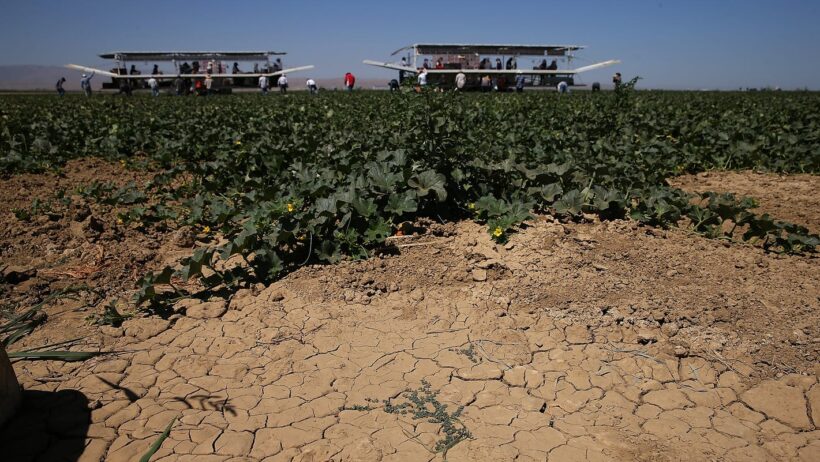
Understanding the relationship between droughts and global warming necessitates an examination of both phenomena independently, followed by their intersection. Droughts are extended periods where water availability falls significantly below the average. In contrast, global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities, predominantly the fossil fuel combustion that results in elevated levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
To identify whether droughts occur as a result of global warming, it’s critical to dissect the different types of droughts: meteorological, agricultural, hydrological, and socioeconomic. Meteorological drought arises from a decrease in precipitation over an extended time span, which can lead to subsequent types of drought. Agricultural drought occurs when the moisture in the soil is insufficient to support crop growth, while hydrological drought relates to the deficits in surface and groundwater resources. Socioeconomic drought integrates the impact of water scarcity on economic and social systems, illustrating how water shortages affect societal functions such as agriculture and industry.
The linkage between global warming and droughts can be elucidated through multifaceted climate models and empirical research. As global temperatures rise, the atmosphere can hold more moisture, modifying precipitation patterns. Certain regions may experience intensified rainfall while others face prolonged dry spells. This results in an inherently paradoxical situation where global warming can exacerbate drought conditions in specific geographic locales even as other areas enjoy wetter conditions. It underscores a crucial aspect: global warming doesn’t create droughts uniformly; instead, it magnifies the geographical variations in drought occurrences.
Studies have shown that climate change has escalated the frequency and severity of droughts in several areas across the globe. One relevant consideration is the phenomenon of heatwaves, which are becoming increasingly prevalent due to rising temperatures. Higher temperatures can intensify evaporation rates, further depleting soil moisture and aggravating the conditions leading to agricultural drought. This connection between elevated temperatures and increased evaporation creates a feedback loop that exacerbates water scarcity.
In California, for instance, a synergy of regional climatic conditions and global warming manifests distinctly in its drought patterns. The state has witnessed formidable multi-year droughts in the past two decades, accompanied by record-high temperatures. Research indicates that human-induced climate change has made the occurrence of such extreme droughts 2 to 3 times more likely than in a pre-industrial climate. The subtleties of this relationship are pronounced, as long-term climatic shifts can fundamentally alter local ecosystems and water availability.
Another important factor to consider is the alteration of seasonal patterns. Climate change influences not only the intensity of rainfall but also its timing. Droughts can ensue if precipitation occurs in more intense, but less frequent bursts, leading to insufficient soil moisture accumulation during critical growing seasons. This non-linear relationship of climate dynamics emphasizes the need for tailored water management practices that account for changing seasonal patterns.
Furthermore, the robustness of water supply systems is increasingly tested under climate-induced pressures. Many regions rely on aquifers and reservoirs that are being depleted faster than they can be replenished. Over-extraction, compounded by the effects of global warming, poses serious challenges. The combination of reduced recharge rates and increased demand for water due to higher temperatures necessitates immediate action in sustainable water management practices.
The influence of anthropogenic activities extends beyond atmospheric changes, reaching into ecology and biodiversity. Prolonged droughts can lead to habitat degradation, threatening the survival of multiple species and disrupting existing ecosystems. The alteration of plant and animal behavior in response to diminishing water sources reinforces the intricate connections between climate systems and biodiversity. Addressing this conundrum requires an integrated approach that combines conservation strategies with climate action.
Additionally, it is paramount to acknowledge that social vulnerability plays a crucial role in the consequences of droughts exacerbated by global warming. Marginalized communities often lack the resources to adapt to shifting climatic conditions effectively. This disparity showcases the intersectionality of climate justice, wherein those least responsible for climate change often bear the greatest burdens. Thus, policies aimed at addressing droughts must incorporate frameworks for social equity and resilience building.
As we peer into the future, the contours of drought intensity and frequency are likely to continue evolving. Adaptive measures must not only address the immediate impacts of drought but also anticipate future patterns arising from ongoing climate change. Implementing innovative agricultural practices, enhancing water conservation technologies, and constructing resilient infrastructure are critical components of a holistic response strategy. Adapting to this new reality, while ensuring the sustainability of natural resources, is essential for preparing for an uncertain climatic future.
In summation, the interplay between global warming and droughts is complex and multifaceted. While global warming does not generate droughts unequivocally, it alters precipitation patterns, evaporation rates, and seasonal dynamics, ultimately magnifying drought conditions in certain regions. Addressing this crisis requires urgent action, comprehensive policy frameworks, and community engagement to forge a pathway toward sustainable futures while affirmatively combating the effects of climate change.