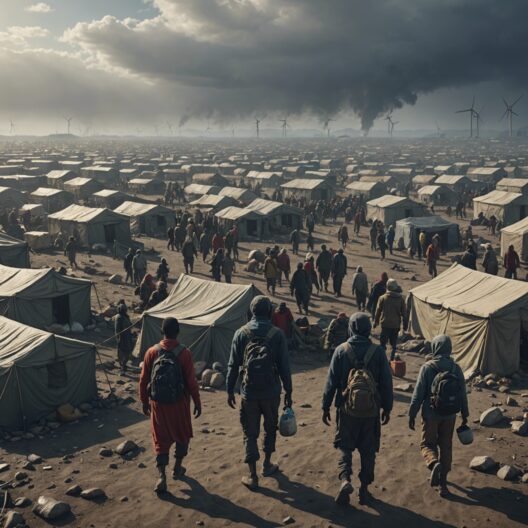
Global warming has accelerated alarmingly over the past century, primarily attributable to anthropogenic activities, particularly the combustion of fossil fuels and deforestation. These actions significantly exacerbate greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). The implications of global warming extend far beyond mere temperature rises; they infiltrate ecosystems, economies, and our daily lives in complex and multifaceted ways.
To appreciate the ramifications of global warming, one must first understand its mechanism. The Earth’s atmosphere functions similarly to a greenhouse, trapping solar radiation to sustain life. However, an excess of greenhouse gases creates an enhanced greenhouse effect, leading to a rise in average global temperatures. This seemingly innocuous increase conceals a Pandora’s box of consequences that merit thorough exploration.
First and foremost, the escalation of temperature plays a paramount role in influencing weather patterns. With rising global temperatures, we witness an increase in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events. Hurricanes, droughts, floods, and heatwaves are becoming more common, disrupting local ecosystems and human habitats alike. For instance, the unprecedented hurricane seasons of recent years have wreaked havoc, leading to extensive damage and loss of life.
Moreover, global warming induces changes in precipitation patterns, leading to arid conditions in some regions while others experience excessive rainfall. This equilibrium disruption adversely affects agriculture, compromising food security worldwide. Predictions project that yields of staple crops may decline as fluctuating temperatures and erratic rain patterns hinder their growth. Consequently, this could lead to escalating food prices and heightened instances of hunger and malnutrition.
In addition to agricultural concerns, global warming directly impacts biodiversity. As temperatures rise, many species struggle to adapt to their new environments, leading to alterations in natural habitats and migration patterns. Some flora and fauna may thrive in warmer conditions, while others face extinction. The loss of biodiversity not only disrupts ecosystems but also diminishes the potential for discovering new medicinal resources vital to human health.
An alarming consequence of global warming is the phenomenon of glacial melt. Polar ice caps and glaciers are retreating at unprecedented rates, contributing to rising sea levels. This metamorphosis poses significant threats to coastal communities that are increasingly vulnerable to flooding and erosion. Cities such as Miami and New Orleans are already grappling with these challenges, while countries such as Bangladesh face existential risks, where millions may be displaced due to persistent inundation.
Further compounding the issue, global warming alters oceanic conditions. Increased temperatures lead to ocean warming and acidification, phenomena that drastically affect marine life. Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” exhibit profound sensitivity to temperature changes. Coral bleaching, resulting from elevated sea temperatures, has become a prevalent concern, threatening biodiversity hotspots and the livelihoods of communities reliant on fishing and tourism.
A transition to a warmer climate also has socio-economic repercussions that extend to human health. As temperatures rise, incidences of heat-related illnesses are expected to surge, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions. Furthermore, the spread of vector-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue fever may escalate as the habitats of mosquitoes expand due to changing climatic conditions.
In addressing these multi-dimensional consequences, it is imperative to recognize the interconnectedness of systems. Global warming does not solely influence environmental aspects; it propels socio-economic disparities exacerbated by climate change-induced migration. Populations in vulnerable regions may be compelled to relocate, leading to tensions over resources, altered demographics, and potential conflicts.
However, amid these challenges lies an opportunity for collective action. Adopting a proactive approach to mitigate global warming can yield substantial benefits. Transitioning to renewable energy sources—such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power—can reduce dependency on fossil fuels and diminish greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, implementing energy efficiency measures can conserve resources, decrease emissions, and lower utility bills, creating a win-win scenario for both the economy and the environment.
Individual actions also contribute significantly toward combatting global warming. Simple lifestyle changes—such as reducing meat consumption, utilizing public transportation, and minimizing waste—can collectively lead to a substantial impact. Education and advocacy play crucial roles in galvanizing communities around this pressing issue, creating a culture of sustainability and environmental consciousness.
In conclusion, the consequences of global warming are profound and far-reaching, with implications that resonate through ecosystems, economies, and human health. While the challenges may appear daunting, they present an invaluable opportunity for transformation. Embracing sustainable practices and fostering a collective commitment to mitigate climate change can engender a more resilient and equitable future. The time to act is now; the fate of our planet hangs in the balance.