Climate change is an intricate phenomenon that poses challenges as daunting as they are complex. At its core, it encapsulates the long-term alteration in temperature and typical weather patterns in a place. While many people often conflate climate change with global warming, they are not synonymous. Global warming refers specifically to the increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to rising levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Understanding the relationship between climate change and global warming unravels a tapestry woven from science, policy, economics, and ethics. Through this exploration, we can gain a deeper appreciation of the underlying dynamics, enabling more informed discussions and decisive actions against this pressing issue.
The connection between climate change and global warming can be traced back to the greenhouse effect, a natural process essential for life as we know it. Solar energy reaches the Earth’s surface, is absorbed, and then radiated back into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), trap some of this outgoing radiation, effectively keeping the Earth warm enough to support ecosystems. However, human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes have dramatically intensified this effect, leading to an increase in global temperatures. The resultant warming influences the climate system extensively, thereby interlinking climate change with global warming.
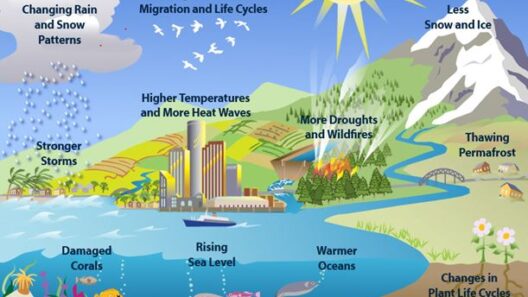
Over the past century, the Earth has experienced a significant rise in average temperatures, largely attributed to anthropogenic influences. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has provided compelling evidence indicating that the global temperature has increased by approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century. This seemingly modest rise conceals profound ramifications: melting polar ice caps, rising sea levels, and an increase in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events. These consequences serve as stark reminders of how intricately linked climate change and global warming are.
The implications of global warming extend far beyond mere temperature increases. Ecosystems around the globe face unprecedented challenges. For instance, coral reefs—often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea”—are particularly sensitive to temperature changes. Even a modest rise in sea temperature leads to coral bleaching, a phenomenon that threatens marine biodiversity. Additionally, terrestrial ecosystems are shifting; flora and fauna are attempting to adapt to new temperature regimes, leading to altered habitats and, in many cases, extinctions. This shifting biological landscape emphasizes the urgency of recognizing the connection between climate change and global warming.
Moreover, the socio-economic effects of climate change cannot be overlooked. Vulnerable populations, particularly those in developing nations, are disproportionately affected. As climate systems become more volatile, agricultural yields may falter, leading to food insecurity. Droughts and floods exacerbate existing inequalities, creating a cascade of economic challenges, migration pressures, and humanitarian crises. These repercussions highlight the intersection of environmental and social justice, urging us to reconsider our approach to both climate policy and governance.
It is imperative to grasp that combating climate change necessitates a multifaceted approach. Mitigation strategies, which aim to reduce and stabilize the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, must be prioritized. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable land use practices are vital steps towards mitigating the effects of global warming. Additionally, adaptation strategies are equally crucial. These measures focus on strengthening our resilience to the ongoing impacts of climate change, such as constructing flood defenses, developing drought-resistant crop varieties, and enhancing water resource management.
The intersection of technology and policy offers promising avenues for addressing the challenges posed by climate change and global warming. Innovations in carbon capture and storage technologies present exciting potential for reducing atmospheric CO2 levels. Policymakers must also engage with scientific communities to ensure that robust, evidence-based policies are implemented at local, national, and global levels. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, reflect an acknowledgment of the necessity for global cooperation in combating climate change. These accords not only illustrate commitment but also establish frameworks for accountability and progress towards shared goals.
The question of climate change and global warming inevitably leads to a critical examination of individual and collective responsibilities. Every action, from reducing waste to advocating for sustainable practices, contributes to the larger narrative. Societal engagement, whether through grassroots movements or educational outreach, plays a pivotal role in fostering awareness and catalyzing change. Together, communities can drive larger systemic shifts towards sustainability, which can effectuate tangible change in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Recognizing the connection between climate change and global warming encourages a shift in perspective, transforming challenges into opportunities for innovation and collaboration. As much as these issues present a formidable obstacle, they also ignite curiosity and drive a collective response. In understanding the interconnectedness of our climate systems and societal structures, we can forge paths that not only mitigate adverse effects but also promote a more harmonious existence with our planet. The journey toward climate resilience is daunting, yet it is one that is rich with potential, inviting us all to partake in the pursuit of a sustainable future.
Ultimately, to navigate the complexities of climate change and global warming, an informed and proactive approach is essential. By embracing interdisciplinary strategies, fostering innovation, and advocating for justice, society can mobilize towards a healthier planet for future generations. The dialogue on climate change must remain dynamic, evolving as our understanding advances, ensuring that the narrative continues to inspire curiosity and collective action.