As we traverse the intricate tapestry of our planet’s climatic systems, a looming question arises: Can we genuinely contend with the formidable challenge of global warming, or are we merely engaging in a Sisyphean endeavor? In dissecting the science of global warming, it is paramount to delve beyond the superficial headlines and unearth the profound implications of our current trajectory.
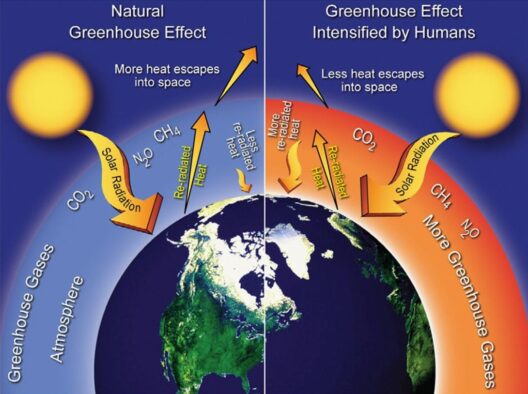
Global warming, at its core, refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature. This phenomenon is primarily instigated by the accumulation of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). These gases are byproducts of various human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. By enhancing the greenhouse effect, these gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to a cascade of environmental changes.
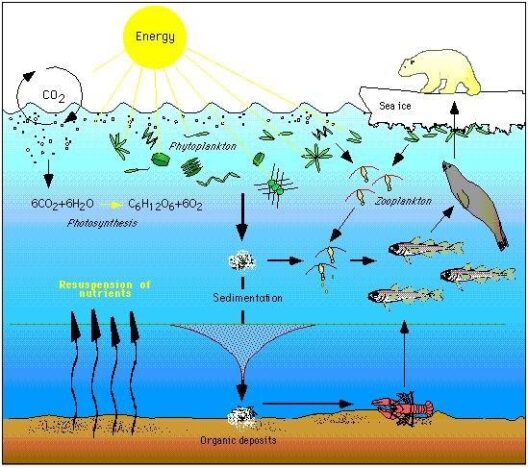
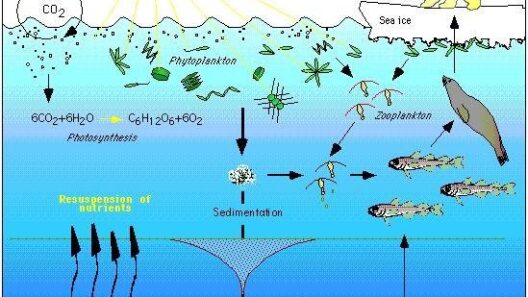
One cannot overlook the ramifications of rising temperatures. Elevated global temperatures are associated with more extreme weather patterns, including intensified hurricanes, droughts, and floods. According to numerous scientific studies, the frequency and severity of these phenomena are projected to escalate as global temperatures continue to rise. Additionally, ecosystems worldwide face unprecedented pressures; species extinction rates are projected to accelerate, disrupting delicate food webs and biogeochemical cycles.
Delving further into these climatic alterations, we encounter the concept of climate feedback mechanisms. These encompass processes that can amplify or mitigate the effects of climate change. For instance, the melting of polar ice caps reduces the Earth’s albedo effect—the reflection of sunlight off the surface—leading to more heat absorption and further warming. Similarly, thawing permafrost releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas that exacerbates warming. This cyclical nature of feedback mechanisms paints a dire picture of self-reinforcing climatic shifts.
Nonetheless, should we resign ourselves to despair? The answer is a resounding no. Humanity possesses the ingenuity and resilience to forge effective solutions to the challenges posed by global warming. Yet, the complexity of the task requires a multi-faceted approach, encapsulating technological innovations, policy reforms, and grassroots initiatives.
One pivotal area of focus is the transition to renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy represent sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels. The ongoing advancements in solar technology, such as photovoltaic cells and solar thermal systems, are making solar energy increasingly viable. Meanwhile, wind turbines are becoming a staple of energy generation across the globe. By shifting our reliance toward these cleaner energy sources, we not only mitigate carbon emissions but also foster energy independence and security.
Moreover, energy efficiency presents a substantial opportunity for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing energy-efficient technologies in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors can yield impressive results. From LED lighting to smart thermostats, the innovations available to us can significantly decrease energy consumption while saving costs. Passive design strategies in architecture—like maximizing natural light and optimizing thermal mass—can also play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency.
Another critical challenge is reforestation and afforestation efforts. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Initiatives aimed at restoring degraded forests and establishing new forests not only help sequester carbon but also preserve biodiversity, protect watersheds, and enhance soil quality. Engaging local communities in these projects is essential; stewardship of the land fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility.
Furthermore, embracing sustainable agriculture practices is vital to combat climate change. Traditional agricultural methods often contribute to significant greenhouse gas emissions through fertilizer application and livestock management. Transitioning to regenerative agriculture, which promotes biodiversity, reduces chemical inputs, and enhances soil health, can turn farms into active carbon sinks. Techniques like agroforestry, crop rotation, and organic farming can help bolster both food security and environmental resilience.
It is essential to recognize that climate change is not an isolated issue but rather intertwined with socio-economic factors. Addressing global warming necessitates a rigorous examination of equity and justice. Vulnerable populations are often disproportionately affected by climate impacts, as they may lack the resources to adapt. Consequently, climate action must encompass a framework of social justice, ensuring that marginalized communities are included in decision-making processes and benefit from green technologies and employment opportunities.
Policy frameworks play a pivotal role in guiding the transition to a sustainable future. Governments worldwide must commit to ambitious emissions reduction targets, evidenced by international agreements like the Paris Accord. Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxing and cap-and-trade systems, can incentivize corporations to reduce their carbon footprints while stimulating green innovation. The political will to implement transformative policies is crucial for catalyzing meaningful change.
Finally, public awareness and education are paramount. Engaging citizens in dialogues about climate change helps demystify the complexities of the science while fostering a culture of accountability. Educational initiatives in schools can cultivate informed generations who are not only aware of the challenges posed by global warming but are also equipped to champion innovative solutions.
In conclusion, global warming is an intricate and pervasive issue that transcends headlines. The science elucidates the formidable challenges we face, yet it also showcases the innovative solutions humanity can harness. By embracing renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency, restoring ecosystems, promoting sustainable agriculture, and implementing equitable policies, we can collectively address this existential threat. The journey ahead may be fraught with challenges, but with collective determination and action, the specter of climate change can be confronted head-on. Are we ready to rise to the occasion?