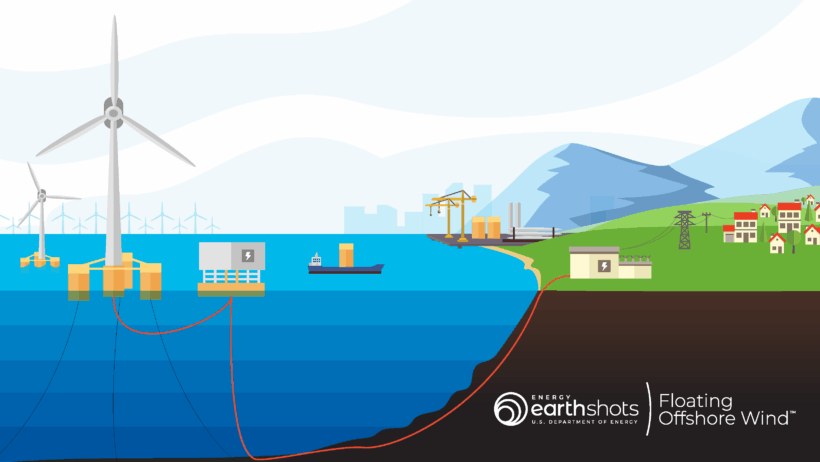
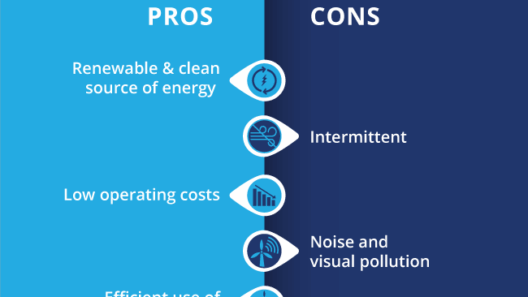
Wind energy stands as one of the cornerstones of sustainable energy solutions in the modern world. Its applications extend far beyond mere electricity generation, inviting us to delve into the multifaceted conveniences and benefits it affords. From powering homes to driving industrial processes, the transformative potential of this renewable resource is both profound and aesthetically remarkable.
Historically, wind energy has been harnessed for centuries, initially utilized by sailors to navigate vast oceans with sails. Today, it is manifest in sophisticated turbines that symbolize the harmonious coexistence of technology and nature. Yet, what exactly do we use this green energy for? This exploration invites a closer look at various aspects where wind energy is not only functional but also inspirational.
Electricity Generation: The Pinnacle of Wind Energy Applications
The most prevalent usage of wind energy is undoubtedly in electricity generation. Wind turbines, with their majestic blades slicing through the air, convert kinetic energy from the wind into electrical energy. Onshore and offshore wind farms proliferate around the globe, illustrating the growing reliance on this renewable resource. By leveraging advancements in turbine technology, energy efficiency has reached unprecedented heights, allowing for maximum energy capture even in low-wind conditions.
These turbines are capable of generating power on a large scale, contributing significantly to national grids while diminishing our dependence on fossil fuels. This practice not only mitigates greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes energy security, making nations less vulnerable to fluctuations in oil and gas prices. The aesthetic allure of massive wind farms adds a striking natural element to the landscape, inviting a sense of progress as they stand sentry against the sky.
Residential Applications: Wind Energy at Home
In addition to large-scale generation, wind energy also finds its way into individual households through small-scale wind turbines, often seen in rural settings. Homeowners can harness wind power to complement traditional energy sources, effectively reducing their energy bills and carbon footprints. Micro-turbines are becoming increasingly popular, enabling homeowners to generate a portion of their energy autonomously. The concept of “energy independence” is highly appealing, as homeowners gain the ability to produce power directly from nature, fostering a deeper connection with the environment.
Moreover, residential wind turbines symbolize self-sufficiency and sustainability, enabling families to contribute positively to the planet’s health one kilowatt at a time. While not suitable for every locale, when implemented correctly, these small installations can significantly enhance energy resilience, particularly in remote areas where conventional electricity grid access is unreliable.
Industrial Power: A Backbone for Manufacturing
Wind energy also plays a crucial role in powering industrial processes. Factories and manufacturing plants are increasingly turning to wind power as a viable alternative to reduce operational costs and promote sustainability. Large-scale operations can establish direct purchase agreements with wind farms, ensuring a steady supply of renewable energy. This not only mitigates their environmental impact but also enhances the corporate image as consumers are notably more inclined to support brands that prioritize sustainability.
Furthermore, the reliability of wind energy promotes stability within power-intensive industries. As companies embrace the wind as a core energy source, they become leaders in the transition towards cleaner production methods, which in the long term fosters broader societal change. The aesthetic of spinning turbines on the horizon reinforces a corporate commitment to environmental stewardship through visual symbolism, inspiring other sectors to follow suit.
Support for Agriculture: A Synergistic Approach
A fascinating aspect of wind energy applications lies in its synergy with the agricultural sector. Farmers and ranchers are increasingly integrating wind turbines into their land-use strategies. Not only do these wind installations provide a source of passive income, but they also create opportunities for diversifying farm revenues. The vast expanses of farmland are ideal for wind turbines, allowing crops to flourish without significant disruption.
This symbiotic relationship supplements traditional agricultural practices, augmenting the overall resilience of rural economies. Wind turbines dotting the landscape become a testament to how innovation can rejuvenate age-old professions while ensuring the preservation of the environment for future generations. The sight of turbines standing tall amidst fields evokes a sense of harmony between progress and nature.
Energy Storage and Grid Stability: Balancing Supply and Demand
Another critical application of wind energy is in its interplay with energy storage systems. Due to the intermittent nature of wind, advances in technology enable the integration of energy storage solutions such as batteries, which can store excess energy generated during peak wind periods. This allows for a stable supply when demand increases or wind intensity wanes, creating a more resilient energy infrastructure.
Innovative energy management systems can optimize the distribution of wind-generated electricity, ensuring that it reaches consumers when they need it most. This capability signifies a major stride in modern energy systems, representing the peak of efficiency and resource management. The aesthetic of sleek, modern storage facilities, combined with turbine installations, embodies the fusion of engineering excellence and environmental consciousness.
The Future of Wind Energy: A Vision of Sustainability
As we look toward the future, the potential applications of wind energy will only continue to grow. Investments in offshore wind technologies and initiatives to enhance turbine efficiency are ongoing, promising to unlock even greater capacities for energy generation. With an ever-expanding role in both developed and developing nations, wind power stands as a flagbearer for innovative energy solutions that are both aesthetically appealing and fundamentally essential.
In summation, the uses of wind energy weave together to create a tapestry of possibilities that extends beyond electricity generation. From residential settings to industrial applications and agricultural synergies, wind power champions a sustainable future while offering a strikingly beautiful presence in our landscapes. As society embraces this inherent power of the wind, it ultimately beckons us to reconsider our relationship with nature and the energy we consume.