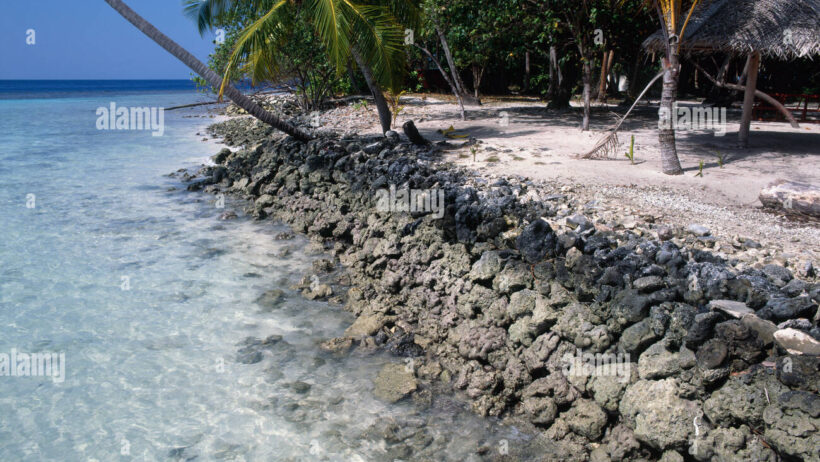
One of the prominent initiatives has been a concerted effort to bolster coastal defenses. Through a combination of natural and artificial systems, the Maldives is investing in building resilient shorelines. This includes the construction of sea walls, which act as barriers to prevent erosion and flooding. These structures are often complemented by a strategy known as “beach nourishment,” where sand from offshore sources is added to beaches to counteract erosion. By replenishing these natural buffers, the Maldives can help secure its tourism-driven economy while simultaneously fostering a healthier marine ecosystem.
Eco-engineering has also taken center stage in this battle against rising seas. The concept involves utilizing ecological processes to strengthen coastal defenses—building coral reefs and mangroves, for example. Both are natural barriers that can absorb wave energy, thereby reducing coastal erosion. Furthermore, these habitats provide essential ecosystems for marine species and contribute to the biodiversity that many fishermen rely upon for their livelihood. By recognizing the importance of integrating environmental science into infrastructural development, the Maldives is embracing a path that contributes not only to human safety but also to ecological health.
In addition to fortifying its physical structures, the Maldives is keenly aware that legislative action is pivotal in addressing climate change. National policies are being shaped to reflect a commitment to sustainability and environmental protection. The government has engaged in international dialogues, advocating for aggressive measures to mitigate climate change globally. By positioning itself as a beacon of climate advocacy, the Maldives aims to galvanize support that translates into tangible action on a larger scale.
Education plays a crucial role in these adaptive measures, as raising awareness about climate change effects is fundamental for local communities. Through outreach initiatives, residents are learning about sustainable practices, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship. Incorporating climate education into school curriculums ensures younger generations grasp the urgency of these ecological challenges. This grass-roots movement not only empowers individuals but cultivates a collective effort to protect their homeland.
Moreover, the Maldivian government has launched a novel approach towards urban planning—urbanization with resilience in mind. New developments are strategically designed to be adaptable to changing climate conditions. Buildings are elevated above anticipated flood levels, and land-use planning prioritizes areas less susceptible to flooding. This foresight in development helps mitigate the risks associated with sea level rise and ensures the longevity of infrastructure.
While much of the focus is on immediate adaptive measures, long-term solutions also beckon attention. One of the more radical solutions has involved discussions about relocating entire communities to higher ground or even other nations. While this solution evokes complex emotions and ethical considerations, it highlights the magnitude of the threat. Such discussions symbolize both a desperation and a proactive stance against an unstoppable force—climate change.
Despite the grim forecasts surrounding climate change, the spirit of the Maldivian people is anything but defeated. The country has become a testament to resilience in the face of adversity. This struggle is not merely about survival; it is a profound lesson in adaptability and innovation. Furthermore, the Maldives stands as a microcosm of a larger global reflection. The plight of its citizens embodies not just local challenges but also the urgency for collective international responsibility in tackling climate-related issues.
Ultimately, the Maldives serves as a bellwether for the repercussions of unchecked environmental degradation. By embracing an array of adaptive measures—from infrastructural improvements to community-driven education—the nation is pushing back against the tides of adversity. Its efforts can inspire other vulnerable regions worldwide to take proactive steps, galvanizing a harmonized global response to climate change. As the narrative of the Maldives unfolds, it beckons the world to join in fostering a sustainable future, lest we allow the rising seas to swallow more than just sand and sun.