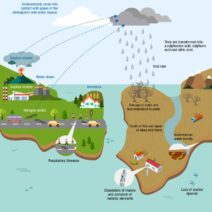
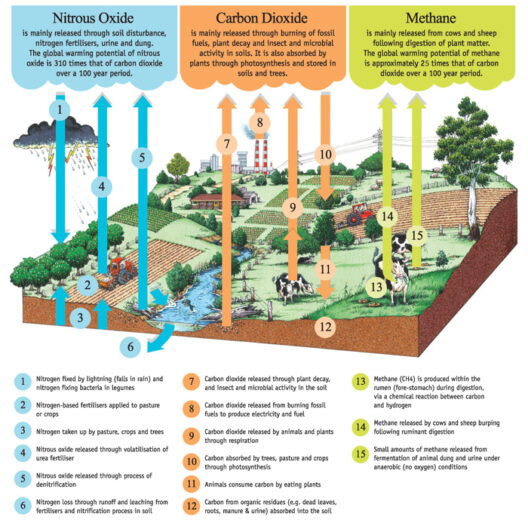
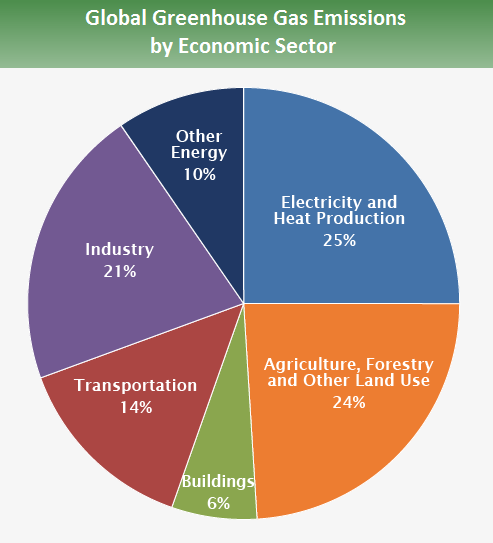
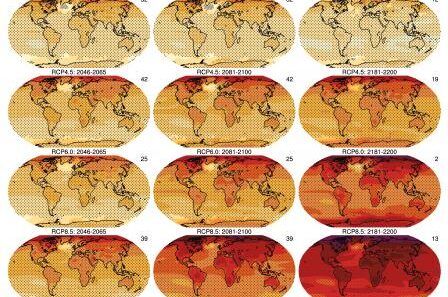
California’s climate is a tapestry woven from a rich interplay of sunshine, moisture, and geographical diversity. It serves as a microcosm for the broader global climate crisis, exhibiting not only stunning natural beauty but also stark contrasts in weather patterns and ecological challenges. As we delve into the nuances of California’s climate map, we uncover the complexity of issues including prolonged droughts, unpredictable weather phenomena, and the overarching impact of climate change.
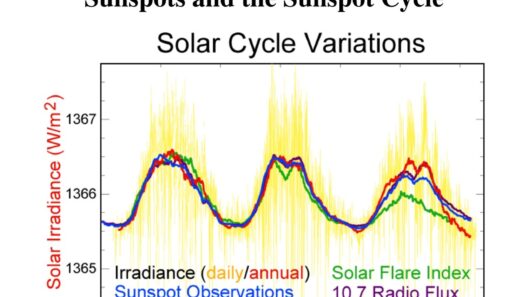
At the heart of California’s climate lies an abundance of sunshine, which the state capitalizes on as a cornerstone of its identity. With an average of over 300 sunny days per year, California has become synonymous with solar energy innovation. The sun-drenched terrain stretches from the pristine beaches of Southern California to the arid deserts and the verdant northern regions. Harnessing this solar potential is paramount as the state seeks to mitigate its carbon footprint and transition towards sustainable energy sources.
