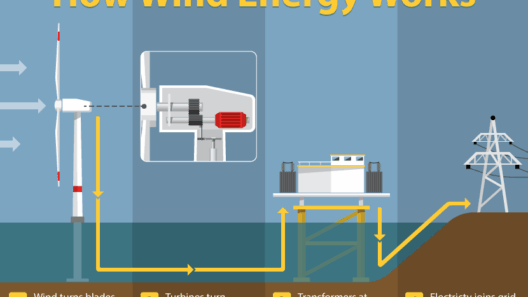
The rapid evolution of renewable energy sources has given rise to significant changes in how the United States generates and consumes power. Among these sources, wind energy stands out as a frontrunner, becoming an integral part of the nation’s energy portfolio. This article delves into the current state of wind energy usage in the U.S., addressing what percent of the American energy mix derives from this renewable resource, while dispelling common misconceptions and highlighting its importance in combating climate change.
Understanding the Proportion of Wind Energy in the U.S. Energy Mix
Wind energy installations have burgeoned over the past few decades, transforming the landscape of power generation in America. As of recent measurements, wind power represents about 8.4% of the total electricity generation in the United States. This figure may seem modest compared to fossil fuels, but its trajectory indicates a robust growth pattern. The percentage of wind energy in the U.S. is expected to climb steadily, influenced by factors such as technological advancements, policy support, and public attitudes toward sustainability.
This shift to wind energy is not merely an incremental change; it symbolizes a broader societal commitment to renewable resources. Wind farms dotting the plains and even offshore coasts are becoming emblematic of an energy revolution—a potent countermeasure against greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel consumption. By expanding the wind power footprint, the U.S. can begin to address two fundamentally critical issues: energy independence and environmental sustainability.
Challenges and Triumphs in Expanding Wind Energy Usage
While the growth of wind energy is promising, it is not without challenges. The integration of wind power into the broader energy grid poses technical hurdles, particularly when it comes to reliability and storage. Wind energy availability fluctuates depending on meteorological conditions, necessitating advancements in energy storage solutions and backup systems to ensure a steady supply of electricity. Innovations, including battery storage and demand response systems, are being developed and implemented to alleviate these issues, showcasing a concerted effort to make wind energy a more reliable and sustainable option.
Government regulations and incentives also play a crucial role in expanding wind energy usage. Policies promoting tax credits and subsidies encourage investment in new wind projects, while renewable portfolio standards set necessary benchmarks for energy companies to meet. Such regulations are instrumental in fostering a conducive environment for the adoption of wind energy, encouraging businesses and individuals alike to consider renewable alternatives.
The Enviable Growth Trajectory of Wind Energy
The growth of wind energy in the U.S. can be traced back to technological advancements in turbine design and efficiency. Modern wind turbines, with their towering heights and expansive rotor diameters, have dramatically improved the amount of energy captured from wind. As efficiency increases, so too does the viability of wind power as a primary energy source. Technological innovations have enabled the construction of larger, more efficient turbines that can harness wind energy in areas previously deemed unsuitable.
Moreover, regional trends have shown varying levels of investment in wind energy. States such as Texas and Iowa lead the pack, with a remarkable percentage of their electricity generation attributed to wind power. In Texas, for instance, wind energy accounts for approximately 30% of the state’s electricity generation. This concentration underscores the potential for local economies to thrive on renewable energy sources, creating jobs and promoting sustainable development.
Addressing Common Concerns: Is Wind Energy Reliable?
One of the foremost concerns related to wind energy is reliability. Critics often argue that wind power is inconsistent and thus cannot serve as a dependable energy source. However, advances in energy storage and grid management have significantly mitigated these concerns. By utilizing energy storage systems, wind-generated electricity can be captured during peak production periods and distributed during times of higher demand or reduced wind output.
Furthermore, the diversification of the energy mix helps in stabilizing electricity supply. Wind energy excels in regions with complementary energy sources, such as solar power, which tends to produce electricity during peak sunlight hours. This synergy allows for a more stable and reliable energy supply overall.
The Future of Wind Energy in the U.S.: What Lies Ahead?
As the United States continues its journey toward a cleaner energy future, wind power will undoubtedly play a pivotal role. Current projections indicate that the share of wind energy in the overall energy mix will increase substantially in the coming years. With ongoing investments and innovations, wind energy could see its percentage rise significantly, positioning it alongside solar and other renewables as a primary energy source for the nation.
As communities recognize the economic and environmental benefits of wind energy, it is expected that public sentiment will remain favorable toward the expansion of wind farms and other renewable energy projects. Education and awareness campaigns will be crucial in encouraging broader acceptance and understanding of the capabilities and benefits of wind energy.
In conclusion, while the current percentage of wind energy in the U.S. energy mix stands around 8.4%, this figure is not static. With the right combination of technological advancement, policy support, and public engagement, wind energy is poised for substantial growth. As America forges ahead in its energy transition, embracing wind energy will be essential in fostering a sustainable, resilient future while addressing the pressing need for an energy system less reliant on fossil fuels.