Global warming represents one of the most formidable challenges faced by humanity. As the planet warms, the consequences extend beyond mere temperature increases; they infiltrate ecosystems, human health, and global economies. This discourse will delve into the grim predictions associated with global warming, exploring timelines, impact scenarios, and the urgency for comprehensive action.
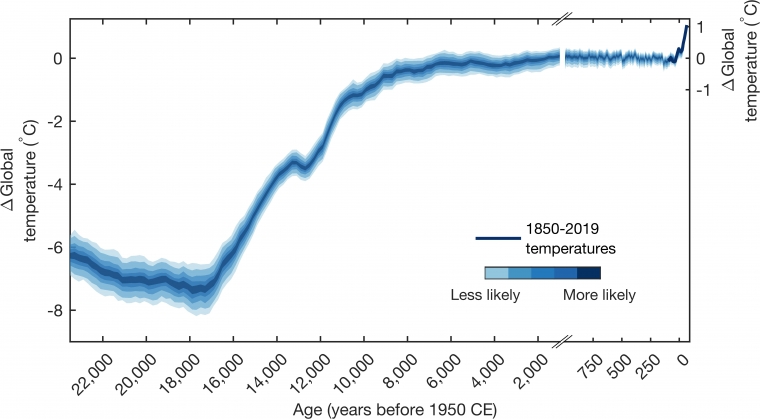
To begin with, it is essential to understand the fundamental mechanisms contributing to global warming. The primary driver is greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2) from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes. These gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, consequently leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect. The result has been an unprecedented rise in global temperatures over the last century, with the last decade being the warmest on record.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has provided numerous models predicting temperature rises under varying greenhouse gas emission scenarios. If emissions continue unabated, we could witness a catastrophic increase in global temperatures by 2°C or more above pre-industrial levels by 2040. This benchmark, while seemingly modest, holds dire implications. An increase of 2°C will precipitate catastrophic events such as intensified storms, droughts, and floods, which will consequently lead to food and water scarcity, displacement of populations, and unprecedented economic disruption.
One of the most alarming predictions concerns the effect on polar regions. The Arctic is warming at more than twice the rate of the global average. As ice melts, not only does it contribute to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities worldwide, but it also exacerbates climate change by reducing the Earth’s albedo effect. This phenomenon results in further warming, creating a feedback loop that hastens the degradation of our planet’s climate systems.
Additionally, the impact on biodiversity is profound. Ecosystems are facing a barrage of stresses due to warming temperatures and shifting climatic zones. Many species are already at risk of extinction. Coral reefs, often dubbed the rainforests of the sea, are experiencing mass bleaching events. The loss of biodiversity undermines ecosystem resilience and disrupts food chains, posing a direct threat to human livelihoods reliant on these systems.
Furthermore, as temperatures escalate, public health challenges escalate concomitantly. Heatwaves become more frequent, leading to heat-related illnesses and exacerbating chronic conditions. Air quality diminishes with increased ozone levels during warmer months, presenting respiratory challenges, especially for vulnerable populations. Vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, may spread to new regions, demonstrating the interconnected nature of climate change and public health.
Numerous studies have modeled the economic implications of unchecked global warming. A rise in global temperatures could fundamentally alter economic structures. The agricultural sector, which relies on stable climate conditions, faces drastic shifts in crop viability. Economic losses from climate-related disasters could reach trillions of dollars annually. Vulnerable communities bear the brunt of these impacts, with developing nations suffering disproportionately, fortifying existing social inequalities.
In terms of timelines, scientists have outlined various scenarios. If greenhouse gas emissions are curbed aggressively, we might limit warming below 1.5°C, thus mitigating some of the worst outcomes. However, without immediate and systemic change, the trajectory points towards increasingly severe consequences. Should we fail to act decisively, scenarios predict possible collapse of global systems by the end of this century.
Public sentiment is a pivotal factor in combating climate change. Movements advocating for sustainable practices, renewable energy adoption, and conservation efforts are burgeoning worldwide. The youth climate movement exemplifies a burgeoning awareness among younger generations of the cohort compressing the timeframes for action. Their cries for accountability echo through social media platforms and international forums, urging leaders to prioritize environmental sustainability.
Governments play a critical role in this paradigm shift. Policy decisions, such as participating in international agreements like the Paris Accord, can galvanize national and global efforts towards emission reductions. The transition to renewable energy sources is paramount—solar, wind, and hydroelectric power present sustainable alternatives that can supplant reliance on fossil fuels.
Moreover, innovative technologies promise to play a crucial role in mitigation efforts. Carbon capture and storage technology can potentially reduce atmospheric CO2 levels while advances in energy efficiency can minimize electricity consumption. Investments in green infrastructure can create resilient urban environments equipped to handle the impacts of climate change.
Ultimately, the question “How long until we all die?” is not merely a grim forecasting statement, but a galvanizing call to action. While the ramifications of unchecked global warming are dire, the narrative is not yet fully written. Our collective actions today determine the world we inhabit tomorrow. Awareness, advocacy, and innovation are essential to reversing trends and fostering a sustainable future.
In summation, global warming poses an existential threat that demands immediate and concerted efforts. While projections paint an ominous picture of a rapidly warming world, resilience against these threats is within our grasp. The time for action is now, and it beckons a united front to combat climate change with urgency, integrity, and resolve. The fate of future generations hinges on our choices today. Let us forge a path towards sustainability and equity, ensuring not only survival but the flourishing of humanity and the natural world.