The rise of wind energy as a formidable contender in the renewable energy landscape has stimulated a rich discourse on its environmental ramifications. As society transitions towards greener energy alternatives, it is imperative to dissect both the favorable and adverse effects of wind energy on the environment. This exploration aims to elucidate the multifaceted relationship between wind energy production and environmental integrity.
In addressing prevalent buyer concerns, one must confront the duality of wind energy’s impacts. While it presents a sustainable alternative that mitigates fossil fuel dependence, various environmental considerations warrant careful examination. Through a thoughtful analysis, stakeholders can achieve a holistic understanding of wind energy’s footprint.
Emphasizing Renewable Energy: The Benefits of Wind Power
Wind energy epitomizes the quest for sustainable power generation. Harnessing the kinetic energy of wind through turbines facilitates the production of electricity without the combustion of fossil fuels, thus significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. As a consequence, wind energy bolsters national goals pertaining to climate change mitigation.
The prominent benefits of wind energy in environmental sustainability can be summarized as follows:
Reduction in Air Pollution
Transitioning from traditional energy sources to wind energy substantially curtails air pollutants. Unlike coal or natural gas, wind energy systems do not emit sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, or particulate matter during operation. By lowering these harmful emissions, wind energy contributes to improved air quality, which is crucial for public health.
Conservation of Water Resources
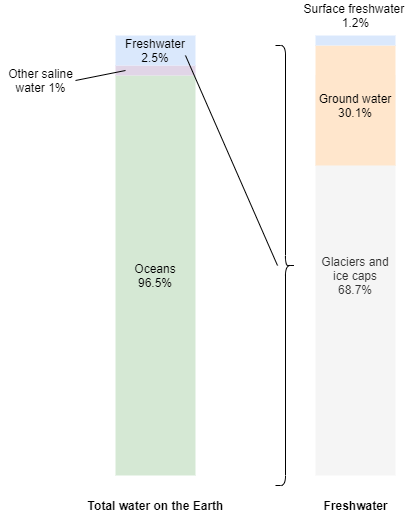
Another seldom-discussed advantage of wind energy is its minimal water consumption. Unlike fossil fuel plants, which require copious amounts of water for cooling processes, wind turbines operate independently of water resources. This characteristic is particularly pertinent in arid regions, where conserving water is essential for ecosystems and communities alike.
Supporting Biodiversity Through Sustainable Practices
Wind energy also promotes biodiversity when implemented responsibly. Modern wind farms are increasingly located in environmentally sensitive areas, with strategic assessments ensuring minimal disruptions to local wildlife. Through careful planning, operators can create habitats that can coexist with wind turbines, contributing to regional biodiversity enhancements.
However, it is equally essential to confront the darker aspects associated with wind energy deployment. A comprehensive understanding of these challenges can inform better practices and regulatory frameworks.
The Unexpected Consequences: Negative Impacts of Wind Energy
While the benefits of wind energy are significant, the environmental implications can be complex and sometimes counterintuitive. The following considerations highlight the less favorable aspects of wind energy installation:
Impact on Wildlife
A notable concern regarding wind energy facilities is their potential to disrupt avian and bat populations. Collisions with turbine blades can result in fatalities for birds and bats, particularly in migratory pathways and nesting areas. Moreover, the construction and maintenance of wind farms necessitate land use changes that can affect local ecosystems. Proactive measures, such as siting assessments and technological innovations, are crucial to minimizing these impacts.
Noise Pollution and Aesthetic Concerns
Wind turbines generate a distinctive sound during operation, which can be a source of annoyance for nearby residents. The auditory impact can pose challenges, particularly in rural settings where people seek tranquility. Additionally, the visual presence of wind turbines can alter landscapes, sparking aesthetic debates among community members. Addressing concerns regarding noise and visual impact is paramount for fostering community acceptance.
Resource Expenditure and Land Use
The production and installation of wind turbines necessitate substantial resource consumption and land use. Manufacturing components such as towers and blades involves extracting raw materials, which can carry their own environmental burdens. Furthermore, the land required for wind farms can intrude upon agricultural or undeveloped territories, raising issues regarding land rights and usage priorities. Striking a balance between energy needs and land conservation is critical in planning wind projects.
Strategizing for Mitigation: Encapsulating Environmental Oversight
The interplay of wind energy’s positive and negative effects on the environment underscores the imperative for thoughtful regulatory practices. It is paramount that stakeholders, including government entities, energy companies, and communities, collaborate in establishing guidelines that safeguard ecological integrity while promoting renewable energy expansion.
Incorporating Environmental Impact Assessments
Transparent and thorough environmental impact assessments (EIAs) are indispensable in the planning phases of wind energy projects. Rigorous assessments should evaluate potential wildlife disturbances, habitat fragmentation, and acoustic implications. Engaging ecologists and environmental specialists can enhance project designs, embodying a more holistic approach to renewable energy development.
Fostering Community Engagement and Education
Community involvement is essential in addressing local concerns and enhancing the socio-environmental fabric of wind energy projects. Empowering residents to participate in discussions about project siting and operations can engender acceptance and collaboration. Educational programs can also demystify the technology, elucidate its benefits, and inform residents about mitigating initiatives.
Innovating for Improvement: Technological Advancements
Harnessing cutting-edge technology to improve turbine design and operational efficiency can significantly ameliorate the negative environmental impacts of wind energy. Innovations such as radar systems to detect and avoid avian collisions or quieter turbine designs can mitigate both wildlife fatalities and noise concerns. Continuous research and development efforts are crucial in refining wind energy practices to align with environmental stewardship.
In summary, while wind energy stands as a pillar of the transition towards sustainable energy solutions, its environmental impacts are both commendable and concerning. By scrutinizing the intricate dynamics at play, stakeholders can navigate the burgeoning wind energy sector with a balanced perspective, ensuring ecological harmony and robust energy production for future generations.