Understanding Earth’s magnetic field is crucial in comprehending the intricacies of our planet’s environmental dynamics. The Earth’s magnetic north pole, which is not a fixed reference point, is shifting due to various geological and geomagnetic processes. This migration has piqued the curiosity of scientists worldwide, especially regarding its potential implications for climate change and global warming. Can the shifting of Earth’s magnetic north genuinely influence temperatures and climate patterns? Let’s delve into this complex relationship.
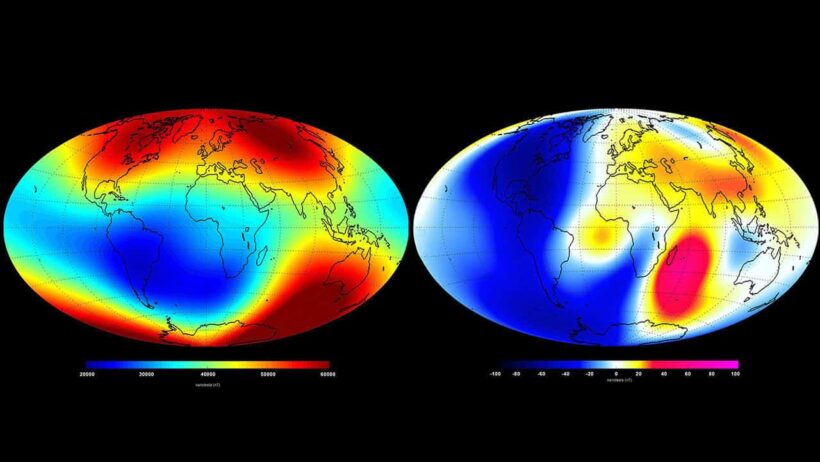
The magnetic field is generated by the movement of molten iron and nickel in the Earth’s outer core, creating a dynamo effect. It protects the planet from solar winds and cosmic radiation, which can have potentially harmful effects on life and technology. As the magnetic north pole moves, it alters the configuration of the magnetic field. This phenomenon has been observed throughout geological history, and its implications extend beyond navigation. However, can it be correlated with climatic changes?
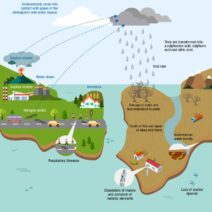
To explore this, it is essential to grasp the fundamental mechanisms underlying climate change. The primary driver of global warming is the greenhouse gas effect, exacerbated by anthropogenic activities such as deforestation, fossil fuel combustion, and industrial processes. As the Earth’s surface temperatures rise, the resulting increase in ocean temperatures leads to a series of environmental repercussions, including rising sea levels, altered weather patterns, and more intense storms.
On the other hand, changes in the Earth’s magnetic field primarily occur over long geological time scales. Nevertheless, the pole’s shift can reveal underlying geological activities, such as tectonic shifts and volcanic eruptions, which can correlate with changes in climate. For instance, volcanic eruptions can inject significant amounts of particulate matter and gases, such as sulfur dioxide, into the atmosphere, influencing climate patterns by reflecting sunlight away from the Earth and cooling the planet temporarily. While these processes can embellish the narrative of climatic shifts, attributing global warming directly to magnetic north shifts remains a speculative endeavor.
Moreover, the relationship between Earth’s magnetic field and climate is further complicated by the cyclical nature of climate changes. Periods of warming and cooling tend to follow natural cycles such as Milankovitch cycles, which involve changes in Earth’s orbit and axial tilt. While these cycles operate independently of the magnetic field, their combined interactions can yield an intricate tapestry of climatic variations. The interplay between these factors raises the question: can magnetic field shifts act as exacerbating agents interacting with these natural cycles?
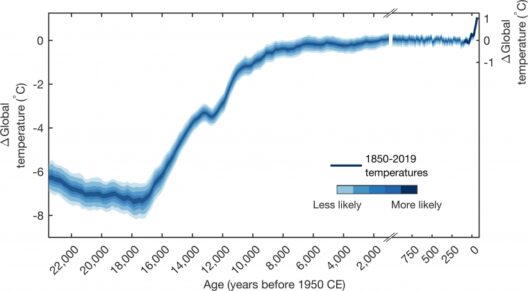
Historically, significant geomagnetic events have coincided with climatic shifts. For example, the Last Glacial Maximum, marked by extensive ice coverage, occurred approximately 20,000 years ago, during a period of fluctuating magnetic intensity. These phenomena underscore the potential for a complex relationship, notwithstanding the inherent limitations of establishing causation. In essence, while the shifting magnetic north may not directly catalyze global warming, it could serve as an indicator of other geological processes which ultimately impact climate.
The conversation surrounding Earth’s magnetic field also enriches our understanding of Earth’s biosphere. The magnetic field has a critical role in shielding the planet from cosmic radiation, a factor influencing the health of living organisms. Increased exposure to cosmic radiation can have detrimental effects on flora and fauna, possibly disrupting ecosystems and biodiversity. Indirectly, any disruption in ecosystems can lead to altered carbon cycles and, consequently, climate impacts. This nuanced perspective encourages a deeper inquiry into the intricate links between geological and ecological systems.
Additionally, as technology evolves, the impacts of the shifting magnetic pole on navigation and communication systems cannot be overlooked. Disruptions caused by the changes in the magnetic field can influence satellite operations, GPS systems, and even power grids. Such issues could lead to economic implications, adding another layer to the discourse about climate change and human adaptability. The economic dimension starkly highlights humanity’s reliance on stable environmental conditions, reinforcing the necessity for sustainable practices and resilience in the face of changing planetary conditions.
Emerging research in geomagnetic studies continues to shed light on the evolving nature of the Earth’s magnetic field. As scientists gather more data, predicting the trajectory and impacts of the magnetic north pole’s shift becomes increasingly feasible. Novel interdisciplinary approaches combining geomagnetism, climate science, and ecological studies can unveil new insights about the connections between magnetic shifts and climate dynamics.
Furthermore, educating the public about the implications of Earth’s magnetic field and its potential correlations with climate change is essential. Cultivating a sense of curiosity and responsibility will ultimately lead to informed decision-making and activism against climate change. Raising awareness about the interplay between Earth’s magnetic dynamics, climatic variables, and human impact on the environment empowers individuals and communities. As our understanding deepens, we stand at the forefront of addressing climate change, ready to honor our planet and foster a sustainable future.
In conclusion, while the shifting of Earth’s magnetic north may not directly cause global warming, it is a vital piece of an intricate puzzle. The implications of magnetic shifts are woven into a larger narrative involving geological activities, climate cycles, and ecological dynamics. Engaging deeply with the interconnectedness of these factors promises to enhance our understanding of the challenges posed by climate change. The path forward hinges upon our capacity to adapt, innovate, and ultimately forge a harmonious existence within the dynamic forces of our planet.