The relentless pursuit of renewable energy solutions continues to shape our world, and wind energy has emerged as a significant player in this ongoing quest. Among the many observations related to this form of energy, the question that often piques interest is: how much energy can a wind turbine produce? Understanding this potential output not only underscores the importance of wind power but also highlights the fascinating interplay between technology, nature, and human ingenuity.
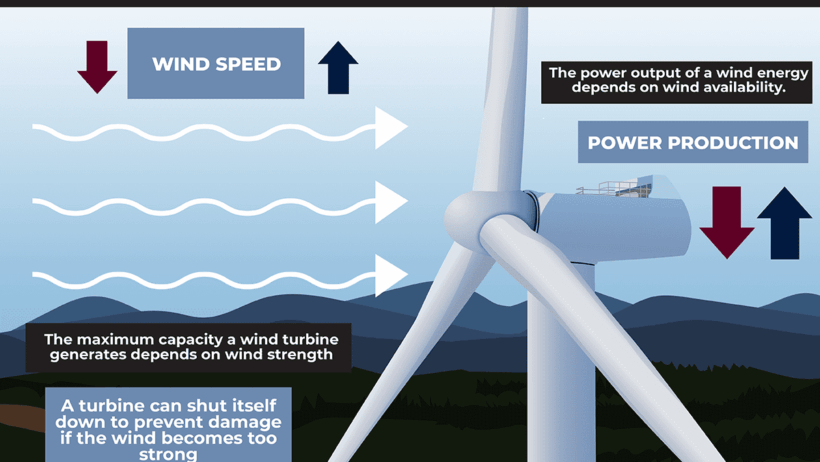
To appreciate the efficacy of wind turbines, it is imperative to consider several factors that contribute to their overall energy production. Various elements interplay to ascertain the potential output, including wind speed, turbine design, and location.
The magic behind wind energy lies in harnessing the kinetic energy of wind. As the wind blows, it causes the turbine blades to rotate, converting this kinetic energy into mechanical energy. The mechanics of this process are elegantly designed to maximize efficiency, but the amount of energy produced is contingent upon several variables.
Most modern wind turbines have a rated capacity that typically ranges from 1.5 to 3 megawatts (MW). However, this number can be a bit misleading; the rated capacity is the maximum power output under ideal wind conditions. In reality, the energy output of a wind turbine is often expressed in terms of its capacity factor, which indicates how frequently it operates at or near its maximum capacity over a given period.
Capacity factors for wind turbines generally fluctuate between 30% to 50%, depending on the site and wind conditions. A turbine with a capacity of 2 MW, therefore, would produce an average of 5,256 to 10,512 megawatt-hours (MWh) annually, contributing significantly to local and national energy grids.
Yet, deeper exploration reveals a fascinating and intricate relationship between wind turbines and their environments.
Location, Location, Location: The Impact of Wind Resources
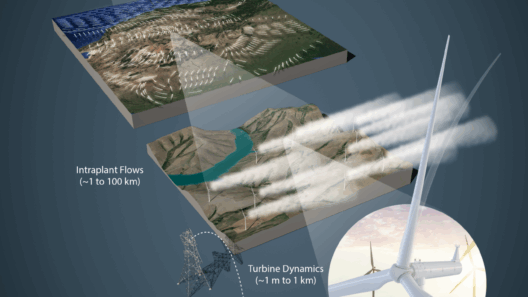
The geographic location of a wind turbine greatly influences its energy production potential. Areas known for their robust and consistent wind patterns are prime candidates for wind farms. Coastal regions, open plains, and elevated terrains typically boast higher wind speeds. Turbines installed in these areas can consistently generate greater amounts of electricity. In some instances, offshore wind turbines can harness even more wind energy due to stronger and more persistent winds found over the oceans.
Additionally, the microclimates created by topographical features can either aid or hinder energy production. Forested regions or areas with significant obstacles can create turbulence and reduce the effective wind speed, ultimately lowering the energy yield.
The shape and design of the turbine also play pivotal roles in determining energy output. Innovations in turbine engineering, such as larger blades and taller towers, allow for increased energy capture. Modern turbines are adept at functioning in a broader range of wind conditions, thereby maximizing efficiency and energy generation.
Harnessing the Wind: Technology and Innovation
Continuous advancements in wind turbine technology contribute significantly to energy production capabilities. The evolution of blade design, for instance, has fostered greater aerodynamic efficiency, enabling turbines to harness energy even in suboptimal conditions. Additionally, innovations like variable speed turbines allow for more effective energy production across a wider variety of wind speeds.
Smart technology integration, such as predictive maintenance systems and IoT connectivity, further enhances operational efficiency. These systems allow for real-time monitoring of turbine performance, enabling proactive adjustments that maximize energy output while minimizing downtime. The future of wind energy looks increasingly bright, with burgeoning research focused on improving turbine performance and efficiency.
The Societal Impact of Wind Energy Production
The ramifications of harnessing wind energy extend far beyond the mere mechanics of energy production. Wind turbines have become symbols of sustainable living and renewable energy potential. They signify a shift away from fossil fuels, addressing pressing environmental concerns such as climate change and pollution. Moreover, the burgeoning wind energy sector creates numerous job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, enhancing local economies while striving for energy independence.
Furthermore, an increasing number of communities are recognizing the value of wind energy in their pursuit of sustainable development. By integrating wind turbines into local energy strategies, towns and cities can enhance their resilience against fluctuating energy prices, reduce their carbon footprints, and foster a more robust connection with their natural surroundings.
As research continues to unveil the vast potential of wind turbines, we witness the broader narrative of energy production fraught with challenges and opportunities. Understanding how much energy a wind turbine can produce is ultimately a testament to humanity’s ability to adapt and innovate in addressing the complexities of our energy needs.
In conclusion, the exploration of wind turbine energy production offers insight into the myriad dynamics of renewable energy generation. Harnessing the wind is not merely a feat of engineering but a crucial aspect of fostering a sustainable future and combating global environmental challenges. With wind turbines leading the charge, the quest for cleaner energy sources is firmly underway, steering us toward a more sustainable world.