Global warming, a profound environmental challenge of our era, largely stems from carbon combustion. The process involves burning fossil fuels—coal, oil, and natural gas—that release carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This article delves into the intricacies of carbon combustion, its implications for global warming, and the multifaceted consequences of our reliance on these energy sources.
At the core of the carbon combustion process is the chemical reaction that occurs when carbon-based fuels are burned, producing energy while simultaneously emitting carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other pollutants. This reaction can be succinctly represented by the equation: C + O2 → CO2 + energy. The emitted carbon dioxide acts as a greenhouse gas, capturing heat within the Earth’s atmosphere and contributing to the greenhouse effect. This effect is crucial for maintaining life on Earth; however, the continuous and exponential increase in carbon emissions is exacerbating climate change.
The origins of carbon combustion can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution when human innovation began harnessing fossil fuels to power machinery, revolutionize transportation, and facilitate mass production. This marked a significant departure from sustainable energy sources, such as wind and water, and initiated a trajectory of rapid industrial growth and urban development. While technological advancements improved living standards, they also set the stage for an environmental crisis characterized by rising global temperatures, melting glaciers, and erratic weather patterns.
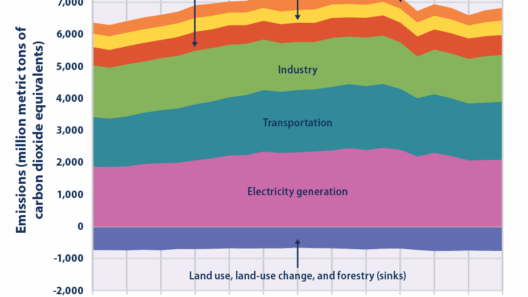
It is essential to differentiate between various forms of carbon combustion. There are three primary types: stationary combustion, mobile combustion, and biomass burning. Each type contributes differently to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Stationary combustion primarily occurs in power plants and industrial facilities, where fossil fuels are burned to generate electricity and heat. Mobile combustion happens in vehicles, planes, and ships, relying on gasoline and diesel. Biomass burning, while sometimes viewed as renewable, can also generate significant carbon emissions, particularly when forests are harvested unsustainably.
To grasp the gravity of the situation, consider the statistics surrounding carbon emissions. According to the latest reports, transportation accounts for approximately 29% of total greenhouse gas emissions in the United States, with personal vehicles being the predominant source. These figures illuminate the need for a concerted effort to advance sustainable transportation alternatives, such as electric vehicles, public transport systems, and non-motorized options like cycling and walking.
Furthermore, the importance of understanding carbon combustion extends beyond individual actions. Corporations and governments play a crucial role in shaping our carbon footprint. Policies that encourage energy efficiency, renewable energy investments, and emissions reductions are vital components of any strategy aimed at mitigating climate change. It is imperative for leaders to embrace comprehensive regulations that cap emissions and incentivize sustainable practices across various sectors, including energy, agriculture, and transportation.
Transitioning to alternative energy sources is a critical aspect of addressing carbon combustion. Renewable energies, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, present viable solutions for reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. These technologies harness natural resources to produce clean energy with minimal emissions. The ongoing advancements in battery storage and grid technology further enhance the feasibility of transitioning away from carbon-intensive fuel sources.
Despite the promising potential of renewables, the challenge remains monumental. The fossil fuel industry is deeply entrenched in global economies, creating a complex web of dependencies that resist change. Financial investments in fossil fuel infrastructure and exploration continue to divert resources away from cleaner alternatives. This presents a unique dilemma: how to phase out carbon combustion while ensuring energy security and economic stability?
Another essential consideration is the impact of carbon combustion on biodiversity and ecosystem health. As temperatures rise and habitats shift, countless species face the threat of extinction, exacerbated by the fragmentation of ecosystems and the erosion of natural habitats. These changes ripple through food webs and disrupt ecological balance, leading to diminished resilience in the face of climate change. Moreover, the acidification of oceans, caused by increased CO2 absorption, threatens marine life, particularly organisms such as corals and shellfish that form the foundation of marine ecosystems.
Citizen engagement and grassroots movements are pivotal in the fight against carbon combustion and global warming. Efforts to raise awareness, advocate for policy changes, and promote sustainable practices can have a profound impact on local communities and beyond. Grassroots initiatives often lead to significant changes in public perception and policy development. Community-based programs that emphasize sustainable living, carbon offsets, and conservation efforts have the potential to inspire broader societal shifts.
In conclusion, the relationship between carbon combustion and global warming is intricate and multifaceted. Understanding this dynamic is crucial in our collective quest to mitigate climate change. By fostering advancements in technology, promoting policy change, and advocating for sustainable practices, it is possible to create a coherent strategy aimed at reducing carbon emissions and safeguarding our planet for future generations. The path forward requires concerted action, innovative thinking, and an unwavering commitment to environmental stewardship. Embracing these challenges is not merely a responsibility; it is an ethical imperative intertwined with our survival.