In recent years, the discourse surrounding renewable energy has intensified, with wind power emerging as a pivotal player in the quest for sustainable solutions. The growing concern over climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels has fueled interest in alternative energy sources. Wind power, harnessed from the natural movement of air, promises a clean and inexhaustible supply of energy. But just how green is wind energy? This examination aims to uncover the realities of wind power, its benefits, challenges, and its role in fostering a sustainable future.
Understanding the core attributes of wind energy is essential in assessing its environmental credentials. Wind energy is generated through wind turbines that convert kinetic energy from wind into electrical power. These turbines, often located in expansive wind farms, can produce large quantities of electricity without the emissions typically associated with fossil fuel energy production. As such, evaluating the green credentials of wind power necessitates an exploration of its environmental impact, economic viability, and technical advancements.
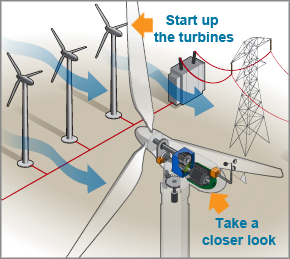
The process of harnessing wind energy begins with large turbines mounted on towers. As the wind turns the rotor blades, this mechanical energy is transformed into electrical energy through a generator. Wind energy is remarkably distinct from conventional energy sources primarily due to its low greenhouse gas emissions during operation. According to industry standards, wind power emits virtually no carbon dioxide or other harmful pollutants during generation, which positions it as an environmentally friendly alternative in energy production.
Moreover, wind energy plays an essential role in mitigating the effects of climate change. By diverting reliance from carbon-intensive fossil fuels, wind power contributes significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, fostering cleaner air and water while preserving natural habitats. Wind farms, often designed to coexist harmoniously with local ecosystems, can provide dual benefits, including agricultural land usage and wildlife preservation.
Wind Energy as a Renewable Power Source
Wind energy is classified as a renewable resource due to the inexhaustible nature of wind. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and subject to depletion, wind is a continuously replenished resource driven by the sun’s heating and the earth’s rotation. Because wind energy relies on natural processes, it has the potential to offer an endless supply of power as long as there are atmospheric winds. This characteristic not only provides energy security but also positions wind as a viable long-term solution to global energy demands.
Transitioning to a wind-powered infrastructure could significantly decrease the global carbon footprint. Projections suggest that by expanding wind power capacity, countries can achieve ambitious renewable energy targets, making substantial strides towards meeting international climate commitments. Additionally, integrating wind energy into the existing power grid will require upgrades and innovations, fostering economic growth and creating new jobs in the process. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) estimates that wind power could employ millions globally in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance sectors.
Challenges of Wind Power Adoption
Despite its remarkable promise, wind energy is not without challenges. One of the most prominent concerns revolves around the intermittency of wind. Unlike other energy sources, wind energy generation is variable, driven by weather conditions. This variability necessitates the implementation of robust energy storage solutions, such as battery systems or complementary power sources, to ensure a reliable energy supply. Developing these technologies is crucial to overcoming the limitations associated with wind energy’s intermittency.
Additionally, the environmental impact of wind turbines during their manufacturing and installation cannot be overlooked. While operational emissions are negligible, the production of turbines involves resource extraction, manufacturing processes, and waste generation. However, advancements in technology are mitigating these concerns, with many manufacturers now employing sustainable practices and repurposing materials to reduce environmental footprints.
Another challenge lies in community opposition to wind farms, often sparked by concerns over land use, noise pollution, and the aesthetic impact on landscapes. Engaging local communities in the planning process, providing transparent information, and delineating the substantial benefits of wind energy can help address these apprehensions and foster broader acceptance of wind projects.
The Future of Wind Energy: Innovations and Opportunities
The future of wind energy is laden with potential, driven by ongoing innovations and technological advancements. The development of larger, more efficient turbines is significantly increasing energy capture while reducing costs. These advancements not only enhance the performance of wind farms but also make wind power increasingly competitive with conventional energy sources.
Emerging technologies, such as offshore wind farms, are expanding the horizons of wind energy potential. Offshore wind turbines can harness stronger and more consistent winds over oceans, generating substantial power, while minimizing land-use conflicts. As research and investment in offshore technology progress, the capacity for wind power to contribute to a more sustainable energy future will grow exponentially.
Furthermore, integrating wind energy into smart grid systems enhances efficiency and reliability. By utilizing predictive analytics, demand response strategies, and energy storage solutions, energy production and consumption can be balanced more effectively, allowing for optimized use of wind energy.
In conclusion, wind power represents a versatile and promising solution to the pressing challenges of climate change and energy demands. With its minimal environmental impact during operation, renewable nature, and potential for economic growth, it is undoubtedly a crucial component of any comprehensive strategy for a sustainable energy future. Although there are hurdles to overcome regarding intermittency and community acceptance, the path forward is illuminated by innovation and the collective commitment to embracing clean energy solutions.