However, this abundant sunshine also contributes to the perennial threat of drought. California has long been characterized by its Mediterranean climate, marked by wet winters and dry summers. Yet, climate change has exacerbated these cycles, leading to increasingly severe drought conditions. The frequency and duration of droughts have intensified, resulting in grave consequences for agriculture, water supply, and the ecosystem. Farmers are faced with dwindling water resources, forcing them to adapt by implementing water-saving technologies or shifting crop types altogether.
Droughts in California are now a common narrative, detailing a relentless struggle against water scarcity. Understanding the implications of drought requires an analysis of the interdependent relationship between weather patterns and human activities. The Californian agricultural sector, which produces over a third of the nation’s vegetables and two-thirds of its fruits and nuts, relies heavily on irrigation. Prolonged droughts can cripple this vital sector, resulting in economic ramifications that ripple throughout the state and into the national economy.
The California Climate Tracker tool is a recent advancement designed to provide comprehensive data on the state’s climatic shifts over the last 120 years. This tool equips policymakers, researchers, and the public with vital information to understand trends in temperature changes, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events. By providing insight into these fluctuations, it becomes evident that climate change is not merely a distant threat—it is an ongoing reality that is reshaping the environment.
The mounting evidence of climate change in California is deeply concerning. Increased average temperatures have altered ecosystems, affecting everything from flowering times of plants to the migration patterns of avian species. This phenomenon has highlighted the pressing need for conservation efforts aimed at preserving biodiversity. As habitats are compromised, species face the risk of extinction, underscoring the urgency of protecting California’s rich flora and fauna.
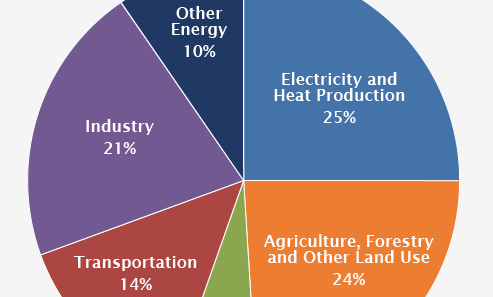
Furthermore, climate change has made the state more susceptible to natural disasters. The frequency of wildfires has surged, culminating in catastrophic events that devastate communities and ecosystems alike. As temperatures rise and vegetation dries out, the risk of fire becomes considerably elevated. The economic costs are staggering, with firefighting efforts and recovery efforts stretching state budgets thin. The impact on air quality can be pervasive, leading to health crises among residents and necessitating comprehensive fire management strategies.
Given the multifaceted challenges that arise from California’s climatic conditions, it is imperative to foster community awareness and engagement in environmental stewardship. Education is crucial in equipping residents with the knowledge and tools required for adaptation. Sustainable practices, such as drought-resistant landscaping, water conservation initiatives, and responsible waste management, can empower communities to mitigate their environmental impact while preserving their quality of life.
The collective response to climate pressures is also an exercise in foresight and innovation. Governments at all levels are tasked with crafting and implementing policies that prioritize climate resilience. This includes investing in infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather, enhancing water management systems, and promoting green technology. By fostering a collaborative approach that engages citizens, scientists, and policymakers, California can build a sustainable future that harmonizes economic growth with environmental preservation.
Looking towards the future, a critical aspect of California’s climate narrative will be its adaptability. As scientists and environmentalists work diligently to address these challenges, the need for actionable solutions becomes increasingly apparent. Whether through carbon capture technologies or the development of sustainable agriculture practices, innovation will be at the forefront of combating climate issues. Together, with an informed citizenry and a proactive government, California can navigate the turbulent waters of climate change and emerge as a leader in environmental resilience.
In conclusion, California’s climate map is a reflection of its complex and dynamic environment. The state’s abundant sunshine, coupled with the stark realities of drought and the repercussions of climate change, creates a narrative that is both inspirational and cautionary. Understanding these interwoven elements is essential for developing strategies that ensure the well-being of its ecosystems, economy, and future generations. As California grapples with its environmental challenges, the call to action is clear: it is imperative to cultivate a culture of sustainability and resilience that honors the delicate balance of nature.