The Future of Wind Energy: Exploring Potential and Growth of Wind Power
As the world confronts the escalating challenges of climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels, wind energy emerges as a pivotal player in the global transition to sustainable energy sources. Wind power is indicative of innovation and commitment to clean energy, positioning itself as a formidable ally in combating the environmental crisis. With advancements in technology, changing policies, and a surge in investment, the future of wind energy appears increasingly promising. This article delves into the potential expansion of wind power, analyzing key factors shaping its growth and addressing common buyer concerns regarding this renewable energy resource.
Understanding Wind Energy: A Primer
Wind energy harnesses the kinetic energy from wind currents to generate electricity. This is accomplished by utilizing wind turbines, which convert the motion of wind into mechanical power. Once transformed into electricity, the power can be transported through the grid to homes, businesses, and industries. Known for its minimal environmental impact and sustainability, wind energy is considerably cleaner compared to conventional fossil fuels. However, the technology is not without its challenges. Addressing these challenges is crucial for wider adoption.
The Mechanisms Driving Growth in Wind Power
Several dynamics contribute to the remarkable growth trajectory of wind energy. Governments around the globe are increasingly adopting renewable energy targets and incentives, fostering an environment conducive to investment in wind infrastructure. Financial mechanisms such as tax credits and grants are alluring to stakeholders, mitigating financial risks associated with renewable energy projects.
Technological advancements mark another cornerstone of wind power expansion. Modern wind turbines are more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective than their predecessors. Innovations such as larger rotor diameters and taller towers increase energy capture rates, making it feasible to generate power in regions previously deemed unsuitable for wind farms. Moreover, the integration of smart technology into wind energy systems facilitates improved performance monitoring and maintenance, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
Furthermore, wind power’s scalability appeals to various market sectors. Be it utility-scale wind farms or smaller distributed generation models, the versatility of wind energy allows for its implementation across diverse settings. This adaptability fosters positive investment sentiment, enabling local communities to play a role in the energy transition while reaping economic benefits.
Environmental Considerations: The Green Footprint of Wind Power
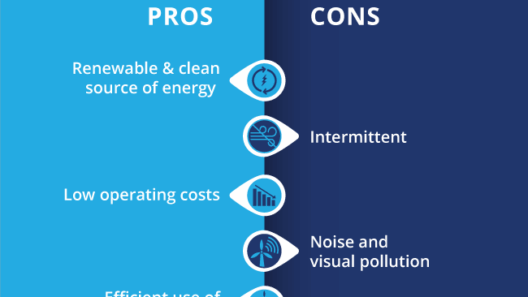
Wind energy is heralded for its clean and sustainable nature, producing electricity without air pollution or greenhouse gas emissions. This inherently supports global climate commitments, effectively reducing reliance on fossil fuels and curtailing the carbon footprint associated with energy consumption.
However, it is essential to consider the ecological ramifications of wind farm installations. The interactions between wind turbines and wildlife, particularly avian species, have raised concerns among environmentalists. Implementing strategic planning for wind farm locations is imperative to mitigate potential harm. Conducting thorough environmental impact assessments can ensure responsible siting of wind projects, effectively balancing energy generation with the preservation of biodiversity.
Addressing Key Buyer Concerns: Reliability and Cost
A typical apprehension among potential buyers considering wind energy revolves around reliability. Unlike conventional energy sources, wind performance can be intermittent. However, advancements in energy storage solutions and grid management practices are bridging this gap. Energy storage systems, such as batteries, can store excess wind-generated power for use during low-wind periods, thereby enhancing the reliability of wind energy as a consistent power source.
Cost also poses a pivotal consideration for stakeholders involved in the energy market. Historically, the financial barrier to entry for wind energy has been perceived as high; however, a paradigm shift is underway. The cost of wind energy has plummeted over the past decade due to technological innovations and economies of scale. Current estimates suggest that onshore wind power can compete with conventional fossil fuels in many regions, rendering it economically attractive.
Global Trends: Wind Energy’s Market Landscape
The global wind energy market is expected to experience exponential growth in the coming years. Countries such as China and the United States have emerged as leaders in wind energy capacity, while developing regions are increasingly recognizing its potential. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects robust expansion, with wind contributing significantly to the global power generation mix. Regional trade agreements and international cooperation further bolster this growth, facilitating knowledge transfer and investment in wind energy solutions.
Conclusion: Wind Energy on the Horizon
The future of wind energy is not merely a vision; it is a reality that is unfolding with each passing year. The convergence of technological advancements, policy support, and growing public awareness forms a solid foundation for the expansion of this renewable energy source. By addressing key concerns such as reliability and cost, stakeholders can capitalize on the unique benefits wind power offers. As it stands, wind energy is poised to assume a central role in the global pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, promoting economic growth while safeguarding the environment for future generations.