Energy has been a vital component of human civilization for centuries, with various forms evolving over time. Among the multitude of renewable resources, wind energy stands out due to its abundance and sustainability. It represents a crucial pillar in the transition towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape. Understanding the definition of wind energy and its significant role in the renewable energy sector is essential for grasping its potential and implications for the future.
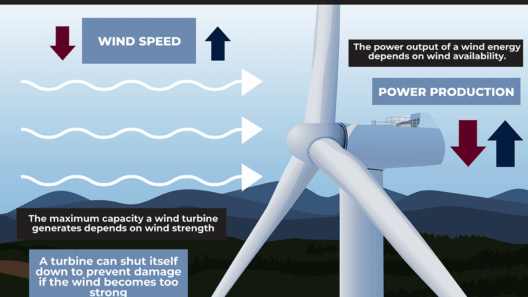
Wind energy, at its core, is the process of harnessing the kinetic energy produced by the movement of air within the Earth’s atmosphere. This energy is primarily driven by solar radiation, which causes differences in temperature and pressure. As warm air rises, cooler air rushes in to replace it, creating wind. By employing specialized technology, such as wind turbines, this kinetic energy is transformed into electrical energy, which can then be utilized to power homes, businesses, and entire communities.
The mechanization of wind energy harvesting has seen remarkable advancements, with modern turbines operating at impressive efficiencies. They consist of large blades mounted on a tall tower, designed to capture wind from various directions. As the wind turns the blades, a generator converts the rotational motion into electricity that can be fed into the power grid. The journey from wind to wattage illustrates the beauty of this natural energy resource and its potential to meet a significant portion of our energy needs.
Wind power is a vital component of the global renewable energy portfolio. Its role cannot be overstated as the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, energy security, and fossil fuel dependency. As countries strive to reduce their carbon footprints and transition towards sustainable energy sources, wind energy offers a clean alternative that does not produce harmful emissions. Additionally, the decentralization of energy production through wind farms can promote local energy independence, bolstering both economic and environmental resilience.
Moreover, wind energy development contributes to job creation in various sectors, from manufacturing to installation and maintenance. In many regions, the establishment of wind farms has revitalized local economies and provided a pathway for workforce development, particularly in rural areas where opportunities might otherwise be limited. Furthermore, as technology continues to evolve, the costs associated with wind energy are declining, making it an increasingly attractive option for energy generation.
Despite its myriad advantages, it is crucial to address some of the challenges facing wind energy expansion. One primary concern revolves around the intermittency of wind. Unlike traditional fossil fuels, which can provide a constant power supply, wind energy generation is reliant on weather patterns, making it less predictable. This variability necessitates the creation of robust energy storage solutions and a diversified energy mix to ensure a reliable power supply. Technological innovations, such as battery storage and grid enhancements, are essential in overcoming these challenges and maximizing the efficiency of wind energy.
Another consideration pertains to the environmental and ecological impacts of wind farms. The construction and operation of large-scale wind installations can pose risks to local wildlife, particularly bird and bat populations. However, ongoing research and development efforts aim to mitigate these effects through better siting practices, turbine design, and operational adjustments. Striking a balance between renewable energy generation and environmental stewardship is imperative for the long-term sustainability of wind power.
In the context of global energy dynamics, the promise of wind power is immense. As nations continue to set ambitious renewable energy targets, wind energy is positioned to play a pivotal role in achieving these goals. According to the Global Wind Energy Council, the installed capacity of wind power worldwide has grown exponentially in recent years. This trend is likely to continue, fostering greater reliance on wind as a principal energy source in the transition towards a low-carbon economy.
In summary, wind energy is defined as the conversion of kinetic energy generated by the motion of air into mechanical energy, and subsequently into electricity, marking it as a significant entity in the renewable energy landscape. Its advantages are multifaceted, contributing not only to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions but also promoting economic growth and job creation within communities. While challenges exist, such as intermittency and ecological concerns, the ongoing advancements in technology and strategic implementation hold promise for a sustainable energy future. As society moves further along the path to decarbonization, recognizing and harnessing the potential of wind energy is essential for achieving a cleaner and more sustainable world.