As Earth continues to experience alarming climate fluctuations, an unsettling question arises: Can Earth truly metamorphose into an inferno reminiscent of Venus? This inquiry invites a closer examination of the potential hazards of climate extremes and the lessons from Venus, often referred to as Earth’s “sister planet.” With its scorching climate and unrelenting atmospheric pressure, Venus acts as a cautionary tale about the ramifications of unchecked greenhouse gases. Understanding the mechanisms and consequences of runaway climate change on Venus provides an invaluable perspective on our own planet’s precarious state.
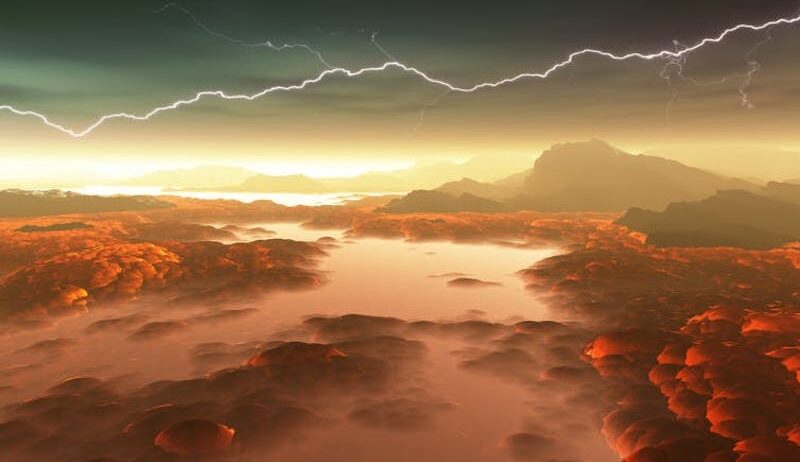
A defining characteristic of Venus is its thick atmosphere, composed predominantly of carbon dioxide, which traps heat through an intensified greenhouse effect. This phenomenon drives surface temperatures to a staggering 900 degrees Fahrenheit (475 degrees Celsius), effectively making Venus the hottest planet in our solar system. By contrasting these conditions with Earth’s more temperate climate, we can better appreciate the delicate balance necessary for sustaining life. The question arises: What threshold must Earth breach to engender irreversible climatic consequences akin to those seen on Venus?
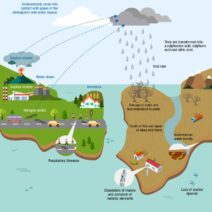
The Earth’s climate is predominantly regulated by a delicate interplay of various factors, including solar energy, atmospheric composition, and oceanic currents. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane have taken center stage in climate discourse, as their increasing concentrations due to human activity threaten to tip this balance. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes contribute to a dramatic uptick in greenhouse gas emissions, overwhelming Earth’s natural carbon sinks.
Consider the concept of positive feedback loops: phenomena where an initial change amplifies the effects of that change, leading to exponential growth. As Earth warms, polar ice melts, reducing the planet’s albedo—the ability to reflect solar energy. Darker ocean waters absorb more heat, causing further warming and even more ice melt. Arctic permafrost, another significant carbon sink, becomes destabilized, releasing methane—a gas far more potent than carbon dioxide—in substantial quantities. These loops evoke the early conditions that led to Venus’s inhospitable atmosphere. The danger lies not merely in rising temperatures but in the compounding effects that can shift a planet’s climate system beyond repair.
To comprehend how Earth could echo the historical transformations of Venus, consider the planet’s tumultuous past. Once thought to possess conditions similar to Earth—a temperate climate and water—Venus underwent a catastrophic transformation. The incessant greenhouse effect led to extreme increases in surface temperature, making liquid water a distant memory. The dense atmosphere created unparalleled atmospheric pressure, capable of crushing submarines before they could even reach the depths of the planet’s surface.
The evolutionary trajectory of Venus serves as a harrowing reminder of the consequences of ignoring climate science. Various studies suggest that our planet is on a similar path. Current global temperatures have already risen approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, compelling humanity to confront the fallout. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts, have become more frequent and severe, suggesting that our climate system is in a state of flux. The very stability of ecosystems that support human civilization hangs in the balance.
But is there a threshold in Earth’s atmospheric evolution past which we cannot return? Scientists assert that moving beyond a global average increase of 2 degrees Celsius could trigger extreme climatic shifts. Tempting as it may be to relinquish hope, understanding the mechanics of climate change both empowers and energizes our fight for preservation. Advocacy for renewable energy sources, sustainable agricultural practices, and enhanced energy efficiency must rise to the forefront of public consciousness. Solutions exist, providing a robust arsenal to combat the unfolding climate crisis.
Transitioning to a renewable energy framework is imperative. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power offer the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and foster a sustainable future. Although these technologies require initial investment and infrastructure development, the long-term benefits reconcile their cost. Moreover, decoupling economic growth from fossil fuel dependency can open avenues for innovation, potentially leading to jobs and a redefined economy that prioritizes ecological integrity.
Equally critical are efforts to nurture and restore natural carbon sinks. Reforestation initiatives, wetland restoration, and sustainable land management practices can significantly counteract the accumulation of greenhouse gases. Protecting and enhancing biodiversity will help ecosystems withstand climatic shifts, ensuring resilience in the face of climatic adversities. Engaging community involvement and fostering a connection to local environments can cultivate a collective ethos rooted in environmental stewardship.
Public awareness and education are essential components in the battle against climate change. Disseminating knowledge about valid scientific research can cultivate informed discourse. Individuals must recognize their agency in affecting positive change, be it through lifestyle adjustments, activism, or policy advocacy. By emboldening grassroots movements, the conversation surrounding climate change can develop into a global campaign demanding immediate and effective action.
While the specter of Earth transforming into Venus casts a shadow over our collective future, it simultaneously implores us to reevaluate our relationship with the planet. Each one of us holds the power to influence the trajectory of our planet’s climate. For humanity’s sake, we must heed the warnings and forge a sustainable path forward, ensuring that the lessons learned from Venus illuminate our journey. The imperative to act is now. Only through decisive and collaborative efforts can we avert the costly and tragic consequences of a climate disaster with consequences reminiscent of our planetary neighbor.