Have you ever stood atop a hill, watching the wind turbine blades spin gracefully against the backdrop of a vibrant blue sky? How do these colossal structures convert the invisible currents of air into a tangible source of energy? In this exploration, we will unravel the intricate processes that enable wind turbines to generate electricity, diving deep into the mechanics and science behind this renewable energy source. As the world pivots towards more sustainable energy solutions, understanding the functionality of wind turbines is not only intriguing but essential.
Wind turbines operate on a simple yet sophisticated principle: they harness the kinetic energy of wind and transform it into electrical energy. While this idea may seem straightforward, the technology involved is anything but rudimentary. In fact, the conversion process engages a series of intricate components, each playing a pivotal role in the journey from wind to watt.
The allure of wind energy lies in its abundance and sustainability. Unlike fossil fuels, wind is renewable and inexhaustible. So, what makes wind turbines the harbingers of this transformation? Let’s embark on a detailed journey through the anatomy of wind turbines and the processes involved in generating power.
Understanding the Components of a Wind Turbine
Before we delve into the energy conversion process, it’s imperative to familiarize ourselves with the essential components of a wind turbine. Each element is specifically designed to contribute to the energy-generating system.
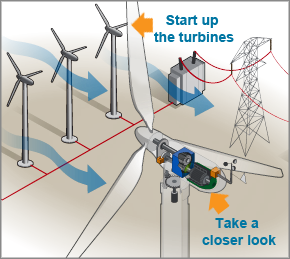
At the forefront is the rotor, composed of two or three blades that catch the wind’s force. The design of these blades is aerodynamic, maximizing the amount of wind energy captured. When the wind blows, it exerts pressure on the blades, causing them to rotate. This rotation is crucial as it initiates the energy conversion process.
Connected to the rotor is the low-speed shaft—where the magic of movement begins. This shaft turns with the rotor and connects to the gearbox, which steps up the revolutions per minute (RPM). This is particularly important because, while the rotor may rotate slowly (about 10-20 RPM), the generator requires a much higher RPM (about 1,500 RPM) to produce electricity. Thus, the gearbox multiplies the rotational speed, optimizing the energy generation potential.
Empowered by its increased speed, the generator is the heart of the turbine, converting mechanical energy from the rotating shaft into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. Here, a magnetic field interacts with coils of wire, prompting an electric current to flow.
Finally, let’s not forget the nacelle—a protective casing that houses the gearbox, generator, and other essential components. The design of the nacelle ensures that these parts are shielded from environmental factors, ensuring operational longevity.
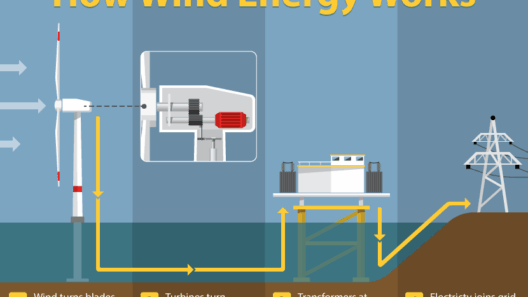
The Fascinating Journey of Wind to Electricity
Now, having recognized the components, let’s elucidate their collective function in generating electricity.
As the wind blows, it strikes the blades of the rotor, creating lift and causing the rotor to spin. The rotational motion travels down the low-speed shaft to the gearbox, which amplifies this motion. This process, while straightforward, must contend with varying wind conditions—sometimes calm, sometimes gusty. Interestingly, wind turbines can adjust their blade pitch to optimize performance amid fluctuating wind speeds. This capability ensures maximum efficiency and safety.
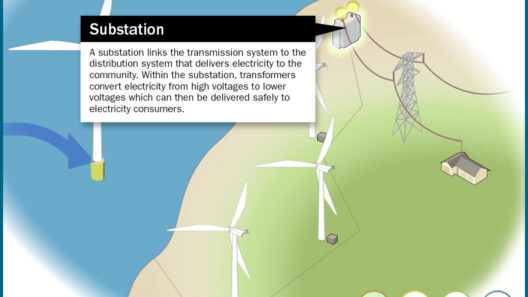
Once the gearbox amplifies the RPM, the generator takes charge. Inside the generator, the spinning shaft turns magnets past coils of wire, inducing electric currents. This process is governed by Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, revealing the beauty of physics in action. The output electricity is initially alternating current (AC), which the turbine can transmit directly to the grid or convert into direct current (DC) if necessary.
But what happens when the wind ceases to blow? This is where energy storage systems come into play. Advanced wind farms are fitted with batteries or other storage technology, allowing them to retain generated electricity for use during calm periods or peak demand times. It poses an interesting challenge: how to seamlessly integrate energy storage solutions into wind energy systems. How can we ensure a steady and reliable power supply, regardless of nature’s whims?
The Environmental Impact and the Future of Wind Energy
Wind turbines represent a commendable leap towards sustaining an eco-friendly energy ecosystem. As we shift from conventional energy practices, it is vital to consider the environmental implications. Wind energy generation boasts significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, presenting an important aspect of mitigating climate change.
However, the proliferation of wind energy isn’t without its challenges. Concerns regarding wildlife, particularly birds and bats, have ignited discussions about the optimal placement of wind farms. Additionally, noise and aesthetic concerns factor into public acceptance, raising questions about land use and community involvement in decision-making.
Looking ahead, innovation in turbine technology, such as offshore wind farms and vertical-axis turbines, promises to reshape the landscape of energy generation. As advancements continue to emerge, the emphasis on decentralized and resilient energy solutions positions wind energy as a cornerstone of our sustainable future.
The nexus of wind turbines and renewable energy goes beyond merely generating power; it encapsulates a vision for a greener planet. As we deepen our understanding of how these magnificent structures operate, we empower ourselves to advocate for a cleaner, more sustainable energy future. Did you ever think—in the gentle rustling of the leaves, in the tousled hair on your face—is a source of power just waiting to be harnessed?
In conclusion, wind turbines exemplify the convergence of engineering, science, and sustainability. By turning the indomitable force of wind into usable electricity, they herald a new era of energy that respects and integrates with our planet’s natural systems while minimizing our carbon footprint. The world stands at a pivotal juncture, where the potential of wind energy beckons us toward greener horizons.