The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that is crucial for sustaining life on Earth as we know it. However, this process is often misunderstood and misrepresented. So, what happens when we think of the Earth as a greenhouse? Let’s delve deeper into the intricate workings of this environmental mechanism.
Imagine, for a moment, our planet encased in a transparent dome, allowing sunlight to pour in while preventing some heat from escaping back into space. This imagery captures the essence of the greenhouse effect. But how does this process impact our climate, and what challenges does it present as we face unprecedented changes in the environment?
To understand the greenhouse effect, we must first explore the role of greenhouse gases. These gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), are crucial players in the ambiance of the Earth. They exist naturally and are released through human activity like burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
In this article, we will traverse through the layers of the greenhouse effect, breaking down its complexities into easily digestible components. Let’s unravel the mysteries behind this vital climatic mechanism!
The Foundations of the Greenhouse Effect
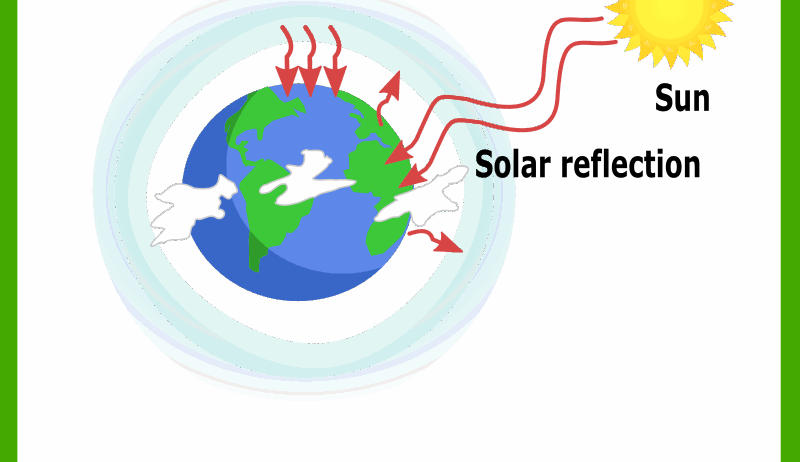
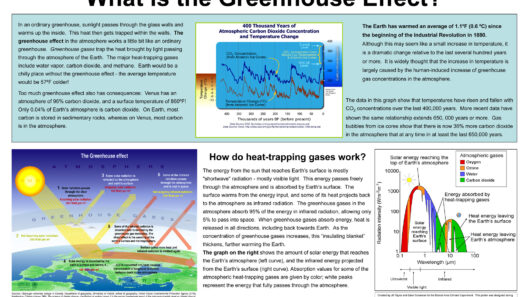
The greenhouse effect begins with sunlight, known scientifically as solar radiation. When sunlight reaches the Earth, some of it gets reflected back into space, while the rest is absorbed by the Earth’s surface. This absorption is critical, as it warms our planet, making it habitable. Without this heating effect, temperatures would plummet, rendering the Earth a frozen wasteland.
Once the Earth absorbs solar energy, it doesn’t keep it stored indefinitely. The surface of the Earth emits this absorbed energy back into the atmosphere in the form of infrared radiation, a type of heat. However, this is where greenhouse gases come into play.
These gases, encompassing water vapor, CO2, and others, effectively create a barrier, trapping some of this heat in the atmosphere. This added warmth is akin to a thermal blanket cuddled up around the planet. The result? A stabilized climate that supports the myriad forms of life we see today. It’s fascinating to think about how this balance epitomizes the delicate interplay of nature!
The Impact of Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
While the greenhouse effect is necessary, the process can become perilous when it is amplified by an excess of greenhouse gases, primarily the result of human actions. This phenomenon is often referred to as the enhanced greenhouse effect.
Picture a scenario where this thermal blanket becomes too thick. As we continue to emit vast amounts of greenhouse gases through industrial activities, transportation, and agriculture, the additional heat trapped in the atmosphere leads to global warming. This warming contributes to a cascade of climate-related calamities: rising sea levels, intense heatwaves, and unpredictable weather systems, among others.
It begs the question: What happens to our planet if we do not collectively challenge these escalating emissions? What world will we be leaving for future generations?
Contributing Factors to the Greenhouse Effect
Understanding the nuanced factors contributing to the greenhouse effect involves delving into various sectors of human activity.
Energy Production
The energy sector remains the largest perpetrator of greenhouse gas emissions. From electricity generation to transportation, the consumption of fossil fuels plays a significant role in releasing CO2 and other harmful gases. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, can significantly reduce these emissions.
Agricultural Practices
Agriculture also contributes vastly to greenhouse gas emissions. Methane, generated from livestock digestion and rice cultivation, offers a profound insight into the environmental footprint of our dietary choices. Practices such as overusing fertilizers can release even more nitrous oxide, another potent greenhouse gas. Therefore, sustainable agricultural practices become paramount in curbing emissions.
Deforestation and Land Use
Forests serve as crucial carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. When we clear forests for agriculture or urban development, we disrupt this balance, releasing stored carbon back into the atmosphere. Reforestation and sustainable land use management emerge as vital strategies to mitigate this impact.
What Can We Do?
Addressing the greenhouse effect is an endeavor that requires collective action and commitment. This challenge may seem daunting, but every small effort counts. Here are a few actionable suggestions:
1. **Adopt Renewable Energy:** Transitioning to energy-efficient appliances and considering renewable energy sources for homes can directly reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
2. **Practice Sustainable Agriculture:** Opt for local, organic produce, and reduce meat consumption to lower methane emissions.
3. **Promote Reforestation:** Engage in or support initiatives aiming at tree-planting activities, which help absorb CO2.
4. **Advocacy and Education:** Engage in conversations about climate change with peers, and support policies focused on sustainability and environmental protection.
As we conclude this exploration of the greenhouse effect, let’s remember that awareness is the first step towards action. The climate crisis may seem overwhelming; yet, understanding the greenhouse effect lays the groundwork for meaningful change. As we embark on this challenge, consider: How can we each contribute to safeguarding our planet? The responsibility lies in our hands.