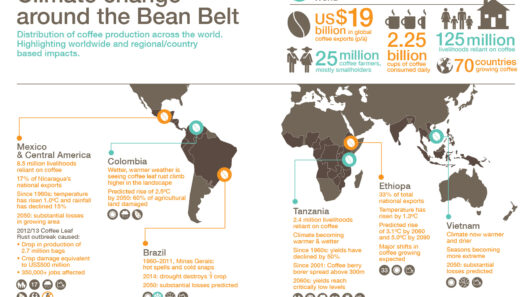
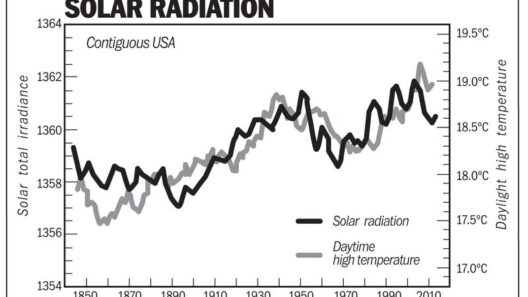
The discourse surrounding electricity usage and its impact on global warming has garnered considerable attention in recent years. As nations industrialize and technology proliferates, the demand for electricity continues to rise exponentially. However, less visible are the consequences of this escalating consumption, particularly in relation to climate change. Understanding the nexus between electricity generation and global warming is paramount in fostering a sustainable future.
Electricity is predominantly generated through the combustion of fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas. These fuels release carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere when burned, contributing to the greenhouse effect—a phenomenon that traps heat and leads to a warming planet. This intricate interplay demonstrates that our reliance on conventional electricity generation methods is inherently linked to climate change. Moreover, the power sector is one of the largest sources of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions globally.
With the energy sector accounting for a significant portion of global emissions, the imperative for a transition to renewable energy sources has never been more pressing. Renewable energy, derived from natural processes that are replenished at a faster rate than they are consumed, includes solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy. These sources generate electricity without producing direct greenhouse gas emissions, presenting a viable pathway toward reducing our carbon footprint.
One cannot overlook the role of energy efficiency in mitigating the climate impact of electricity consumption. Energy-efficient appliances, lighting, and industrial processes reduce the amount of electricity required to deliver the same level of service. This is critical, as a decrease in electricity demand lessens the burden on power plants, many of which remain reliant on fossil fuels. Research demonstrates that merely improving energy efficiency within homes and businesses can lead to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, reinforcing the notion that how we use electricity matters as much as how it is generated.
While the transition to renewable energy and enhanced efficiency are paramount, the conversation surrounding electricity usage and global warming must also address behavioral factors. Consumer habits, societal norms, and cultural perspectives on energy consumption play a substantial role in shaping electricity demand. For instance, the increasing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) has the potential to curb emissions from the transportation sector. However, the overall impact of EV adoption is contingent upon the electricity used to charge these vehicles. If the charging infrastructure predominantly relies on fossil fuels, the intended benefits may be undermined, thus illustrating the intricate relationships among technological advancements, energy sources, and consumer behavior.
Furthermore, complex socio-economic factors influence energy consumption patterns. In developed nations, individuals often enjoy high levels of energy consumption, leading to greater per capita emissions. Conversely, in developing countries, access to electricity may be limited, resulting in lower emissions overall. However, as these countries strive for economic growth, the demand for electricity is likely to increase, potentially leading to heightened greenhouse gas emissions if sustainable practices are not prioritized during this development phase.
Education and awareness are crucial elements in driving responsible electricity usage. By fostering an understanding of the environmental implications associated with electricity consumption, individuals are empowered to make informed choices. Awareness campaigns can galvanize community action towards energy-efficient practices, such as utilizing public transport, adopting renewable energy technologies, and advocating for policies that support sustainable energy systems. Each action, no matter how small, can contribute to a collective impact, amplifying the urgency of the climate challenge.
Policy frameworks also play an indispensable role in shaping the future of electricity generation and consumption. Governments can implement regulations that promote cleaner energy sources, provide incentives for energy efficiency upgrades, and support research and development in innovative technologies. Nationally and internationally coordinated efforts to address climate change can create a transitioning landscape where electricity fuels economic growth sustainably.
Investing in infrastructure is another pivotal element in steering energy consumption towards a more sustainable trajectory. The development of smart grids, which enhance the efficiency and reliability of electricity distribution, facilitates better integration of renewable energy sources and can minimize transmission losses. Such advancements not only help stabilize energy costs but also fortify the resilience of energy systems against the growing impacts of climate change.
Finally, it is essential to recognize the interconnectedness of global systems. Climate change knows no borders; therefore, international cooperation is vital in combating its perils. Global initiatives, such as the Paris Agreement, underscore the shared responsibility of nations to reduce emissions and promote sustainable practices. Collaboration among countries, sectors, and communities can lead to innovative solutions, fostering a more sustainable future for generations to come.
In conclusion, the unequivocal link between electricity usage and global warming necessitates a multifaceted approach. Powering our planet responsibly involves not only transitioning to renewable energy sources and enhancing energy efficiency but also addressing behavioral nuances, socio-economic considerations, and policy frameworks. By fostering awareness, improving infrastructure, and promoting international cooperation, we can navigate the delicate interplay between electricity consumption and a changing climate. Ultimately, a collective commitment to sustainable practices is paramount in mitigating the adverse effects of global warming, ensuring a livable planet for future generations.