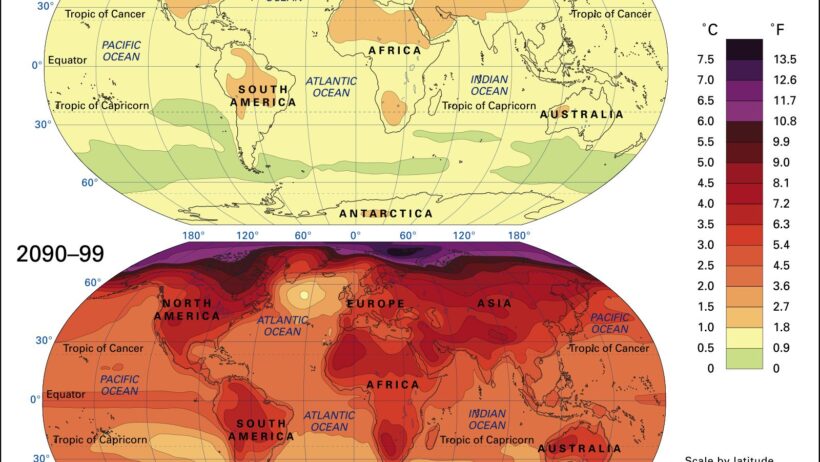
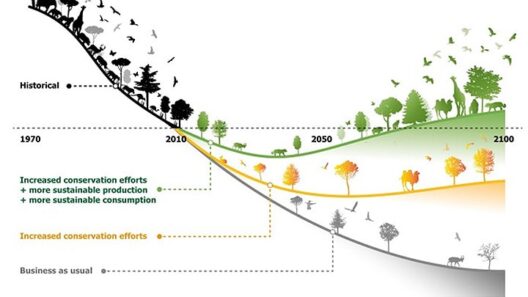
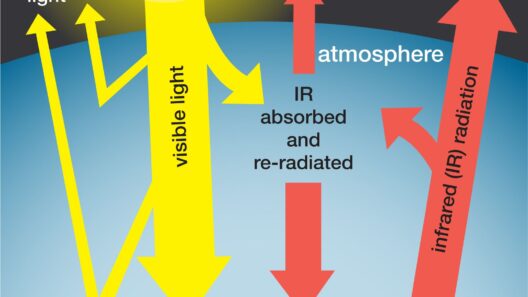
Global warming, a term that has become increasingly prevalent in both scientific discourse and public awareness, affects not only the average temperature of our planet but also intricately alters various weather patterns. To comprehend the depth of climate change’s pervasive influence, one must look beyond mere predictions and grasp how these transformations manifest in everyday meteorological phenomena. From the frequency and intensity of storms to shifts in seasonal norms, global warming engenders a compelling metamorphosis in our environment.
The projection of a warmer globe leads to heightened evaporation rates, which, in turn, influence precipitation patterns. As atmospheric temperatures rise, the capacity of air to hold moisture increases—a principle rooted in the fundamental laws of thermodynamics. Consequently, this leads to phenomena such as heavier downpours and more potent storms during the wet seasons, significantly impacting regions that historically experienced moderate precipitation.
Torrential rainstorms—once considered aberrations—are predicted to become more commonplace. This escalation of extreme weather events poses severe threats to infrastructure, agriculture, and ecosystems alike. Flooding, a direct byproduct of intense rainfall, impacts soil health, disrupts local economies, and exacerbates soil erosion. As communities grapple with these newly frequent deluges, adaptability becomes paramount.
Conversely, regions that traditionally bask in regular rainfall may confront the specter of drought as climate change shifts atmospheric circulation patterns. The interplay of climate systems plays an unsettling role here; arid areas could see prolonged dry spells as moisture is transported away, leaving ecosystems in dire straits. Aqua-centric systems, like lakes and rivers, face dwindling water levels that can lead to cascading biodiversity losses and diminished agricultural productivity.
Moreover, temperature extremes—both heatwaves and colds spells—are becoming increasingly pronounced. Heatwaves, in particular, exemplify the paradox of climate change. While some regions may see increased periods of excessive heat, others can experience drastic shifts toward colder conditions, usually driven by disrupted polar vortex patterns. Scientists now hypothesize that as ice melts in the Arctic, the jet streams that regulate weather can meander significantly, leading to erratic weather phenomena across vast distances.
These complex interactions illustrate that global warming alters not just averages but rather the systems that govern climate. For example, the modulation of these jet streams may result in prolonged cool spells, defying expectations during typically warm periods. Such inconsistencies engender confusion among citizens and policymakers alike, urging a recalibration of approaches to weather preparedness and disaster management.
This intricate dance of climate dynamics underscores the urgency of embracing innovative, multifaceted strategies to combat climate change effects. Coastal regions, for instance, face unique challenges from rising sea levels and increased storm intensity. As glaciers and ice sheets continue to melt at an alarming rate, communities situated along coastlines must reimagine infrastructural resilience. The development of storm surges and flooding barriers, alongside sustainable urban planning, becomes vital for safeguarding these vulnerable areas.
Additionally, the interaction between climate change and wind patterns warrants exploration. Global warming may alter the strength and direction of wind currents, which has profound implications not only for weather but also for wind energy potential. In the face of decreased predictability, energy strategies must evolve, incorporating renewable sources that can withstand the capricities of changing weather.
It’s crucial to note that ecosystems are not immune to the shifting weather patterns driven by global warming. Biomes that once thrived in specific climatic conditions now face existential threats. Flora and fauna must adapt to altered temperature ranges and precipitation regimes, or risk extinction. These biological realignments challenge our understanding of biodiversity and conservation. New adaptive strategies must be implemented to protect these species, taking adequate measures to foster resilience.
On the societal front, understanding the socio-economic implications of changing weather patterns cannot be overstated. Agriculture, for instance, is at the nexus of climate change. Warmer temperatures may extend growing seasons in some locales while simultaneously reducing yields in others due to increased pest activity and shifts in crop viability. Failure to come to terms with this evolving landscape could culminate in food insecurity on a global scale.
Consequently, this imperative for adaptation necessitates a collaborative approach, where stakeholders from diverse sectors including agriculture, urban planning, and public health convene to jointly address the implications of climate change. Education systems must evolve to ensure future generations are equipped with the knowledge needed to navigate and mitigate these challenges.
Furthermore, individuals play a critical role in responding to climate-driven shifts. Participate in community resilience initiatives, support sustainable practices, and engage in advocacy aimed at demanding robust climate policies. Collective action can escalate awareness and incite changes that ultimately lead to systemic shifts in addressing climate change.
In conclusion, beyond the forecast lies a complex web of interactions poised to redefine weather patterns globally. The transformations wrought by global warming necessitate an acute awareness of the inherent interconnectedness of climate systems. Embracing this perspective paves the way for innovative solutions that can empower both humanity and the planet to adapt and thrive in the face of unprecedented environmental changes. Such an understanding invites curiosity and responsibility—ensuring that as climate activists, policymakers, and citizens, we can pivot towards a sustainable future.