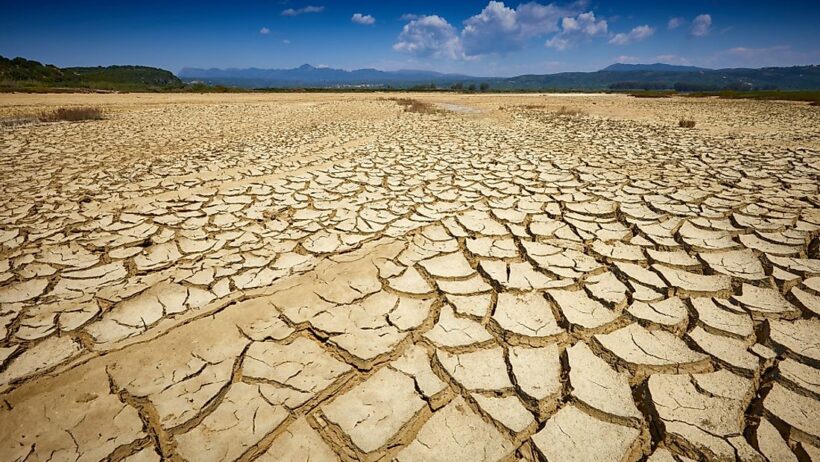
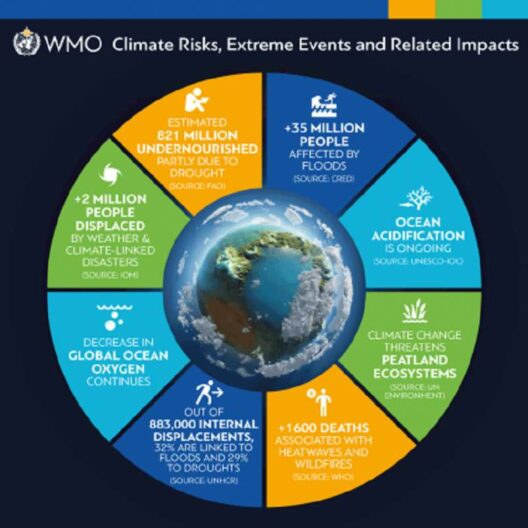
Throughout history, the ebb and flow of natural phenomena have shaped the tapestry of our planet. However, the current discourse surrounding climate change compels us to examine a particularly alarming aspect of this phenomenon: the increasing prevalence of droughts. These parched periods, once seen as sporadic anomalies, are now becoming the norm, challenging our understanding of climate systems and their complex interdependencies. As the climate warms due to anthropogenic influences, the question begs—does climate change cause droughts, and if so, how do shifting climate patterns contribute to increasingly arid conditions?
To fathom the connection between climate change and drought, one must first grasp the intricate components of climate systems. Climate is not a mere backdrop; it is a dynamic, living entity that thrives on the delicate balance of temperature, precipitation, atmospheric currents, and humidity. Each component interacts with the others, existing in a constant state of flux. Thus, when human activities alter the Earth’s climate, the repercussions are manifold, turning once-nurturing climates into inhospitable landscapes.
The metaphor of the orchestra is a fitting analogy for climate—each instrument plays a crucial role in the overall harmony. However, when the temperature rises like a dramatic crescendo, it disrupts this harmony, leading to a discordant symphony. The increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, particularly carbon dioxide and methane, acts as a conductor whose influence can extend across vast regions, causing sustained alterations in weather patterns. These changes manifest as extended dry spells, leaving landscapes thirsting for the revitalizing touch of rainfall. In this context, the orchestration of climate patterns becomes a palpable force driving drought.
One of the hallmarks of climate change is the rise in global temperatures. As heat becomes more concentrated near the Earth’s surface, the water cycle undergoes substantial transformation. Even as rainfall may continue in some regions, the overall evaporation rates increase due to the elevated temperatures. This yin and yang of precipitation and evaporation leads to a situation where even moderate declines in rainfall can precipitate severe drought conditions. The inability of the soil to retain sufficient moisture creates a vicious cycle; plants struggle to survive, agricultural yields dwindle, and communities confront dwindling water supplies.
Climate change does not exert its influence uniformly; it exacerbates existing vulnerabilities. Regions that are already arid, such as the Southwestern United States, face an escalated threat of drought as temperatures soar and precipitation becomes increasingly erratic. This phenomenon can be likened to a magnifying glass focusing the sun’s rays—while the rays may be somewhat benign on their own, their concentration leads to searing effects. For farmers, the ramifications are dire; crop failures and livestock losses contribute to food insecurity and economic instability, creating a ripple effect that reaches far beyond local boundaries.
Moreover, the concept of megadroughts—prolonged droughts lasting decades—has gained traction within scientific circles. These megadroughts, now characterized by their association with climate change, are shifting the very fabric of ecosystems, leading to irreversible alterations. As soil moisture evaporates, plants die, disrupting the food web and endangering local flora and fauna. This devastating cycle can target entire ecosystems, transforming vibrant landscapes into parched expanses devoid of life, resembling barren canvases waiting to be filled again with the brush of rainfall.
Interestingly, the phenomenon of drought is not solely confined to lack of precipitation. Rather, it encompasses an array of interconnected factors that collectively delineate dry conditions. Increased wildfires represent an additional consequence of heightened temperatures and prolonged dry spells, wreaking havoc not just on forested areas, but also on air quality and human health. The interplay between drought and fire reflects a ferocious dance, where the two feed off one another—dry conditions contribute to the ignition and spread of fires, while fires exacerbate drought by consuming vegetation that would otherwise hold moisture in the soil. This grim association cries out for urgent conservation measures and long-term mitigation strategies.
In addressing the pressing issue of drought, we must confront the crux of our reliance on carbon-intensive activities. As fossil fuels and deforestation propel climate change, alternative energy sources and sustainable land management practices prove imperative. Transitioning to renewable energy and improving irrigation techniques are strategies that can mitigate the consequences of climate-induced droughts. Additionally, fostering resilience in communities vulnerable to changing climatic conditions enables a proactive stance against the specters of drought.
The conversation surrounding climate change and its role in exacerbating drought cannot afford to be a tangential discussion; it is foundational to our survival and the health of the planet. The growing incidences of drought underscore the immediate need for collective action—there is no room for hesitation in addressing this existential threat. As we stand at the crossroads of environmental responsibility, we must embrace an ethos of stewardship that recognizes the symbiotic relationship between humans and the natural world. The clock is ticking, its hands moving toward a future that hinges on our choices today.
In summary, climate change serves as a catalyst, facilitating conditions ripe for drought through increased temperature, altered precipitation patterns, and ecological disruptions. As the specter of drought looms larger in our collective consciousness, it becomes increasingly evident that addressing these challenges is not merely an act of environmental concern—it is an ethical imperative. Acknowledging and combatting climate-induced drought will ultimately define our stewardship of the Earth. The droughts we face today are not simply weather patterns; they are harbingers of our future, weaving a narrative that demands our immediate attention and unwavering action.