As the dawn breaks over Germany, the landscape unveils itself—a picturesque tableau of rolling hills, lush forests, and quaint villages. Yet, beneath this tranquil veneer lies an insidious threat, quietly poisoning the earth and the air we breathe: acid rain. This phenomenon, often likened to a silent assassin, emerges from the confluence of human activity and atmospheric chemistry. To grasp the severity of acid rain’s toll on Germany, one must delve into its multifaceted causes and far-reaching effects.
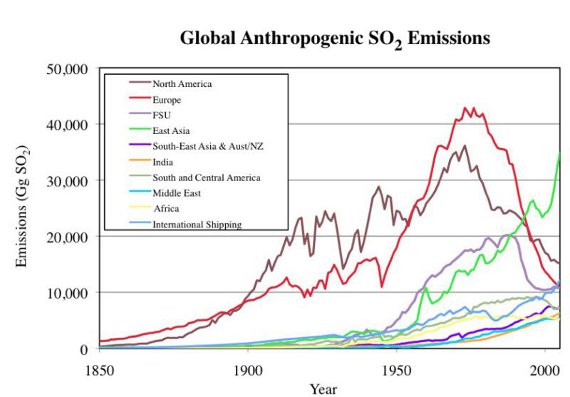
Acid rain is not a mere meteorological curiosity; it is a consequence of our industrialized world. The primary culprits behind this environmental scourge are sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), which are released during the combustion of fossil fuels. Imagine towering smokestacks releasing plumes of smoke that dance like malevolent spirits into the stratosphere. These emissions, sourced from power plants, vehicles, and industrial processes, undergo a chemical transformation in the atmosphere, reacting with water vapor and oxygen to form sulfuric and nitric acids. Subsequently, these acids precipitate back to the earth as acid rain, often arriving in the guise of a gentle shower, yet wielding devastating power.
Germany, as one of Europe’s industrial titans, has not been immune to this fallout. The nation’s reliance on coal, once regarded as the backbone of its energy infrastructure, has led to a surge in sulfur dioxide emissions. The metaphor of coal as the “black gold” of industry belies the dark consequences of its extraction and use. Moreover, with the ascendance of diesel vehicles as a symbol of German engineering prowess, the compounded emissions of nitrogen oxides have exacerbated the dire situation, creating a perfect storm for acid rain formation.
The effects of acid rain unfold like a catastrophic symphony that impacts both the natural and human worlds. The immediate aftermath can be likened to a painter’s brush, carelessly spilling corrosive colors about the canvas of the environment. Forest ecosystems, particularly sensitive to the acidifying effects, suffer as tree roots absorb the toxic rain, leading to nutrient leaching and ultimately tree die-off. A once-vibrant forest can morph into a skeletal remnant of its former glory, a mausoleum for the myriad forms of life that thrived beneath its canopy.
Additionally, soil health deteriorates under the relentless assault of acid rain. Beneficial microorganisms and essential nutrients are washed away, leaving the earth impoverished and lifeless. This process can create a feedback loop detrimental to agriculture; the once-fertile German farmlands, renowned for producing bountiful yields, falter under the weight of acidified soil. Farmers, akin to heavyhearted stewards of a diminishing legacy, may struggle against poor crop yields and increased reliance on chemical fertilizers, further jeopardizing the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
Water bodies are not spared the havoc that acid rain wreaks. Rivers and lakes, once pristine reflections of the sky, become cauldrons of compromised aquatic health. The introduction of acidified waters disrupts the pH balance, endangering fish populations and other aquatic life. Species such as trout, which thrive in stable environments, decline alarmingly in acidic waters, akin to musicians falling silent in a discordant orchestra. The ecological ramifications extend to entire food webs, with the decline of fish threatening the livelihoods of local fishermen and the biodiversity critical to maintaining robust aquatic ecosystems.
Furthermore, human health bears the brunt of acid rain’s indirect consequences. The pollutants that lead to acid rain—sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides—are also significant contributors to atmospheric particulate matter. This corrosion of air quality can exacerbate respiratory conditions, including asthma and bronchitis, creating a public health crisis that reverberates through communities. Here, the metaphor of pollution as an unseen specter looms large, cloaking the citizens in a haze of health risks that are often overlooked until it’s too late.
In response to the growing awareness of acid rain’s devastating implications, Germany has instituted several measures aimed at mitigation. The transition to renewable energy sources, including wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, is akin to a phoenix rising from the ashes of past reliance on fossil fuels. Policies aimed at reducing emissions, such as the European Union’s stringent regulations on air quality, reflect a collective awakening to environmental stewardship. Yet, these efforts require sustained commitment and innovation, for the specter of acid rain beckons as both a challenge and a call to action.
In conclusion, the tale of acid rain in Germany unfolds as a poignant narrative filled with complexities and interconnections. It serves as a stark reminder of the profound impact of industrialization on natural systems and human health. Each droplet of acid rain is a siren song, urging humanity to engage in an ongoing dialogue with nature and to champion sustainable practices that protect our planet. The quest for balance between progress and preservation is fraught with challenges, yet therein lies the unique appeal of our shared responsibility to safeguard the extraordinary beauty and health of our environment for generations to come.