The greenhouse effect is a fundamental phenomenon that plays a pivotal role in regulating Earth’s climate. But have you ever wondered what it would be like if there were no greenhouse gases? Would our planet be the cold, inhospitable sphere floating silently in the dark void of space? This hypothetical scenario proposes an intriguing challenge: understanding how greenhouse gases influence our weather, ecosystems, and overall habitability.
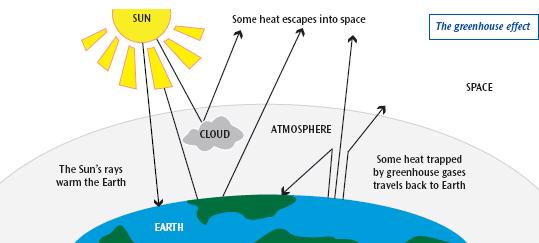
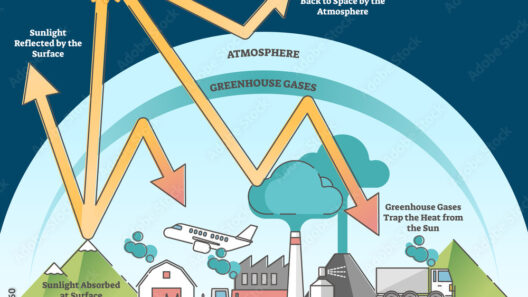
At its core, the greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. Solar radiation from the sun enters the Earth’s atmosphere, some of it being absorbed by the land and oceans while the rest is reflected back into space. However, greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), act like a blanket that traps some of this energy, preventing it from escaping back into space. This trapped energy effectively keeps the planet warm enough to sustain life as we know it.
To comprehend the mechanics of the greenhouse effect, it is essential to delve into the science of radiation. The sun emits energy primarily in the form of visible light and ultraviolet radiation. This energy interacts with the Earth’s surface, which absorbs sunlight and subsequently emits it as infrared radiation, or heat. This is where the greenhouse gases come into play. These gases possess molecular structures capable of absorbing and re-emitting infrared radiation, creating a warming effect—a characteristic referred to as radiative forcing.
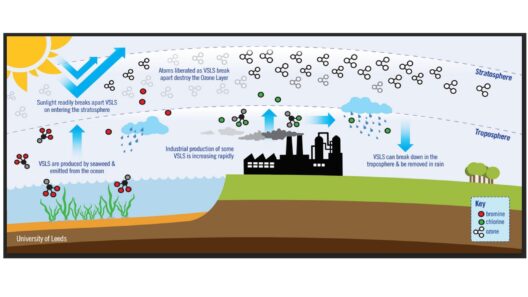
But what happens when the concentration of these greenhouse gases increases dramatically? Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, have introduced an unprecedented amount of CO2 and other potent greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This escalation in greenhouse gas concentrations enhances the greenhouse effect, leading to an increase in global temperatures—a phenomenon better known as global warming.
Global warming, a consequential consequence of the enhanced greenhouse effect, has far-reaching implications for the planet. It induces alterations in weather patterns, resulting in more frequent and severe weather events such as hurricanes, droughts, and extreme heat waves. The drastic shifts in climatic conditions can exacerbate existing vulnerabilities in agriculture, water supply, and biodiversity. As temperatures rise, polar ice caps and glaciers melt, contributing to rising sea levels that threaten coastal communities.
Moreover, the psychological and economic ramifications of global warming are monumental. Communities that rely on agriculture could face devastating crop failures due to changing precipitation patterns. The effects of warming oceans have begun to imperil marine life, disrupting intricate ecosystems and threatening fish stocks that millions depend on for their livelihoods. A reflection on these changes invokes an existential question: how prepared are we to adapt to the unfolding challenges posed by climate change?
In addition to the spatial impacts, the temporal aspect of climate change underscores the urgency of the situation. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has provided clear timelines and projections indicating that we have only a limited window of opportunity to mitigate climate change and safeguard the environment. If the global temperature rise exceeds 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, the consequences could be dire, including the loss of biodiversity and the collapse of ecosystems.
Human action can significantly influence the trajectory of climate change. Implementing stringent policies aimed at reducing emissions, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting renewable energy sources can mitigate the ominous trends associated with global warming. Transitioning to a circular economy, where waste is minimized, and products are reused, can also contribute substantially to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
As individuals, we can play an integral role in combating climate change. Adopting sustainable practices in our daily lives, such as reducing energy consumption, utilizing public transportation, and supporting local, environmentally friendly businesses, can cumulatively have a marked impact. Engaging in advocacy and raising awareness about climate issues within our communities is another crucial aspect of fostering a collective response to this global challenge.
The greenhouse effect is not merely a scientific concept but a vivid illustration of our interconnectedness with the environment. It prompts us to consider how every action has repercussions, reverberating through the atmosphere and impacting future generations. As we stand at a crossroads, the choices we make today will dictate the conditions of tomorrow’s climate.
In sum, understanding the mechanics behind the greenhouse effect is integral to grasping the broader implications of climate change. Its implications radiate through the social, economic, and environmental spheres, urging us to not only comprehend but actively engage in mitigating its effects. Let us confront this challenge head-on, using knowledge as a tool for advocacy and action.
As we ponder our role in this intricate web of life, the clarion call remains: How will we respond to the unfolding saga of climate change? The answer lies within our actions, choices, and unwavering commitment to safeguarding our planet for future generations.