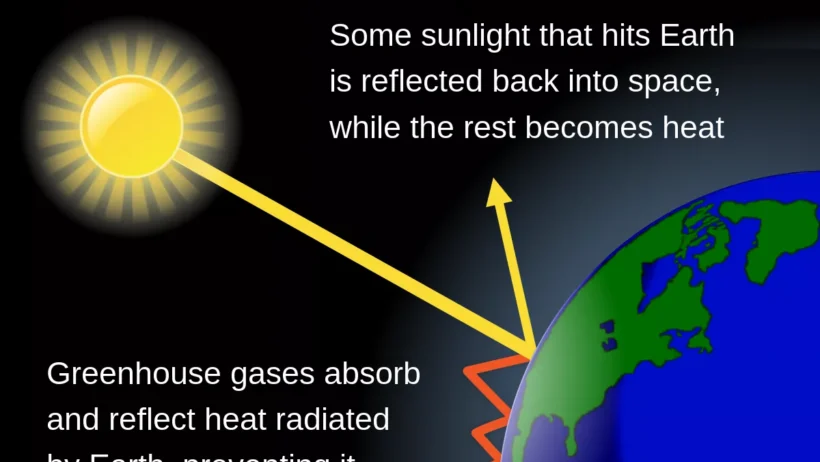
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that allows life on Earth to flourish by maintaining a stable temperature. However, human activities have intensified this effect, resulting in significant alterations to the Earth’s climate. Understanding the intricate dynamics of the greenhouse effect is essential for comprehending the impact of carbon dioxide (CO2) on global warming and climate change.
The greenhouse effect begins with the sun emitting energy towards the Earth. This energy reaches the planet’s surface, where it is absorbed and subsequently re-radiated as infrared radiation. Greenhouse gases, including CO2, methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), are pivotal in trapping some of this outgoing infrared radiation, thereby preventing it from escaping back into space. The balance between incoming solar energy and outgoing infrared radiation determines the Earth’s temperature. Without greenhouse gases, the planet would be inhospitable, with average surface temperatures plummeting to approximately -18°C (0°F).
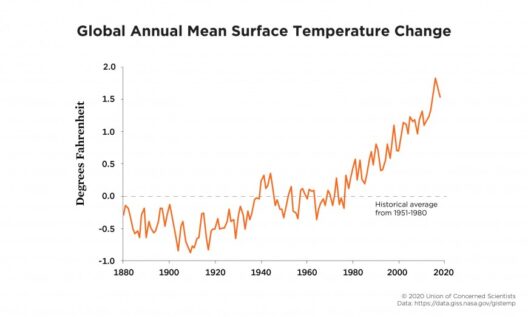
However, the anthropogenic augmentation of CO2 levels due to fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes has led to an enhanced greenhouse effect. In the pre-industrial era, atmospheric CO2 concentrations hovered around 280 parts per million (ppm). Presently, that number has skyrocketed to over 410 ppm, an increase unattested in at least 800,000 years. This rise in CO2 concentration exacerbates the greenhouse effect, leading to higher global temperatures and numerous environmental consequences.
The repercussions of increased greenhouse gas concentrations are manifold. Primarily, they contribute to global warming, which results in climatic perturbations, including more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and altered precipitation patterns. For instance, agricultural sectors face disruptive changes due to unpredictable weather, which may propagate food insecurity. Furthermore, increasing ocean temperatures lead to the bleaching of coral reefs, thereby decimating marine biodiversity.
Aside from CO2, other greenhouse gases also play a crucial role in climate change. Methane, for instance, is more effective at trapping heat than CO2, albeit existing in smaller quantities. Its sources include agricultural practices, livestock farming, and landfills. Similarly, nitrous oxide emitted from fertilizers and various industrial processes contributes to the greenhouse effect. Together, these gases represent a significant threat to the planetary balance and underscore the urgency for substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
Addressing the issues surrounding CO2 and the greenhouse effect necessitates a multifaceted approach. Transitioning to renewable energy sources—such as solar, wind, and hydropower—can drastically curtail CO2 emissions. The shift away from coal and natural gas towards cleaner energy alternatives is imperative for mitigating climate change. Moreover, adopting energy-efficient technologies can bolster efforts to reduce emissions in various sectors, including transportation, industry, and residential spaces.
Moreover, enhancing carbon sequestration methods can mitigate existing atmospheric CO2 levels. Forest conservation and reforestation efforts not only absorb CO2 but also contribute to habitat preservation and biodiversity enhancement. Additionally, innovative agricultural techniques, such as agroforestry and regenerative agriculture, can enhance soil carbon storage while promoting sustainable land management practices.
Public awareness and education regarding the greenhouse effect and CO2’s role are paramount in inspiring collective action. Advocating for policy changes—such as carbon pricing mechanisms—can foster accountability among corporations and individuals alike. Moreover, grassroots movements can galvanize communities to adopt sustainable practices and support initiatives aimed at environmental preservation.
While individual actions are significant, systemic changes are crucial for comprehensive and lasting impact. Governments must implement policies that encourage sustainable development and emissions reduction. International cooperation is essential, as climate change knows no borders and requires a unified global response. Agreements such as the Paris Agreement aim to limit global temperature rise by actively engaging countries in setting measurable targets to decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
In conclusion, decoding the greenhouse effect and understanding CO2’s role in climate change is imperative for safeguarding our planet’s future. The ramifications of enhanced greenhouse gas concentrations are profound, affecting ecosystems, human health, and global economies. Addressing these challenges calls for decisive action on multiple fronts—transitioning to renewable energy, enhancing natural carbon sinks, fostering public awareness, and engaging in robust policy frameworks. Though the path forward may be fraught with challenges, collective action can pave the way for a sustainable and resilient future, ensuring that Earth remains a livable habitat for generations to come.
As the global community grapples with the nuanced complexities of climate change, it is paramount that individuals, organizations, and governments unite in their efforts to mitigate its effects. Embracing sustainable practices and advocating for responsible stewardship of our planet can catalyze transformative change in the fight against global warming. The quest to decode the greenhouse effect is not merely an academic exercise; it is a rallying cry for the existential imperative of our time.