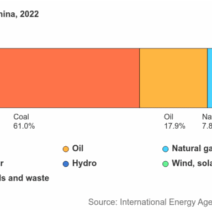
In recent years, discussions about climate change have permeated various spheres of society, gathering a cacophony of opinions. The reality of global warming, however, transcends mere conjecture. Numerous studies and observations illustrate a persistent increase in global temperatures, profoundly impacting ecosystems, weather patterns, and human societies. This exploration delves into the existence of global warming, examining the scientific evidence, its implications, and the various perspectives surrounding this pressing issue.
One of the cornerstones of climate science is the greenhouse effect. A fundamental process that sustains life on Earth, it occurs when certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun. This is a natural phenomenon, crucial for maintaining a habitable climate. However, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, have exacerbated this effect by significantly increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases. Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) are principal contributors. Their heightened presence acts like a thickening blanket, preventing heat from escaping back into space.
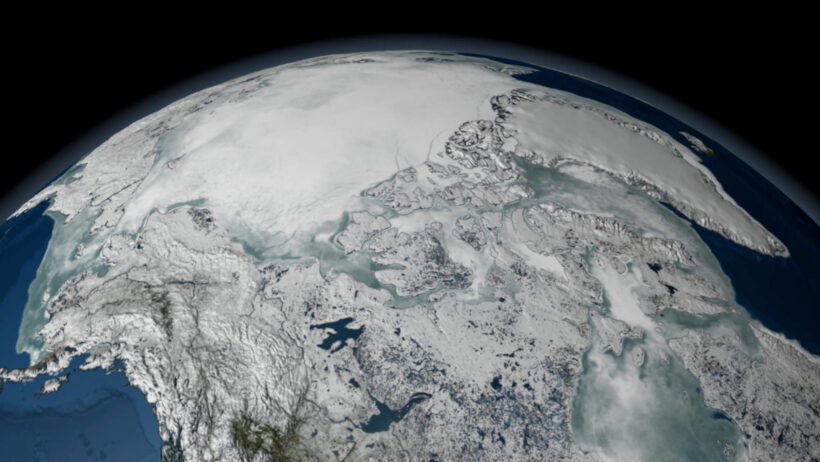
Over the past century, we have witnessed a staggering rate of change. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports that the global temperature has risen by approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial times. Although this figure may seem deceptively small, its ramifications are monumental. Even slight temperature increases can lead to significant alterations in weather patterns, coral bleaching, and glacial melting. The direct correlation between anthropogenic activities and climate change is increasingly evident.
One cannot overlook the implications of global warming on natural disasters. The frequency and intensity of hurricanes, droughts, and floods are increasing, wreaking havoc on communities worldwide. The changing climate disrupts long-established weather patterns, leading to unpredictable and often catastrophic events. For instance, the devastating wildfires in California and Australia illustrate how exacerbated heat and drought conditions give rise to unprecedented fire seasons. These calamities inflict severe economic damage and displace countless individuals, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive climate action.
Beyond environmental consequences, global warming possesses dire implications for biodiversity. Ecosystems face unprecedented stress levels as species struggle to adapt to rapidly changing habitats. A multitude of species are at risk of extinction as their natural environments shift and fragment. Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are particularly vulnerable. The rise in ocean temperatures leads to coral bleaching, which, in turn, endangers the myriad of marine organisms that depend on reefs for sustenance and shelter.
Temperature increases also exert profound effects on agricultural practices. Changes in precipitation patterns and the prevalence of extreme weather conditions impact crop yields, threatening food security. Regions that have historically been fertile may become arid, while others may experience flooding. Adaptation strategies for farmers are crucial; however, the transition can be arduous and costly, particularly for smallholder farms in developing countries. The intersection between global warming and food production raises pressing questions about equity, sustainability, and global collaboration.
In addition to these tangible impacts, global warming evokes public sentiment and polarizes opinions. Skepticism remains prevalent, with some individuals questioning the validity of climate science. This skepticism can stem from various sources, including misinformation and vested interests. However, the overwhelming consensus among climate scientists affirms that global warming is a reality. It is essential to address the root causes of disbelief, presenting clear, comprehensible scientific evidence that demystifies the complexities of climate science.
Discourse surrounding climate change is rich and multifaceted. Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectricity emerges as a pivotal solution to mitigate the impacts of global warming. Investments in clean technologies and infrastructure can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Policymakers, industries, and citizens alike have vital roles to play in this transition. Advocacy for sustainable practices, conservation initiatives, and environmental legislation are essential components of an effective response to climate change.
Moreover, community engagement and education are crucial in fostering a proactive approach to climate action. Grassroots movements, local initiatives, and collaborative projects can spur significant changes at the community level. Empowering individuals to make informed choices promotes a collective commitment to sustainability, enabling communities to become resilient against the adverse effects of a warming planet.
As the evidence mounts, the question of whether global warming exists evolves into one of action. Climate change is not an abstract concept reserved for scientific discourse; it is a present-day reality that we cannot ignore. The urgency for decisive action to combat global warming has never been more pronounced. Through collective effort, innovation, and an unwavering commitment to sustainability, we can navigate this critical juncture and safeguard the planet for future generations. Whether through policy changes or individual behaviors, every action counts in the fight against climate change, and the time to act is now.