Throughout history, humans have sought ways to harness the inexorable power of nature. Among these pursuits, wind energy stands out as one of the oldest forms of renewable energy, dating back thousands of years. The intrigue surrounding wind power is not just about its practical applications; it reflects a deeper relationship between humanity and the natural world, one marked by innovation and adaptation to the environment. As we delve into the storied origins of wind energy, we unveil the trailblazers whose ingenuity paved the way for modern wind power.
The Dawn of Wind Power: Ancient Innovations
The utilization of wind as an energy source can be traced back to ancient civilizations, which ingeniously harnessed its force for various purposes. The earliest known windmills appeared in Persia around 500-900 AD, where they were employed primarily for grinding grain and pumping water. Made from vertical sails mounted on a central post, these windmills transformed the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy, demonstrating remarkable engineering prowess for the time.
In China, wind energy took on different forms as early as 200 AD, when small sailboats utilized wind propulsion for trade and transportation. The craft of sailing further exemplified humanity’s ability to engage with natural forces. The connection to wind was palpable, fostering a respect for its might and potential. This admiration for the wind would carry through centuries as civilizations evolved, shaping the way we approach energy solutions today.
The Emergence of Modern Wind Turbines
Fast forward to the late 19th century, a time characterized by rapid industrialization and a growing fascination with technological advancement. In the United States, a pivotal figure emerged: Charles F. Brush, credited with developing one of the first practical wind turbines in 1888. Brush’s turbine, a 17-meter tall structure equipped with 144 blades, produced electricity for his home in Cleveland, Ohio. This groundbreaking achievement solidified the concept of generating electricity from wind, while establishing Brush as a visionary in renewable energy.
Across the Atlantic, in Denmark, a similar wave of innovation was unfolding. Paul LaCour, a Danish inventor, created an empirical wind turbine design in the 1890s. This device was characterized by its use of wooden blades, which allowed for an efficient conversion of wind energy into usable power. Even though these early designs were relatively primitive by today’s standards, they laid the groundwork for the sophisticated turbine technology of the present day.
The Interwar Period: A Time of Experimentation
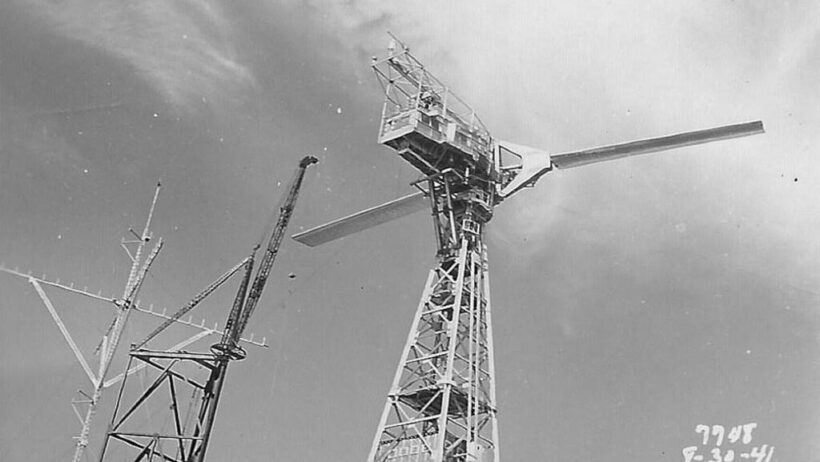
The revolutionary developments in wind energy didn’t cease with Brush and LaCour; rather, they galvanized a movement. In the early 20th century, as the world grappled with the implications of industrial growth, various inventors and engineers experimented with wind turbine designs to enhance efficiency and scalability. During the 1930s, notable efforts emerged in the United States with the construction of larger wind turbines capable of generating significant amounts of electricity.
One of the most celebrated examples came from the seeds of innovation sown in the barren expanses of California. The Pacific Coast produced some of the largest wind turbines of the era, which were used to power remote farms and communities. These developments were not without their challenges, as societal aspirations for electrification often clashed with traditional energy paradigms reliant on fossil fuels. Nonetheless, this period of exploration represented not only a technical pursuit but also an auditory social discord, illuminating humanity’s ever-growing reliance on energy and climate perils.
Modern Wind Energy: The Renaissance of Renewables
With the mid-20th century came an awakening. After decades languishing in the shadows of coal and oil, wind energy would once again rise to prominence. The 1970s energy crises, exacerbated by geopolitical events and economic uncertainty, triggered renewed interest in alternative energy sources. The quest for sustainable solutions became more pressing, and wind power re-emerged as a legitimate contender.
During this era, pioneers like Danes and Americans pushed the envelope on turbine design and efficiency. The establishment of organizations such as the Danish Wind Industry Association in 1978 further stimulated growth in wind technology. Countries like Denmark initiated significant investment in research and development, enabling more efficient turbines to hit the market. Innovations such as horizontal-axis wind turbines became the gold standard, significantly impacting the landscape of renewable energy.
Navigating Towards the Future: The Promise of Wind Power
As humanity stands at the precipice of climate crisis, the resurgence of wind power signifies promise and possibility. Today, this vibrant sector continues to evolve. Wind farms proliferate across continents, each turbine standing as a testament to the ingenuity of the countless individuals who have sought to harness one of nature’s most abundant resources. In the modern context, wind energy has become synonymous with sustainability and environmental stewardship, paralleling a growing awareness of the urgent need for clean energy solutions.
The fascination with who invented wind energy intertwines with the broader narrative of humanity’s quest for harmony with nature. It exemplifies a fundamental truth: innovation often springs from necessity and ingenuity. As we reflect on the innovators, from ancient civilizations to modern engineers, it’s crucial to acknowledge the enduring legacy of wind power and its potential to empower future generations in their pursuit of a sustainable and energy-efficient world.