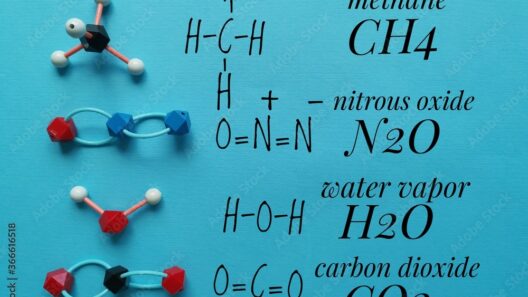Solar energy, akin to an infinite tapestry of light woven by the cosmos, plays a pivotal role in the intricate ballet of Earth’s atmosphere. As solar rays cascade down, they engage in an elaborate interplay with the atmosphere, affecting weather patterns, climate systems, and even the fundamental physics of life. To understand how solar energy interacts with Earth’s atmosphere, it is crucial to delve into the layers of this unseen symphony.
The atmosphere is not merely a blanket enveloping the Earth; it is a dynamic interface where solar energy meets the intricate dance of molecules and particles. This interaction can be likened to a grand orchestra, where sunlight serves as the conductor, guiding various components to produce melodies of temperature changes, winds, and precipitation.
The essence of solar energy lies in its dual nature—part transformational energy as it lights up our days, and part passive energy as it warms our planet. The first engaging phenomenon to consider is how solar radiation enables the greenhouse effect, needed for sustaining life.
The Dance of Solar Radiation: How Sunlight Enters the Atmosphere
When solar radiation reaches the Earth, it encounters the atmosphere, which consists of numerous layers enriched with gases, aerosols, and water vapor. This celestial embrace governs how much energy is absorbed or reflected back into space. Approximately 30% of incoming solar energy is reflected by clouds, aerosols, and the Earth’s surface, while the remaining 70% is absorbed.
This absorption process is critical; it warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth, giving rise to weather phenomena. Picture the Earth as a lively theater stage, with sunlight acting as the spotlight illuminating actors—clouds, wind, and rainfall—who perform their roles in ever-changing synchrony. The absorbed sunlight catalyzes various atmospheric processes, initiating the water cycle and influencing local and global climates.
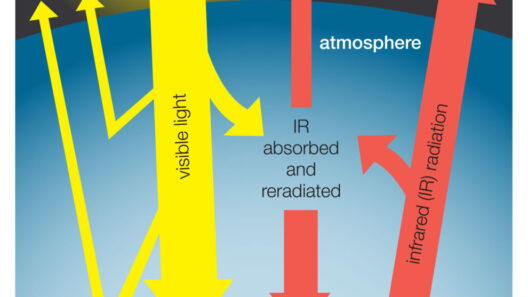
Moreover, the wavelength of solar radiation plays an essential role in this interaction. Ultraviolet (UV) rays have short wavelengths and are potent, responsible for the heating of the atmosphere and the ionization of gases. On the other hand, infrared (IR) radiation, with its longer wavelengths, carries warmth and is essential in regulating temperatures, culminating in what we colloquially term the “greenhouse effect.”
The Greenhouse Effect: An Essential Blessing or a Double-edged Sword?
The greenhouse effect can be envisioned as a cozy blanket wrapping around the planet. It keeps Earth warm enough to sustain life, yet it can also become a detriment if overburdened by anthropogenic influences. Solar energy, when trapped by greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, leads to a warming of the Earth, a phenomenon that is magnified by human activities like fossil fuel combustion and deforestation.
As solar energy enters the atmosphere, it resonates within this greenhouse layer. The solar energy, converted into heat, is absorbed by the Earth’s surface, only to be re-emitted as infrared radiation. However, instead of escaping back into the vastness of space, the greenhouse gases ensnare this heat, leading to an equilibrium that is continually shifting. It is in this delicate balance that we find ourselves at a crossroads—either nurturing this equilibrium through sustainable practices or propelling ourselves toward an era of climatic upheaval.
The Ultimate Feedback Loop: Solar Energy and Climate Change
The relationship between solar energy and climate is richly complex and fraught with feedback loops that can amplify or mitigate climate processes. As global temperatures rise due to excessive greenhouse gas emissions, the behavior of atmospheric phenomena shifts; for instance, warmer air can hold more moisture, leading to more intense storms and altered precipitation patterns.
In this metaphorical ecosystem, consider solar energy as the seed, climate change as the twisted vine, and our atmosphere as the garden. If left untended through negligence, the vine spreads uncontrollably, choking the delicate plant-life. Conversely, with careful cultivation—investments in renewable energy, reforestation, and carbon capture—the garden can bloom vibrantly, ensuring ecosystem resilience.
Furthermore, changes in solar energy absorption due to anthropogenic alterations on the Earth’s surface, such as urbanization and land-use changes, illustrate another layer of complexity. Urban areas, with their high albedo surfaces and heat-absorbing materials, can create urban heat islands that disrupt local climatic patterns, further convoluting the solar-atmosphere interactions.
In conclusion, exploring how solar energy interacts with the Earth’s atmosphere unveils a captivating narrative of balance, complexity, and responsibility. Like a masterful painter wielding a brush, humanity holds the potential to create a luminous future grounded in sustainable energy practices. The task ahead is daunting yet invigorating. By understanding and appreciating the symphony between solar energy and our atmosphere, we can play our part in orchestrating a harmonious existence with our planet, ensuring it remains vibrant for generations to come.