In the intricate tapestry of our planet’s climate, a looming specter known as global warming casts a long shadow, pervading every corner of the earth and altering ecosystems irreparably. This warming, a result of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, is not merely a distant threat but a present reality, wreaking havoc on the delicate balance of nature. To understand the expansive ramifications of this phenomenon, one must first grasp the fundamental processes at play in our biosphere, where heat, though essential for life, can transform into a harbinger of destruction.
The phenomenon known as climate change is akin to a relentless tide, inexorably eroding the shores of our environment. As atmospheric temperatures rise, glaciers and ice caps, once steadfast sentinels of the polar regions, melt into the sea, contributing to rising water levels that threaten coastal communities worldwide. These regions, teetering on the precipice of inundation, face an uncertain future as saltwater intrudes upon freshwater sources, rendering arable land unfit for cultivation and jeopardizing food security for millions.
In addition to the physical displacement of human settlements, the ecological implications of melting ice are profound. Biodiversity—the variety of life that calls Earth home—finds itself on the brink of extinction as habitats are altered at an unprecedented pace. The polar bears that traverse the thinning ice, emblematic of climate’s impact, are not merely victims of a changing climate; they are a poignant reminder of our own fragility. As species struggle to adapt or migrate, the intricate web of life frays, leading to cascading effects in food chains and entire ecosystems.
Beyond the arctic expanses, rising temperatures manifest in more ominous ways. Savannas, rainforests, and arable fields are increasingly susceptible to droughts, wrought by fluctuating weather patterns and intensified heat. The phenomenon of increased evaporation exacerbates water shortages, forcing entire regions to contend with the specter of desertification. This shift not only strips the land of its richness but also exacerbates the plight of communities reliant on agriculture, placing them in a precarious position where sustenance becomes a daily struggle.
Moreover, the oceans—a vast reservoir of life—bear the dual brunt of warming and acidification, a consequence of absorbing excess carbon dioxide. Coral reefs, known as the “rainforests of the sea,” are transforming into ghostly graveyards. The dazzling arrays of color that once adorned these underwater marvels are dissipating, leaving behind bleached remnants as marine species scramble to find new habitats. The loss of coral reefs signals more than the demise of a habitat; it represents the collapse of a thriving ecosystem that supports countless marine species and provides livelihoods for millions of fishermen and coastal communities.
As climate change reshapes the landscape, extreme weather events emerge with alarming frequency and intensity. Hurricanes, wildfires, and floods have transitioned from anomalies to harbingers of a new normal. These phenomena wreak havoc on infrastructure and ecosystems alike, while simultaneously displacing populations and straining global resources. The economic ramifications of such disasters extend beyond immediate recovery; they reverberate through supply chains and global markets, instigating a cascade of consequences that touch every aspect of human life.
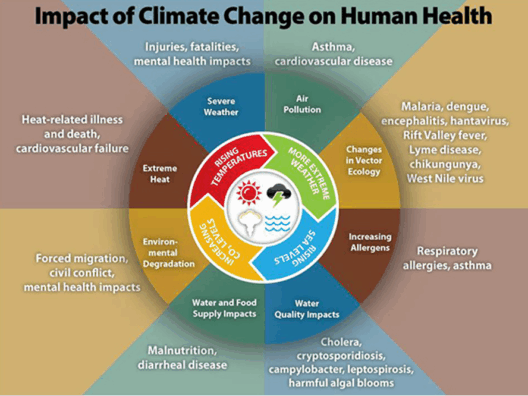
The implications of global warming reach far beyond the immediate physical and environmental changes. These shifts also influence social dynamics and geopolitical stability. Resources deemed scarce—such as water and arable land—become points of contention, igniting conflicts that can destabilize regions and lead to humanitarian crises. Climate refugees, displaced by environmental degradation, are emerging as a pressing issue, requiring a comprehensive global response that acknowledges the intertwined nature of environmental health and human equity.
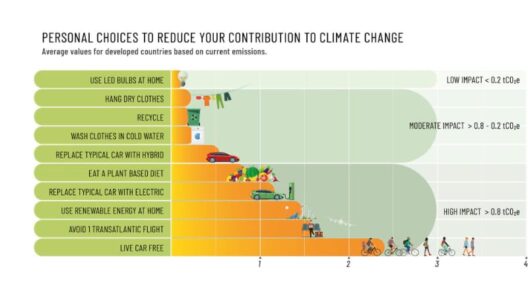
Recognizing the severity of global warming’s impact necessitates a multifaceted approach to mitigation and adaptation. One of the most pressing tasks at hand is the transition toward renewable energy sources. The fossil fuel industry, with its profound carbon footprint, must be complemented and ultimately supplanted by cleaner alternatives—solar, wind, and geothermal energies. This transition not only curtails greenhouse gas emissions but also fosters a more sustainable economy that prioritizes ecological integrity.
Moreover, reforestation and afforestation initiatives present a dual opportunity. Trees act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and enhancing biodiversity. Establishing and restoring forests can revive degraded ecosystems while providing critical habitat for wildlife. These efforts not only help combat climate change but also promote resilience within communities that depend on these ecosystems for their livelihood.
Education and awareness also play a pivotal role in combating global warming. By fostering an environmentally conscious populace, societies can inspire collective action, advocating for policies that prioritize sustainability. Engaging individuals in local conservation efforts can create a ripple effect, empowering communities to take charge of their environmental impact and advocate for systemic change.
Ultimately, confronting global warming requires an intricate understanding of the interconnectedness of natural systems and human activity. This coherent awareness can transform despair into action, as it emphasizes the role we play in either perpetuating harm or nurturing healing. The challenge is significant, but for those who dare to envision a sustainable future, it is an opportunity to forge a path towards environmental stewardship that honors the fragility of our planet. By acknowledging the multifaceted effects of global warming, humanity can rally to mitigate its impact, fostering a renewed relationship with nature and instilling a legacy of resilience for generations to come.