Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are a vital yet often overlooked component in the discourse surrounding climate change. These invisible culprits, though unperceived by human senses, play an outsized role in the planet’s thermal dynamics. Delving deeper into their nature, sources, and profound implications reveals a complex narrative that demands our attention and action.
At its core, the greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. When the sun’s energy reaches our atmosphere, some is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases. This process maintains the Earth’s temperature at a level conducive to life. However, an unprecedented accumulation of GHGs in the atmosphere, largely due to anthropogenic activities, has intensified this effect, leading to global warming.
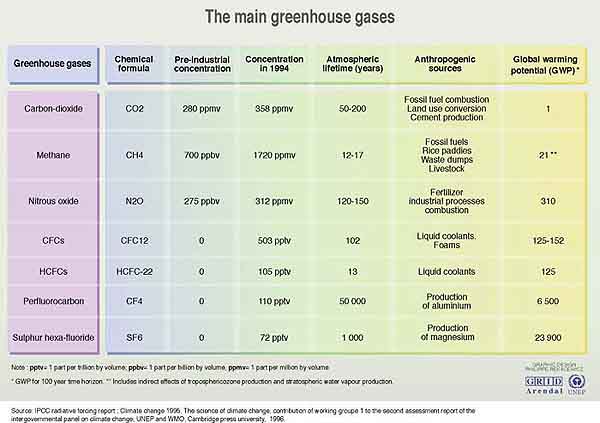
Understanding the various types of greenhouse gases is crucial. Carbon dioxide (CO2), a primary GHG, arises predominantly from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and various industrial processes. Methane (CH4), another significant player, emanates from agricultural practices, waste management, and the decay of organic matter under anaerobic conditions. Nitrous oxide (N2O), while less abundant, is far more potent as it can trap heat in the atmosphere more effectively than CO2. Lastly, industrial gases, including hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and perfluorocarbons (PFCs), although present in lower concentrations, boast a high global warming potential, contributing to climate change disparities.
The quantitative domination of these gases poses a grim reality. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the levels of CO2 in the atmosphere have surged from approximately 280 parts per million (ppm) before the industrial revolution to over 400 ppm today. This increase has been directly correlated with rising global temperatures, leading to unsettling weather patterns and ecological disruptions.
The cycles of life on Earth—a delicate balance of ecosystems—are profoundly influenced by climate change. Altered precipitation patterns, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and shifting habitats threaten biodiversity and natural resources upon which humanity relies. The impact of these changes reverberates through food security, water supplies, and health, influencing both economic and social stability.
Yet, despite the dire circumstances, there lies a glimmer of hope. Awareness of greenhouse gases and their effects is crucial for fostering meaningful dialogue and spurring action. Innovative technologies aimed at reducing GHG emissions are gaining traction. Renewable energy resources—such as solar, wind, and geothermal—offer promising alternatives to fossil fuels, potentially curtailing our dependency on carbon-intensive energy sources.
Moreover, practices such as reforestation, sustainable farming, and carbon capture and storage are pivotal in mitigating GHG emissions. Educating communities and empowering them to adopt sustainable practices can lead to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas outputs. Behavioral changes, such as minimizing waste and promoting conscious consumption, can transform GHG contributions at an individual and collective level.
Globally, nations are beginning to realize the importance of collaboration and commitment to climate action. Agreements like the Paris Accord aim to limit global warming and stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations. Countries are setting ambitious goals, pledging to transition to greener economies and implement stringent regulations to control emissions. These efforts signal a global shift towards recognizing the inherent value of preserving the planet for future generations.
The momentum for change is palpable. As societal awareness of climate change intensifies, so does the demand for accountability from corporations and governments alike. Activism, facilitated by digital platforms, is mobilizing communities to advocate for environmental policies and sustainable practices. Grassroots movements are flourishing, embodying the spirit of collective action in confronting one of the most pressing challenges of our time.
Understanding the intricate workings of greenhouse gases also paves the way for intellectual curiosity. How do these gases interact with other atmospheric components? What are the long-term physiological effects of climate change on human health? Exploring such questions can spark a deeper understanding of Earth’s systems and our role within them.
As individuals, we hold the power to impact change. Each decision we make, from the foods we consume to the modes of transportation we choose, contributes to the larger narrative of greenhouse gas emissions. Embracing an eco-centric lifestyle not only diminishes our carbon footprint but also cultivates a sense of responsibility toward the planet and future generations.
In summary, greenhouse gases, though invisible, wield tremendous influence over the planet’s climate. Understanding their sources, effects, and the mechanisms by which they operate can inspire meaningful actions and policies. The looming crisis of global warming presents both challenges and opportunities. As nations, communities, and individuals unite in addressing the menace of climate change, a more sustainable and equitable future is not only possible but within reach. By confronting the unseen forces behind global warming, humanity can reclaim its stewardship of the Earth, ensuring a thriving planet for generations to come.