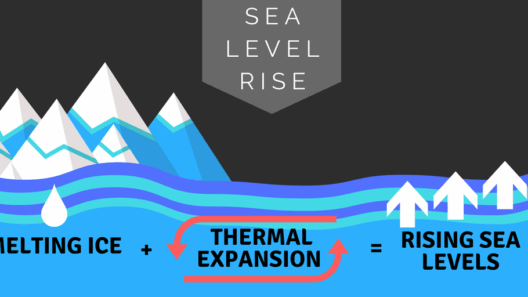
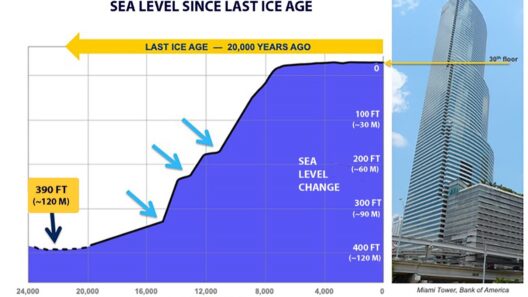
Climate change is an inexorable reality, and one of its most profound manifestations is the phenomenon of rising sea levels. This gradual yet persistent change poses a myriad of challenges to coastal communities, ecosystems, and global economies. Understanding the effects of rising sea levels not only sheds light on the urgency of environmental advocacy but also motivates public discourse and policy changes. In this exploration, we will examine the various implications that arise from this pressing issue, with a focus on human, economic, and environmental perspectives.
Coastal Erosion: The Disappearing Shores
As sea levels rise, coastal areas experience increased erosion, which can drastically alter landscapes and reduce the land available for habitation and agriculture. Erosion can occur gradually or suddenly, influenced by storms and extreme weather events. This process threatens not only natural habitats but also the livelihoods of those who depend on the land for their income.
Communities located along coastlines face the immediate threat of losing homes and essential infrastructure, such as roads and bridges. Moreover, agricultural lands that provide food and resources are increasingly susceptible to saltwater intrusion; thus, the land once fertile may become barren. These changes can result in a cascade of socio-economic issues, including displacement and loss of agricultural output.
Flood Risks: The Dreaded Inundation
Rising sea levels significantly exacerbate the risk of flooding, particularly during extreme weather events like hurricanes and typhoons. As ocean levels rise, storm surges become more formidable. Coastal cities and regions often find themselves grappling with severe flooding, leading to extensive damage to properties and critical infrastructure.
The consequences of increased flood risk extend beyond immediate physical damage; they can lead to long-term economic repercussions. Disrupted businesses and overwhelmed emergency services can strain regional economies, eventually requiring large sums of public investment to recover. Furthermore, as sea levels continue to rise, climate refugees may emerge—individuals and families forced to abandon their homes due to flooding, prompting a humanitarian crisis that spans borders.
Biodiversity Under Threat: The Fragile Interplay of Ecosystems
The effects of rising sea levels extend far beyond human societies. Natural ecosystems, particularly coastal and marine environments, are profoundly impacted. Wetlands, marshes, and mangroves serve as critical buffers against rising tides, but as sea levels encroach upon these habitats, their existence is threatened.
Wetlands are not only vital for maintaining biodiversity but also act as natural water filtration systems, improving water quality and providing habitat for countless species. As these habitats are submerged or converted to open water, essential wildlife may find themselves struggling for survival, leading to declines in population and even extinction.
Moreover, the intrusion of saltwater into freshwater ecosystems can alter the delicate balance necessary for sustaining diverse life forms. Fish populations that rely on specific salinity levels may migrate or perish, affecting not only the ecosystem but also the fishing industry that depends on these species for sustenance and economic stability.
Global Implications: The Economic and Political Landscape
At a global scale, rising sea levels carry significant economic burdens. Many countries heavily depend on coastal tourism as a source of income. As beaches erode and destinations face increased flooding, the tourism industry may suffer catastrophic losses, seriously affecting local and national economies. The construction and maintenance of coastal defenses, such as sea walls and levees, also require substantial financial investment, which often falls disproportionately on local governments.
Politically, rising sea levels can intensify existing tensions between nations, especially when territory is at stake. Nations may engage in disputes over maritime boundaries as coastal areas diminish. Furthermore, climate migration can lead to geopolitical instability as people move to seek safer grounds, leading to cultural clashes and resource competition.
Mitigation Efforts: Navigating Forward
Given the profound implications of rising sea levels, proactive measures must be initiated. Mitigation and adaptation strategies can range from improving coastal infrastructure to integrating sustainable land-use practices. Investing in green solutions like restoring mangroves or creating artificial wetlands can bolster resilience against rising tides while simultaneously protecting biodiversity.
Urban planning must evolve to account for the realities of climate change. Communities can benefit from proactive zoning regulations that limit construction in vulnerable coastal areas and promote the development of “buffer zones” that can absorb flood waters. Additionally, awareness and education campaigns can empower individuals and communities to adopt practices that mitigate their contribution to climate change.
Collective Action: A Global Call to Arms
Addressing the effects of rising sea levels is not solely the responsibility of coastal nations; it requires a concerted global effort. Intergovernmental cooperation and treaties focused on climate action and adaptation are paramount. Wealthier nations must aid developing countries that may lack the resources to combat these changes effectively.
As the world grapples with the implications of rising sea levels, the clarion call for action reverberates. The interplay of environmental, economic, and social challenges necessitates comprehensive responses. Knowledge, awareness, and advocacy can empower individuals and communities to navigate the tumultuous waters of climate change, ultimately steering a course toward a sustainable future.